Integrated ESG reporting combines environmental, social, and governance metrics to provide a comprehensive view of a company's sustainability and ethical impact, while carbon accounting specifically measures and tracks greenhouse gas emissions to assess climate-related risks and opportunities. ESG frameworks are increasingly adopted by investors demanding broader transparency beyond carbon footprints, emphasizing overall corporate responsibility and long-term value creation. Explore the distinctions and strategic benefits of both approaches to enhance your organization's sustainability reporting.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between integrated ESG reporting and carbon accounting is crucial for comprehensive corporate sustainability management. Integrated ESG reporting encompasses environmental, social, and governance factors, offering a holistic view of a company's ethical impact and operational risks. Carbon accounting specifically measures greenhouse gas emissions, enabling precise carbon footprint tracking and regulatory compliance. This distinction helps businesses align their sustainability strategies with both broad ESG goals and targeted environmental metrics.
Comparison Table
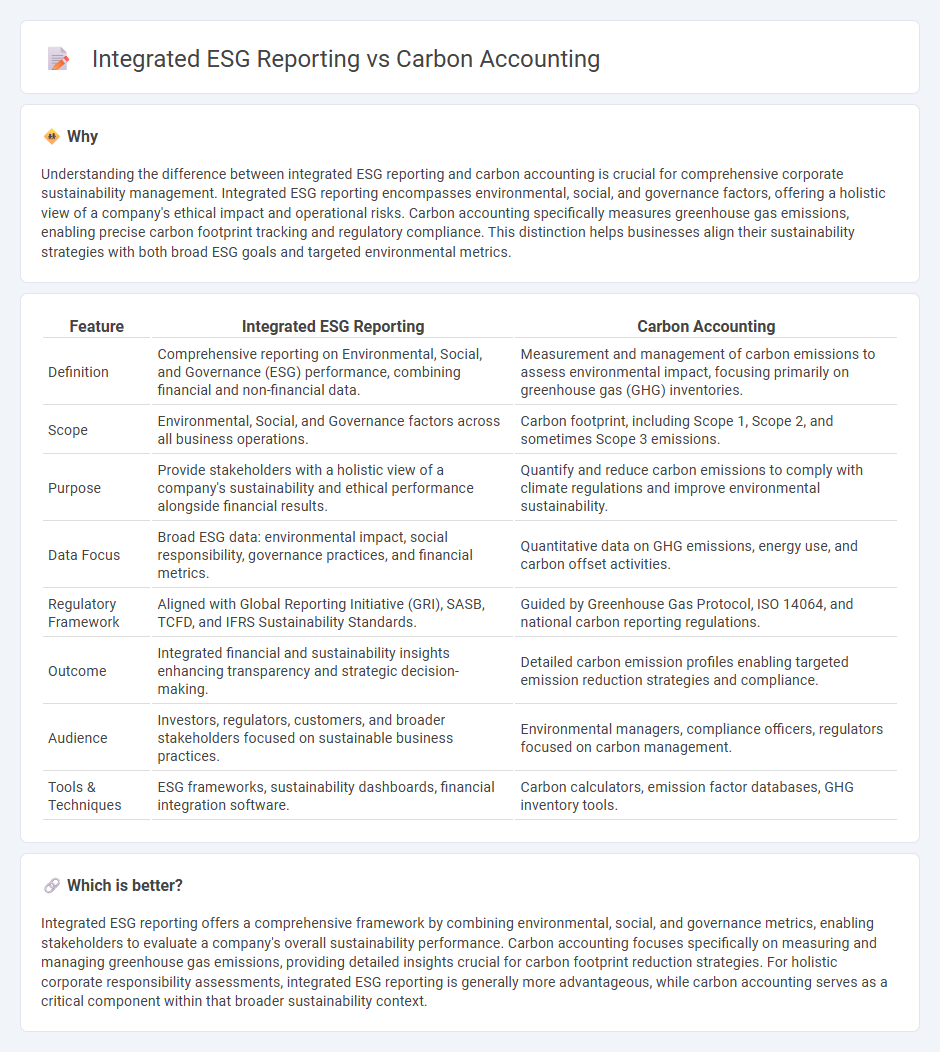
| Feature | Integrated ESG Reporting | Carbon Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Comprehensive reporting on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) performance, combining financial and non-financial data. | Measurement and management of carbon emissions to assess environmental impact, focusing primarily on greenhouse gas (GHG) inventories. |
| Scope | Environmental, Social, and Governance factors across all business operations. | Carbon footprint, including Scope 1, Scope 2, and sometimes Scope 3 emissions. |
| Purpose | Provide stakeholders with a holistic view of a company's sustainability and ethical performance alongside financial results. | Quantify and reduce carbon emissions to comply with climate regulations and improve environmental sustainability. |
| Data Focus | Broad ESG data: environmental impact, social responsibility, governance practices, and financial metrics. | Quantitative data on GHG emissions, energy use, and carbon offset activities. |
| Regulatory Framework | Aligned with Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), SASB, TCFD, and IFRS Sustainability Standards. | Guided by Greenhouse Gas Protocol, ISO 14064, and national carbon reporting regulations. |
| Outcome | Integrated financial and sustainability insights enhancing transparency and strategic decision-making. | Detailed carbon emission profiles enabling targeted emission reduction strategies and compliance. |
| Audience | Investors, regulators, customers, and broader stakeholders focused on sustainable business practices. | Environmental managers, compliance officers, regulators focused on carbon management. |
| Tools & Techniques | ESG frameworks, sustainability dashboards, financial integration software. | Carbon calculators, emission factor databases, GHG inventory tools. |
Which is better?
Integrated ESG reporting offers a comprehensive framework by combining environmental, social, and governance metrics, enabling stakeholders to evaluate a company's overall sustainability performance. Carbon accounting focuses specifically on measuring and managing greenhouse gas emissions, providing detailed insights crucial for carbon footprint reduction strategies. For holistic corporate responsibility assessments, integrated ESG reporting is generally more advantageous, while carbon accounting serves as a critical component within that broader sustainability context.
Connection
Integrated ESG reporting and carbon accounting are connected through their shared focus on measuring and disclosing environmental impact, particularly greenhouse gas emissions. Carbon accounting provides quantifiable data on carbon footprints that feeds into ESG reports, enabling companies to transparently communicate sustainability performance to stakeholders. This synergy enhances decision-making by linking financial outcomes with environmental responsibilities, promoting accountability and compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Key Terms
Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Emissions
Carbon accounting specifically measures and tracks Greenhouse Gas (GHG) emissions to quantify an organization's carbon footprint and comply with regulatory requirements. Integrated ESG reporting encompasses GHG emissions within a broader framework, combining environmental, social, and governance metrics to provide a holistic view of sustainability performance. Discover how these approaches differ in scope and impact on corporate transparency and strategy.
Materiality Assessment
Materiality assessment in carbon accounting centers on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions and identifying significant carbon sources within an organization's operations. Integrated ESG reporting expands this focus by evaluating material environmental, social, and governance factors, ensuring a holistic view of an organization's impact and risk. Explore further to understand how materiality drives transparency and strategic decision-making in both frameworks.
Double Materiality
Carbon accounting primarily measures and reports greenhouse gas emissions to quantify environmental impact, while integrated ESG reporting encompasses a broader scope including environmental, social, and governance factors aligned with corporate strategy. The concept of Double Materiality highlights the importance of assessing both the financial materiality for investors and the impact materiality on society and the environment, guiding more comprehensive disclosure. Explore how adopting Double Materiality enhances transparency and drives sustainable business practices.
Source and External Links
What Is Carbon Accounting? | IBM - Carbon accounting quantifies an organization's greenhouse gas emissions, enabling them to understand their climate impact and set emission reduction goals.
Carbon accounting, explained - Normative.io - Carbon accounting is a method for calculating greenhouse gas emissions and helping organizations achieve net zero emissions and comply with reporting legislation.
Carbon Accounting | CarbonNeutral - Carbon accounting tracks and manages greenhouse gas emissions, enabling businesses to understand their emissions, implement reduction strategies, and report results to stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com