Digital ledger technology (DLT) offers decentralized data management, enhancing transparency and security by allowing multiple participants to access and verify transactions independently. In contrast, centralized databases rely on a single authority to control data storage and access, which may pose risks of data tampering and single points of failure. Explore the advantages and challenges of both systems to understand their impact on modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
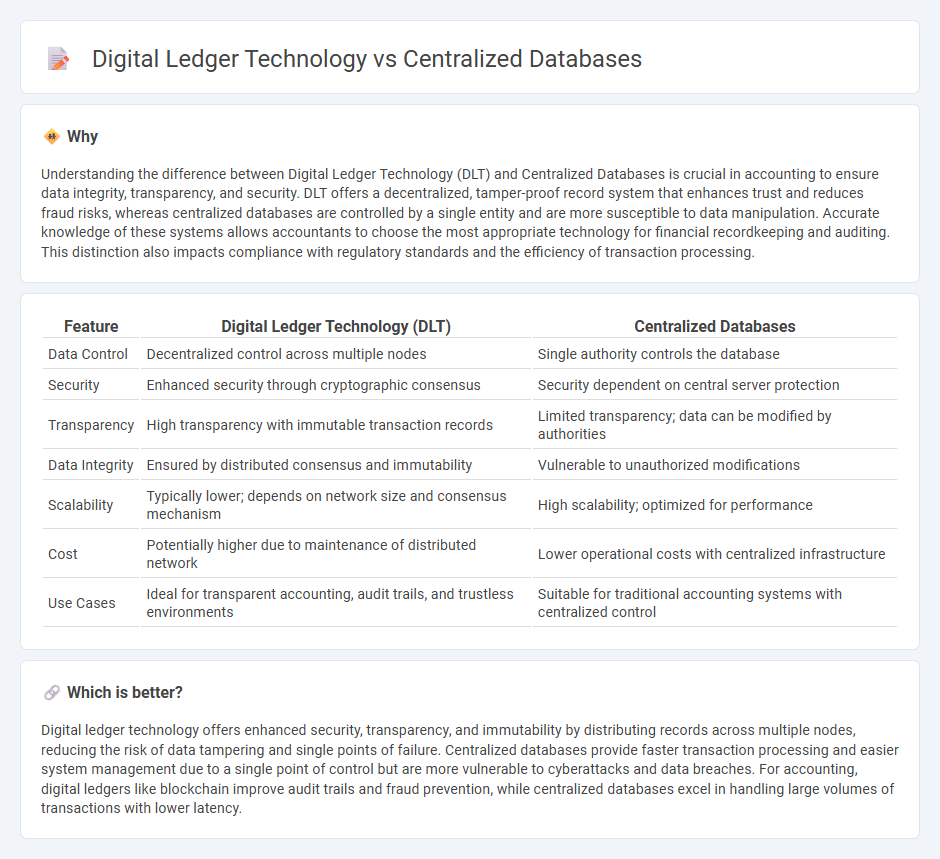
Understanding the difference between Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) and Centralized Databases is crucial in accounting to ensure data integrity, transparency, and security. DLT offers a decentralized, tamper-proof record system that enhances trust and reduces fraud risks, whereas centralized databases are controlled by a single entity and are more susceptible to data manipulation. Accurate knowledge of these systems allows accountants to choose the most appropriate technology for financial recordkeeping and auditing. This distinction also impacts compliance with regulatory standards and the efficiency of transaction processing.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Digital Ledger Technology (DLT) | Centralized Databases |
|---|---|---|
| Data Control | Decentralized control across multiple nodes | Single authority controls the database |
| Security | Enhanced security through cryptographic consensus | Security dependent on central server protection |
| Transparency | High transparency with immutable transaction records | Limited transparency; data can be modified by authorities |
| Data Integrity | Ensured by distributed consensus and immutability | Vulnerable to unauthorized modifications |
| Scalability | Typically lower; depends on network size and consensus mechanism | High scalability; optimized for performance |
| Cost | Potentially higher due to maintenance of distributed network | Lower operational costs with centralized infrastructure |
| Use Cases | Ideal for transparent accounting, audit trails, and trustless environments | Suitable for traditional accounting systems with centralized control |
Which is better?
Digital ledger technology offers enhanced security, transparency, and immutability by distributing records across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of data tampering and single points of failure. Centralized databases provide faster transaction processing and easier system management due to a single point of control but are more vulnerable to cyberattacks and data breaches. For accounting, digital ledgers like blockchain improve audit trails and fraud prevention, while centralized databases excel in handling large volumes of transactions with lower latency.
Connection
Digital ledger technology, such as blockchain, and centralized databases both serve as methods for storing and managing accounting records, but differ in structure and control. Digital ledgers provide decentralized, immutable transaction records enhancing transparency and security, while centralized databases rely on a single authority for data management, offering faster processing and easier updates. Integrating these systems can optimize accounting by combining blockchain's trustworthiness with centralized database efficiency.
Key Terms
Data Integrity
Centralized databases store data in a singular location controlled by an authority, making them vulnerable to single points of failure and unauthorized modifications, which can compromise data integrity. Digital ledger technology (DLT), such as blockchain, ensures data integrity through decentralized consensus mechanisms and cryptographic security, making records immutable and transparent across distributed nodes. Explore the advantages and technical differences of these systems to understand how they impact data integrity in various applications.
Transaction Transparency
Centralized databases rely on a single authority to control and verify transactions, often limiting transparency to internal audit mechanisms. Digital ledger technology, such as blockchain, ensures distributed transaction records that enhance transparency by allowing multiple participants to view and validate entries in real-time. Explore how these differences impact security, efficiency, and trust in digital transactions.
Access Control
Centralized databases rely on a single authority to manage and control access, often through role-based permissions and authentication protocols, ensuring data integrity within a confined system. Digital ledger technology (DLT), such as blockchain, distributes access control across network participants using consensus mechanisms and cryptographic techniques, enhancing transparency and security while reducing single points of failure. Explore the differences in access control to understand how each system can meet your security and governance needs.
Source and External Links
Centralized Database - A centralized database is a database that is located, stored, and maintained in a single location, often used by organizations for managing data efficiently.
Database Management: Centralized vs. Decentralized - This article discusses the differences between centralized and decentralized databases, highlighting centralized databases' advantages in security and data consistency.
Why You Need a Centralized Database for Your Business - This article explains how a centralized database can aid businesses by ensuring data consistency and automation.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com