Tokenized assets accounting requires specialized recognition and measurement principles to accurately reflect digital ownership and blockchain-based transactions, differing significantly from traditional investment property accounting that focuses on tangible real estate valuation and rental income recognition. While investment property accounting adheres to IAS 40 standards, tokenized assets demand evolving frameworks to address their unique valuation, liquidity, and regulatory challenges. Explore in-depth insights on how these accounting treatments impact financial reporting and compliance.
Why it is important
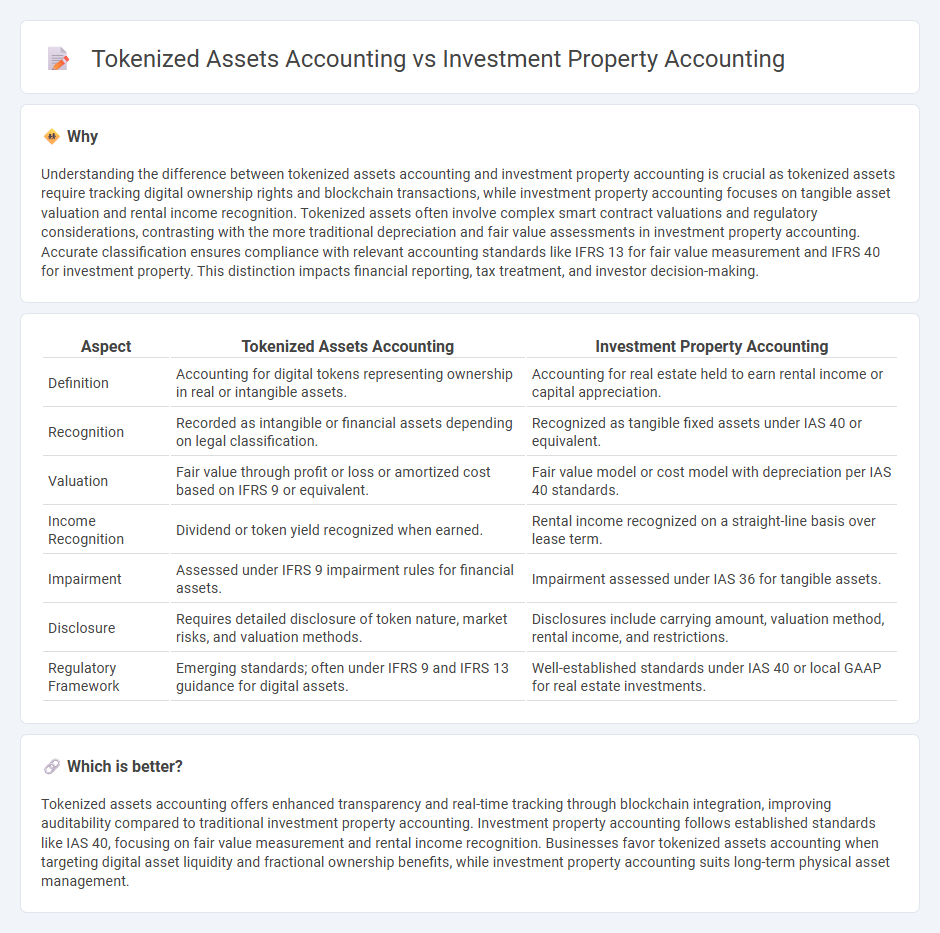
Understanding the difference between tokenized assets accounting and investment property accounting is crucial as tokenized assets require tracking digital ownership rights and blockchain transactions, while investment property accounting focuses on tangible asset valuation and rental income recognition. Tokenized assets often involve complex smart contract valuations and regulatory considerations, contrasting with the more traditional depreciation and fair value assessments in investment property accounting. Accurate classification ensures compliance with relevant accounting standards like IFRS 13 for fair value measurement and IFRS 40 for investment property. This distinction impacts financial reporting, tax treatment, and investor decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Tokenized Assets Accounting | Investment Property Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting for digital tokens representing ownership in real or intangible assets. | Accounting for real estate held to earn rental income or capital appreciation. |
| Recognition | Recorded as intangible or financial assets depending on legal classification. | Recognized as tangible fixed assets under IAS 40 or equivalent. |
| Valuation | Fair value through profit or loss or amortized cost based on IFRS 9 or equivalent. | Fair value model or cost model with depreciation per IAS 40 standards. |
| Income Recognition | Dividend or token yield recognized when earned. | Rental income recognized on a straight-line basis over lease term. |
| Impairment | Assessed under IFRS 9 impairment rules for financial assets. | Impairment assessed under IAS 36 for tangible assets. |
| Disclosure | Requires detailed disclosure of token nature, market risks, and valuation methods. | Disclosures include carrying amount, valuation method, rental income, and restrictions. |
| Regulatory Framework | Emerging standards; often under IFRS 9 and IFRS 13 guidance for digital assets. | Well-established standards under IAS 40 or local GAAP for real estate investments. |
Which is better?
Tokenized assets accounting offers enhanced transparency and real-time tracking through blockchain integration, improving auditability compared to traditional investment property accounting. Investment property accounting follows established standards like IAS 40, focusing on fair value measurement and rental income recognition. Businesses favor tokenized assets accounting when targeting digital asset liquidity and fractional ownership benefits, while investment property accounting suits long-term physical asset management.
Connection
Tokenized assets accounting involves recording digital representations of ownership interests on a blockchain, ensuring transparency and traceability in financial statements. Investment property accounting requires valuation and depreciation tracking of real estate held for rental income or capital appreciation, often relying on frameworks like IAS 40. The connection lies in the emerging practice of tokenizing investment properties, where accounting must integrate blockchain-based asset registers with traditional investment property valuation and income recognition methods.
Key Terms
Fair Value Measurement
Fair value measurement in investment property accounting involves appraising real estate assets at market value, reflecting current conditions and potential income generation, typically following IFRS or GAAP standards. Tokenized assets accounting applies blockchain technology to represent ownership rights digitally, requiring ongoing fair value assessments based on market demand and liquidity across digital exchanges. Explore how emerging digital frameworks transform traditional valuation approaches in asset management.
Ownership Ledger
Investment property accounting traditionally relies on physical asset registers and manual ownership ledgers, recording transactions in compliance with IFRS or GAAP standards. Tokenized assets accounting utilizes blockchain technology to create a decentralized, immutable ownership ledger that enhances transparency, traceability, and real-time updates. Explore how the ownership ledger revolutionizes asset management and financial reporting in emerging digital ecosystems.
Digital Asset Valuation
Investment property accounting relies on standardized valuation methods such as fair value and cost models under IFRS and GAAP, emphasizing physical asset depreciation and rental income recognition. Tokenized assets accounting incorporates blockchain technology, requiring real-time digital asset valuation, smart contract verification, and regulatory compliance with evolving crypto standards. Explore the latest frameworks and best practices for accurate digital asset valuation in tokenized environments.
Source and External Links
IAS 40 Investment Property - Investment property is initially measured at cost and subsequently measured either using the fair value model, where changes in fair value are recognized in profit or loss, or the cost model, where the property is measured at cost less depreciation and impairment; disclosures of fair value are required under both models.
IFRS(r): Investment Property (IAS 40) | Courses - This course provides detailed guidance on initial classification, recognition, and measurement of investment property under IAS 40, including relevant disclosures and accounting issues after initial recognition, helping practitioners apply the IFRS requirements globally.
IAS 40 Investment Property (full standard) - Investment property is property held to earn rentals or for capital appreciation, distinguished from owner-occupied property, with specific accounting treatment such as including integral equipment in fair value and excluding prepaid lease income from fair value measurement.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com