Sustainability reporting focuses on an organization's impact on environmental, social, and economic factors, aiming to provide transparency on sustainable practices and long-term business resilience. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting offers a framework for investors to assess corporate responsibility through specific metrics related to environmental stewardship, social impact, and governance standards. Explore the distinctions and integration of these reporting approaches to enhance your understanding of sustainable accounting practices.
Why it is important
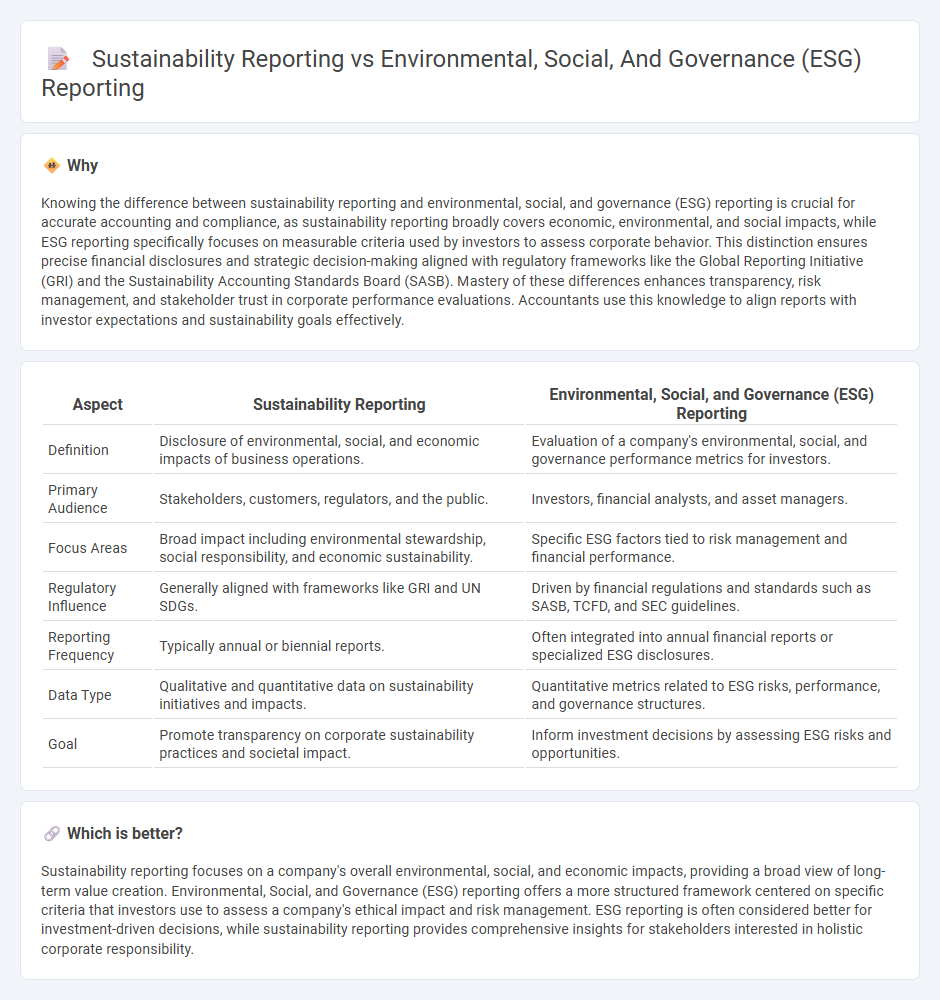
Knowing the difference between sustainability reporting and environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting is crucial for accurate accounting and compliance, as sustainability reporting broadly covers economic, environmental, and social impacts, while ESG reporting specifically focuses on measurable criteria used by investors to assess corporate behavior. This distinction ensures precise financial disclosures and strategic decision-making aligned with regulatory frameworks like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Mastery of these differences enhances transparency, risk management, and stakeholder trust in corporate performance evaluations. Accountants use this knowledge to align reports with investor expectations and sustainability goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Reporting | Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disclosure of environmental, social, and economic impacts of business operations. | Evaluation of a company's environmental, social, and governance performance metrics for investors. |
| Primary Audience | Stakeholders, customers, regulators, and the public. | Investors, financial analysts, and asset managers. |
| Focus Areas | Broad impact including environmental stewardship, social responsibility, and economic sustainability. | Specific ESG factors tied to risk management and financial performance. |
| Regulatory Influence | Generally aligned with frameworks like GRI and UN SDGs. | Driven by financial regulations and standards such as SASB, TCFD, and SEC guidelines. |
| Reporting Frequency | Typically annual or biennial reports. | Often integrated into annual financial reports or specialized ESG disclosures. |
| Data Type | Qualitative and quantitative data on sustainability initiatives and impacts. | Quantitative metrics related to ESG risks, performance, and governance structures. |
| Goal | Promote transparency on corporate sustainability practices and societal impact. | Inform investment decisions by assessing ESG risks and opportunities. |
Which is better?
Sustainability reporting focuses on a company's overall environmental, social, and economic impacts, providing a broad view of long-term value creation. Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting offers a more structured framework centered on specific criteria that investors use to assess a company's ethical impact and risk management. ESG reporting is often considered better for investment-driven decisions, while sustainability reporting provides comprehensive insights for stakeholders interested in holistic corporate responsibility.
Connection
Sustainability reporting encompasses the disclosure of an organization's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, integrating these factors into financial accounting frameworks. ESG reporting provides detailed metrics on environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance practices, which enhances transparency and supports stakeholder decision-making. Companies use these reports to align accounting processes with global sustainability standards such as GRI, SASB, and TCFD, driving accountability and long-term value creation.
Key Terms
Materiality
Materiality in environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting centers on identifying and disclosing factors that significantly impact a company's financial performance and stakeholder decisions, emphasizing risk and opportunity management. Sustainability reporting broadens this focus, addressing economic, environmental, and social impacts that affect long-term value creation and stakeholder interests beyond financial metrics. Explore the nuances between ESG and sustainability reporting to deepen your understanding of materiality's role in corporate transparency.
Non-financial Disclosure
Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reporting centers on quantifiable non-financial metrics that assess a company's risk exposure and management effectiveness across environmental impact, social responsibility, and corporate governance. Sustainability reporting emphasizes the broader disclosure of a company's long-term impacts and initiatives related to environmental stewardship, social equity, and economic viability, often aligned with frameworks like GRI or SASB. Explore further to understand how integrating ESG and sustainability reporting can enhance transparency and stakeholder trust.
Stakeholder Engagement
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting emphasizes quantifiable metrics and risk management to inform investors and regulatory bodies, while sustainability reporting centers on broader stakeholder engagement, including community involvement and employee well-being. ESG reports typically highlight governance structures, carbon emissions, and labor practices with the aim of transparency for shareholders, whereas sustainability reports adopt a holistic approach integrating stakeholder feedback to drive long-term social and environmental impact. Explore how both reporting frameworks can complement each other to enhance stakeholder engagement and corporate responsibility.
Source and External Links
What Is ESG Reporting? - IBM - ESG reporting is the disclosure of information about business operations in relation to environmental, social, and governance areas of the business.
The ABCs of ESG reporting: What are ESG and sustainability reports ... - ESG reporting is the disclosure of environmental, social, and corporate governance data aimed at shedding light on a company's performance in these areas.
What is ESG reporting, and should you be doing it? - Greenly - ESG reporting involves disclosing data on a company's environmental, social, and governance performance, including energy use, emissions, and sustainability practices.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com