Embedded finance compliance involves ensuring financial services integrated within non-financial platforms adhere to regulatory standards like anti-money laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements. Tax compliance focuses on accurately reporting income, calculating liabilities, and adhering to tax laws such as the Internal Revenue Code (IRC) and International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS). Explore further to understand how these compliance areas impact modern accounting practices.
Why it is important
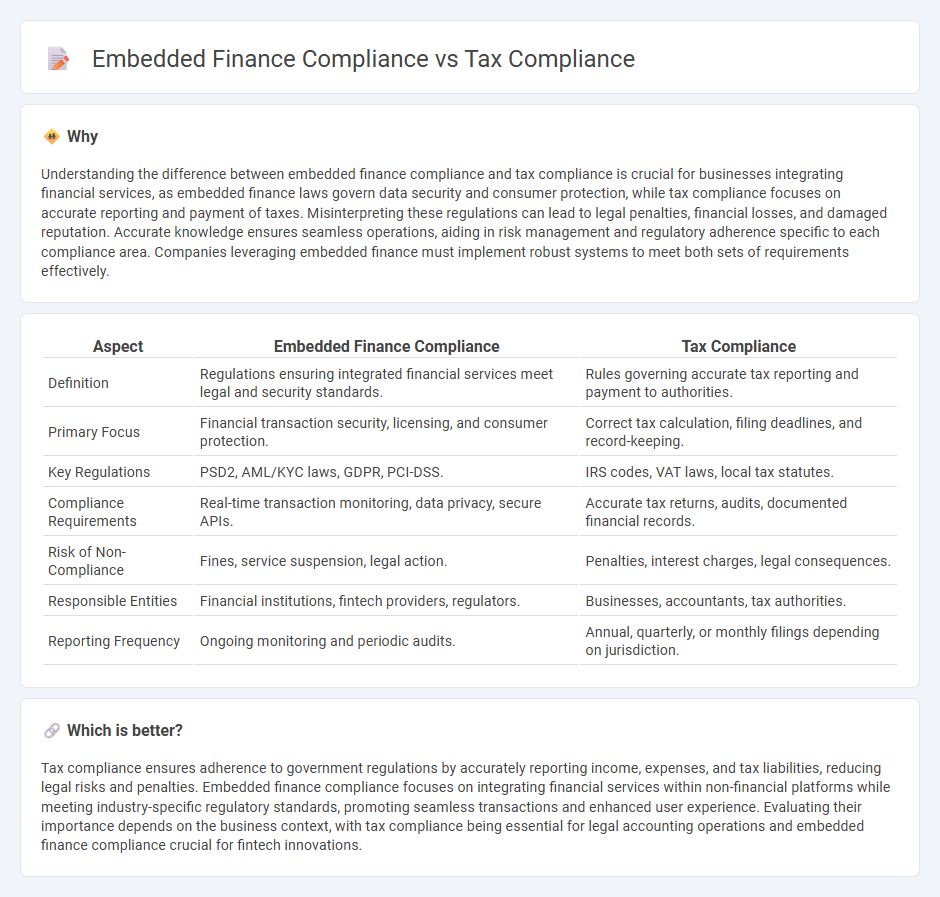
Understanding the difference between embedded finance compliance and tax compliance is crucial for businesses integrating financial services, as embedded finance laws govern data security and consumer protection, while tax compliance focuses on accurate reporting and payment of taxes. Misinterpreting these regulations can lead to legal penalties, financial losses, and damaged reputation. Accurate knowledge ensures seamless operations, aiding in risk management and regulatory adherence specific to each compliance area. Companies leveraging embedded finance must implement robust systems to meet both sets of requirements effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Compliance | Tax Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Regulations ensuring integrated financial services meet legal and security standards. | Rules governing accurate tax reporting and payment to authorities. |
| Primary Focus | Financial transaction security, licensing, and consumer protection. | Correct tax calculation, filing deadlines, and record-keeping. |
| Key Regulations | PSD2, AML/KYC laws, GDPR, PCI-DSS. | IRS codes, VAT laws, local tax statutes. |
| Compliance Requirements | Real-time transaction monitoring, data privacy, secure APIs. | Accurate tax returns, audits, documented financial records. |
| Risk of Non-Compliance | Fines, service suspension, legal action. | Penalties, interest charges, legal consequences. |
| Responsible Entities | Financial institutions, fintech providers, regulators. | Businesses, accountants, tax authorities. |
| Reporting Frequency | Ongoing monitoring and periodic audits. | Annual, quarterly, or monthly filings depending on jurisdiction. |
Which is better?
Tax compliance ensures adherence to government regulations by accurately reporting income, expenses, and tax liabilities, reducing legal risks and penalties. Embedded finance compliance focuses on integrating financial services within non-financial platforms while meeting industry-specific regulatory standards, promoting seamless transactions and enhanced user experience. Evaluating their importance depends on the business context, with tax compliance being essential for legal accounting operations and embedded finance compliance crucial for fintech innovations.
Connection
Embedded finance compliance integrates financial services within non-financial platforms, requiring adherence to regulations such as KYC, AML, and data privacy laws that directly influence tax reporting obligations. Tax compliance depends on accurate financial data and transactional transparency provided by embedded finance systems, ensuring proper calculation and remittance of taxes like VAT, GST, and income tax. The interconnectedness of embedded finance compliance and tax compliance streamlines regulatory adherence, reduces risks of penalties, and enhances financial accountability within accounting processes.
Key Terms
**Tax compliance:**
Tax compliance involves adhering to regulations set by tax authorities, including accurate reporting, timely filing, and payment of taxes such as income, sales, and VAT. Businesses must maintain detailed records and utilize tax software or consulting services to ensure compliance and avoid penalties. Discover more about effective tax compliance strategies and tools to optimize your financial operations.
Tax filing
Tax filing within tax compliance mandates accurate reporting of income, deductions, and tax liabilities to meet regulatory standards set by authorities like the IRS or HMRC. Embedded finance compliance integrates tax filing requirements seamlessly within financial platforms, ensuring real-time tax calculations, automated form generation, and regulatory adherence without manual intervention. Explore how these compliance frameworks transform financial operations and simplify tax responsibilities.
Deductions
Tax compliance involves adhering to governmental regulations related to income reporting, withholding, and deductions to accurately calculate tax liabilities and avoid penalties. Embedded finance compliance, particularly concerning deductions, requires integrating financial services within platforms while ensuring all transactional deductions align with legal standards and reporting requirements across jurisdictions. Discover how these compliance frameworks intersect and impact modern financial operations by exploring detailed guidelines and case studies.
Source and External Links
What is tax compliance? - Tax compliance is the commitment of individuals or businesses to adhere to tax laws and regulations, involving accurate reporting and timely payment to avoid penalties and build trust with stakeholders.
Tax Compliance: Definition, Importance, and Key Elements - Tax compliance involves following all tax laws including filing accurate returns and paying taxes on time, with non-compliance risking financial penalties and audits, especially complex for global businesses.
What is Tax Compliance? - Tax compliance means fulfilling legal tax obligations such as income reporting, tax payments, and record keeping, critical for operational integrity and avoiding penalties or prosecution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com