Smart contracts accounting involves recording and verifying transactions executed automatically through blockchain-coded agreements, enhancing transparency and reducing reconciliation errors. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws and regulations, emphasizing accurate reporting of income, deductions, and liabilities to optimize tax obligations. Explore the distinctions to understand how technology reshapes financial management and regulatory adherence.
Why it is important
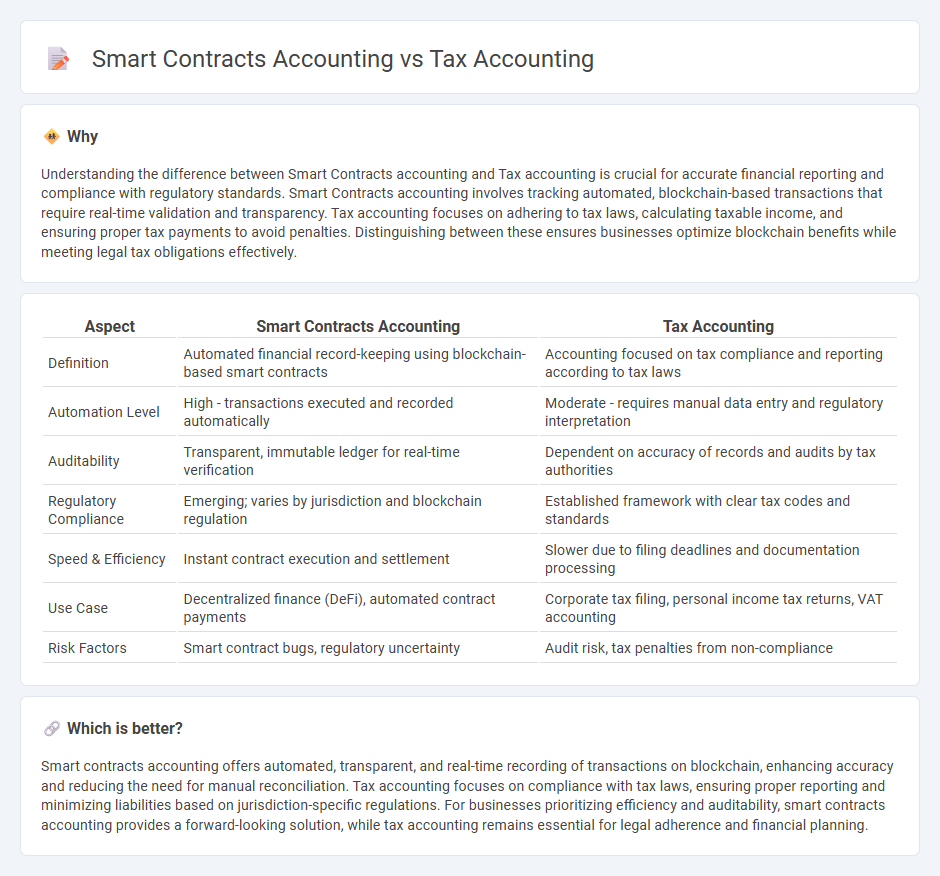
Understanding the difference between Smart Contracts accounting and Tax accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting and compliance with regulatory standards. Smart Contracts accounting involves tracking automated, blockchain-based transactions that require real-time validation and transparency. Tax accounting focuses on adhering to tax laws, calculating taxable income, and ensuring proper tax payments to avoid penalties. Distinguishing between these ensures businesses optimize blockchain benefits while meeting legal tax obligations effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Smart Contracts Accounting | Tax Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated financial record-keeping using blockchain-based smart contracts | Accounting focused on tax compliance and reporting according to tax laws |
| Automation Level | High - transactions executed and recorded automatically | Moderate - requires manual data entry and regulatory interpretation |
| Auditability | Transparent, immutable ledger for real-time verification | Dependent on accuracy of records and audits by tax authorities |
| Regulatory Compliance | Emerging; varies by jurisdiction and blockchain regulation | Established framework with clear tax codes and standards |
| Speed & Efficiency | Instant contract execution and settlement | Slower due to filing deadlines and documentation processing |
| Use Case | Decentralized finance (DeFi), automated contract payments | Corporate tax filing, personal income tax returns, VAT accounting |
| Risk Factors | Smart contract bugs, regulatory uncertainty | Audit risk, tax penalties from non-compliance |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers automated, transparent, and real-time recording of transactions on blockchain, enhancing accuracy and reducing the need for manual reconciliation. Tax accounting focuses on compliance with tax laws, ensuring proper reporting and minimizing liabilities based on jurisdiction-specific regulations. For businesses prioritizing efficiency and auditability, smart contracts accounting provides a forward-looking solution, while tax accounting remains essential for legal adherence and financial planning.
Connection
Smart contracts accounting automates transaction recording by embedding programmable rules within blockchain technology, ensuring real-time, tamper-proof financial data. This automation directly impacts tax accounting by providing precise, transparent records that simplify tax reporting, compliance, and audit processes. Integration of smart contracts in accounting frameworks enhances accuracy, reduces errors, and streamlines tax obligations for businesses and regulatory bodies.
Key Terms
**Tax accounting:**
Tax accounting focuses on the accurate reporting of financial transactions to comply with tax laws and regulations, ensuring proper calculation of tax liabilities and deductions. It involves detailed record-keeping, preparing tax returns, and staying updated on changing tax codes to minimize risks and penalties. Explore how tax accounting integrates with emerging technologies for enhanced compliance and efficiency.
Taxable income
Tax accounting meticulously tracks and reports taxable income based on established financial regulations and tax codes, ensuring compliance and accurate IRS filings. Smart contracts accounting automates transaction verification and income recognition within blockchain platforms, potentially improving transparency but still requiring integration with traditional tax rules to determine taxable income. Explore how combining smart contracts with tax accounting can optimize income reporting accuracy and compliance.
Deductions
Tax accounting primarily emphasizes identifying and documenting eligible deductions such as business expenses, depreciation, and charitable contributions to minimize taxable income. Smart contracts accounting automates deduction verification and application through programmable logic on blockchain, ensuring accuracy, transparency, and real-time compliance with tax rules. Explore how integrating smart contract technology can revolutionize deduction management and tax reporting accuracy.
Source and External Links
Tax Accounting | Definition, Types & Examples - Study.com - Tax accounting is a specialized field focused on minimizing tax liability and ensuring compliance with tax laws for individuals, businesses, and non-profits, involving preparation of tax returns and applying tax-specific rules distinct from financial accounting standards.
Tax Accountant Careers - Tax accountants prepare tax filings, advise on tax planning, analyze financial data, and stay current with tax laws to help clients manage their tax obligations legally and efficiently.
What Is a Tax Accountant? - TurboTax Tax Tips & Videos - Intuit - Tax accountants specialize in tax filing, planning, and compliance to minimize tax liabilities and ensure accurate tax reporting, often possessing credentials like CPA or enrolled agent.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com