Sustainable ledgers focus on minimizing environmental impact through energy-efficient bookkeeping methods, while blockchain ledgers prioritize decentralization and immutability using cryptographic consensus mechanisms. Both systems enhance transparency and security in financial record-keeping but differ significantly in energy consumption and scalability. Explore the key distinctions and benefits of sustainable ledgers versus blockchain ledgers to determine the best fit for your accounting needs.
Why it is important
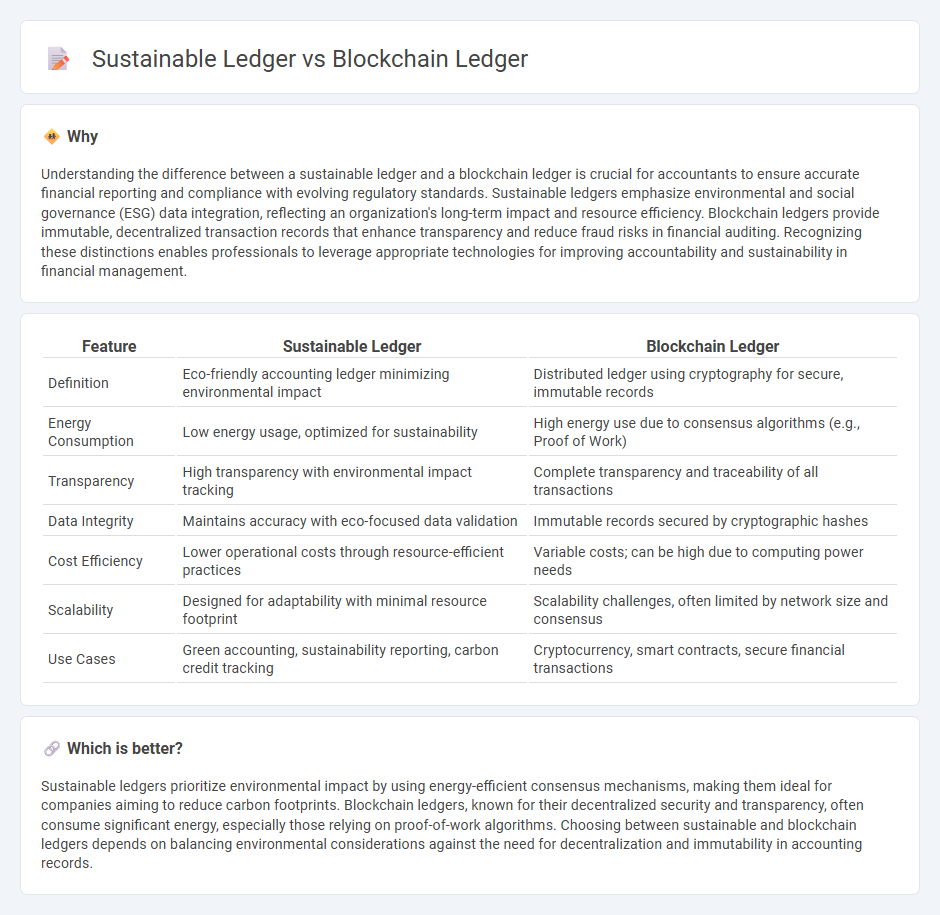
Understanding the difference between a sustainable ledger and a blockchain ledger is crucial for accountants to ensure accurate financial reporting and compliance with evolving regulatory standards. Sustainable ledgers emphasize environmental and social governance (ESG) data integration, reflecting an organization's long-term impact and resource efficiency. Blockchain ledgers provide immutable, decentralized transaction records that enhance transparency and reduce fraud risks in financial auditing. Recognizing these distinctions enables professionals to leverage appropriate technologies for improving accountability and sustainability in financial management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Sustainable Ledger | Blockchain Ledger |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Eco-friendly accounting ledger minimizing environmental impact | Distributed ledger using cryptography for secure, immutable records |
| Energy Consumption | Low energy usage, optimized for sustainability | High energy use due to consensus algorithms (e.g., Proof of Work) |
| Transparency | High transparency with environmental impact tracking | Complete transparency and traceability of all transactions |
| Data Integrity | Maintains accuracy with eco-focused data validation | Immutable records secured by cryptographic hashes |
| Cost Efficiency | Lower operational costs through resource-efficient practices | Variable costs; can be high due to computing power needs |
| Scalability | Designed for adaptability with minimal resource footprint | Scalability challenges, often limited by network size and consensus |
| Use Cases | Green accounting, sustainability reporting, carbon credit tracking | Cryptocurrency, smart contracts, secure financial transactions |
Which is better?
Sustainable ledgers prioritize environmental impact by using energy-efficient consensus mechanisms, making them ideal for companies aiming to reduce carbon footprints. Blockchain ledgers, known for their decentralized security and transparency, often consume significant energy, especially those relying on proof-of-work algorithms. Choosing between sustainable and blockchain ledgers depends on balancing environmental considerations against the need for decentralization and immutability in accounting records.
Connection
Sustainable ledgers integrate blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability in accounting processes, ensuring accurate recording of environmentally responsible transactions. Blockchain ledger's decentralized and immutable nature supports sustainability by providing secure, verifiable data that reduces fraud and errors in financial reporting. This connection promotes trust and accountability in sustainable accounting practices across various industries.
Key Terms
Transparency
Blockchain ledgers ensure transparency through decentralized and immutable records, enabling all participants to verify transaction history without intermediaries. Sustainable ledgers emphasize transparency by integrating environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, promoting accountability in resource usage and ethical practices. Explore how these ledger systems enhance transparency in different sectors and their impact on trust and sustainability.
Traceability
Blockchain ledgers provide immutable, transparent records that enhance traceability by securely tracking asset provenance and transaction history across decentralized networks. Sustainable ledgers emphasize environmental impact, integrating eco-friendly consensus mechanisms and promoting data accuracy to support ethical supply chains and resource management. Explore how traceability innovations in these ledgers transform accountability and sustainability efforts.
Environmental Impact
Blockchain ledgers often consume substantial energy due to their reliance on proof-of-work consensus mechanisms, resulting in high carbon footprints and environmental concerns. Sustainable ledgers utilize energy-efficient consensus protocols like proof-of-stake and incorporate carbon offset initiatives to minimize ecological damage. Explore how evolving ledger technologies can balance transparency with environmental responsibility.
Source and External Links
Ledger Meaning - This webpage explains how blockchain serves as a type of digital ledger, validating and storing transactions within its network.
Legends & Ledgers: How the Bitcoin Ledger Works - This article delves into the structure and operation of the Bitcoin ledger, highlighting its decentralized and transparent nature.
Distributed Ledger - Wikipedia - This Wikipedia page describes distributed ledger technology, including blockchain, as a system where data is replicated and synchronized across multiple nodes without a central administrator.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com