Deferred revenue recognition records cash received before goods or services are delivered, reflecting an obligation to fulfill future performance. Accrued revenue recognition captures revenue earned but not yet received in cash, indicating entitlement to payment for completed work. Explore in-depth differences and applications of these revenue recognition methods.
Why it is important
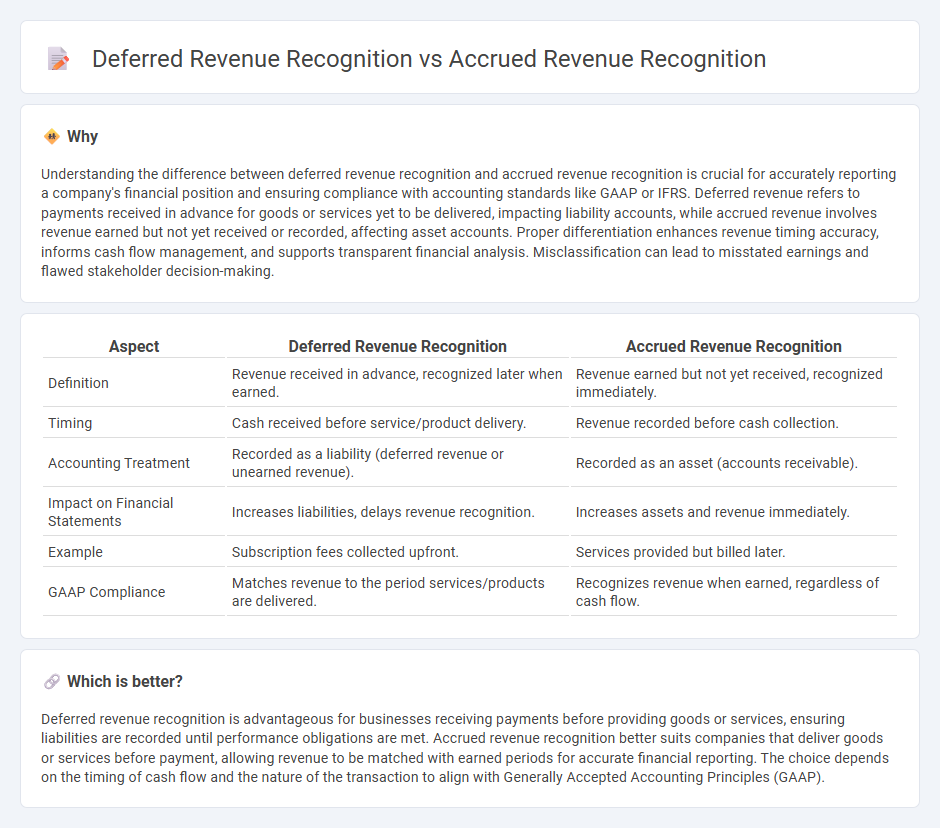
Understanding the difference between deferred revenue recognition and accrued revenue recognition is crucial for accurately reporting a company's financial position and ensuring compliance with accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS. Deferred revenue refers to payments received in advance for goods or services yet to be delivered, impacting liability accounts, while accrued revenue involves revenue earned but not yet received or recorded, affecting asset accounts. Proper differentiation enhances revenue timing accuracy, informs cash flow management, and supports transparent financial analysis. Misclassification can lead to misstated earnings and flawed stakeholder decision-making.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Deferred Revenue Recognition | Accrued Revenue Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Revenue received in advance, recognized later when earned. | Revenue earned but not yet received, recognized immediately. |
| Timing | Cash received before service/product delivery. | Revenue recorded before cash collection. |
| Accounting Treatment | Recorded as a liability (deferred revenue or unearned revenue). | Recorded as an asset (accounts receivable). |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Increases liabilities, delays revenue recognition. | Increases assets and revenue immediately. |
| Example | Subscription fees collected upfront. | Services provided but billed later. |
| GAAP Compliance | Matches revenue to the period services/products are delivered. | Recognizes revenue when earned, regardless of cash flow. |
Which is better?
Deferred revenue recognition is advantageous for businesses receiving payments before providing goods or services, ensuring liabilities are recorded until performance obligations are met. Accrued revenue recognition better suits companies that deliver goods or services before payment, allowing revenue to be matched with earned periods for accurate financial reporting. The choice depends on the timing of cash flow and the nature of the transaction to align with Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP).
Connection
Deferred revenue recognition and accrued revenue recognition are connected through the matching principle in accounting, ensuring revenues are recorded in the period they are earned regardless of cash flow timing. Deferred revenue represents cash received before services are delivered, recorded as a liability, while accrued revenue reflects earned income not yet billed or received, recorded as an asset. Both methods optimize financial accuracy by aligning revenue recognition with the delivery of goods or services, complying with GAAP standards.
Key Terms
Accrual Basis
Accrued revenue recognition under the accrual basis records revenue when earned, regardless of cash receipt, capturing earned but unbilled income to reflect true financial performance. Deferred revenue recognition defers recording revenue until goods or services are delivered, treating advance payments as liabilities until fulfillment. Explore deeper insights into accrual basis accounting principles and its impact on financial reporting.
Unearned Revenue
Accrued revenue recognition records income earned but not yet received, while deferred revenue recognition applies to unearned revenue, which is money received before delivering goods or services. Unearned revenue appears as a liability on the balance sheet until the performance obligation is met, converting it into earned revenue. Explore the differences in timing and accounting treatments to optimize financial reporting accuracy.
Accounts Receivable
Accrued revenue recognition records income earned but not yet billed, increasing accounts receivable as services are delivered or goods provided before payment. Deferred revenue recognition involves cash received in advance, recorded as a liability until the service or product is fulfilled, not impacting accounts receivable immediately. Explore detailed accounting treatments and impacts on financial statements to understand accrual and deferral processes fully.
Source and External Links
Accrued Revenue Explained: Key Concepts & Examples - Accrued revenue is recognized when earned, not when received, based on SEC criteria including evidence of an arrangement, delivery of goods or services, fixed price, and reasonable assurance of payment.
Accrued Revenue - Definition & Examples - Under GAAP, accrued revenue is recognized when a performance obligation is satisfied, regardless of cash receipt, aligning with the revenue recognition and matching principles.
What is Accrued Revenue? - Accrued revenue is a current asset recorded upon earning income before billing or payment, contrasting with deferred revenue, and is vital for accurately matching revenues to performance periods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com