Zero Knowledge Proofs revolutionize accounting by enabling verification of financial records without revealing sensitive data, enhancing confidentiality and security. Unlike traditional auditing, which requires extensive data access for validation, zero knowledge proofs provide cryptographic assurance while preserving privacy. Explore how this cutting-edge technology transforms financial transparency and trust.
Why it is important
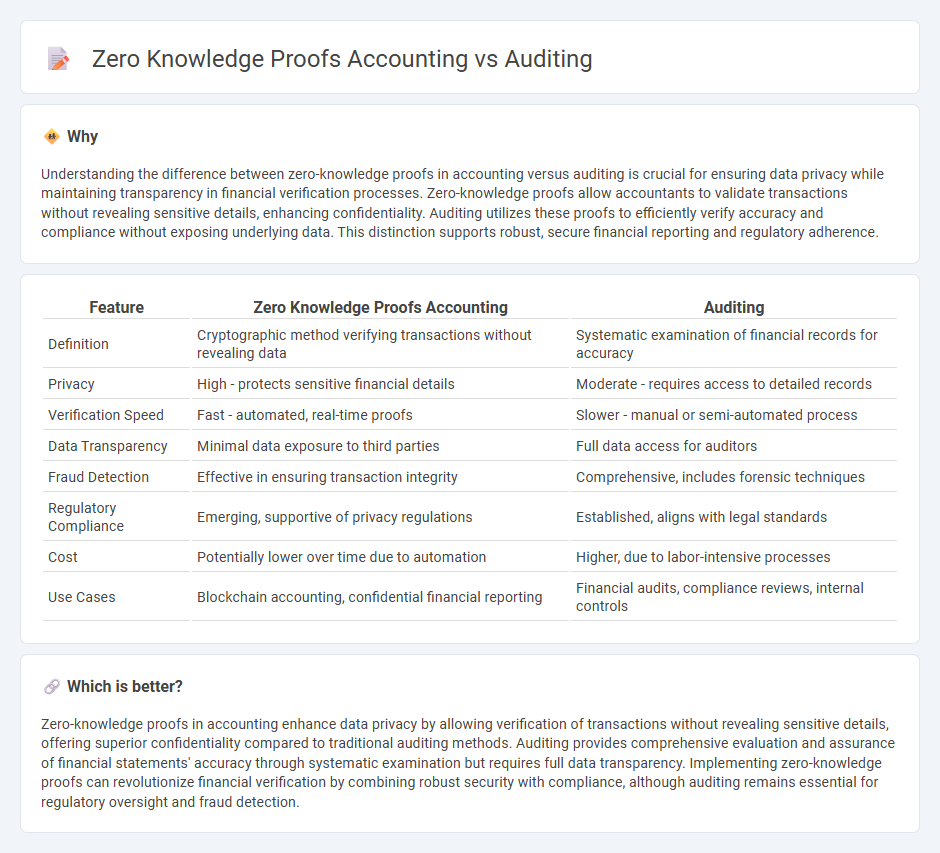
Understanding the difference between zero-knowledge proofs in accounting versus auditing is crucial for ensuring data privacy while maintaining transparency in financial verification processes. Zero-knowledge proofs allow accountants to validate transactions without revealing sensitive details, enhancing confidentiality. Auditing utilizes these proofs to efficiently verify accuracy and compliance without exposing underlying data. This distinction supports robust, secure financial reporting and regulatory adherence.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Zero Knowledge Proofs Accounting | Auditing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cryptographic method verifying transactions without revealing data | Systematic examination of financial records for accuracy |
| Privacy | High - protects sensitive financial details | Moderate - requires access to detailed records |
| Verification Speed | Fast - automated, real-time proofs | Slower - manual or semi-automated process |
| Data Transparency | Minimal data exposure to third parties | Full data access for auditors |
| Fraud Detection | Effective in ensuring transaction integrity | Comprehensive, includes forensic techniques |
| Regulatory Compliance | Emerging, supportive of privacy regulations | Established, aligns with legal standards |
| Cost | Potentially lower over time due to automation | Higher, due to labor-intensive processes |
| Use Cases | Blockchain accounting, confidential financial reporting | Financial audits, compliance reviews, internal controls |
Which is better?
Zero-knowledge proofs in accounting enhance data privacy by allowing verification of transactions without revealing sensitive details, offering superior confidentiality compared to traditional auditing methods. Auditing provides comprehensive evaluation and assurance of financial statements' accuracy through systematic examination but requires full data transparency. Implementing zero-knowledge proofs can revolutionize financial verification by combining robust security with compliance, although auditing remains essential for regulatory oversight and fraud detection.
Connection
Zero-knowledge proofs enhance accounting and auditing by enabling verification of financial transactions without revealing sensitive data, ensuring privacy and security. This cryptographic technique supports compliance with regulatory standards while maintaining transparency in audit trails. Integration of zero-knowledge proofs in accounting systems reduces fraud risk and streamlines the verification process in complex financial environments.
Key Terms
Verification
Auditing ensures financial statements' accuracy through third-party verification of transactions and balances, providing transparency and trust in accounting practices. Zero knowledge proofs enable verification of data authenticity without revealing the underlying information, enhancing privacy and security in financial reporting. Explore how these methods revolutionize verification processes in modern accounting systems.
Confidentiality
Auditing in accounting relies on third-party verification of financial statements to ensure accuracy and compliance, often exposing sensitive data in the process. Zero-knowledge proofs enable verification of accounting information without revealing any underlying confidential details, enhancing privacy and data security. Explore how zero-knowledge proofs transform confidentiality in financial audits by securing information while maintaining trust.
Compliance
Auditing ensures compliance by verifying financial records through transparent documentation and external review, while zero knowledge proofs enhance compliance by enabling validation of data without revealing sensitive information. Zero knowledge proofs support privacy-focused compliance frameworks in sectors like finance and healthcare by cryptographically proving adherence to regulations without exposing underlying data. Explore how zero knowledge proofs redefine compliance and auditing processes for more secure and efficient verification systems.
Source and External Links
What Is Auditing? Definition, Types & Importance - Deskera - Auditing is the systematic, independent examination and verification of financial records to ensure accuracy, compliance with accounting standards, fraud detection, risk management, and enhancement of stakeholder confidence.
Auditing: Definition, Types, and Importance - FreshBooks - Auditing is an objective review of financial records to verify accuracy, regulatory compliance, and financial transparency for businesses and individuals.
Auditing - Overview, Importance, Types, and Accounting Standards - Corporate Finance Institute - An audit is an independent examination of financial statements to ensure they fairly represent a company's financial position and comply with relevant accounting standards, often performed by an external party.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com