Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by adding a cryptographic receipt recorded on a distributed ledger, improving transparency and reducing fraud. Smart contracts automate financial agreements by executing predefined actions when specific conditions are met, enhancing accuracy and efficiency in transactions. Explore how integrating triple entry bookkeeping with smart contracts can revolutionize financial record-keeping and auditing processes.
Why it is important
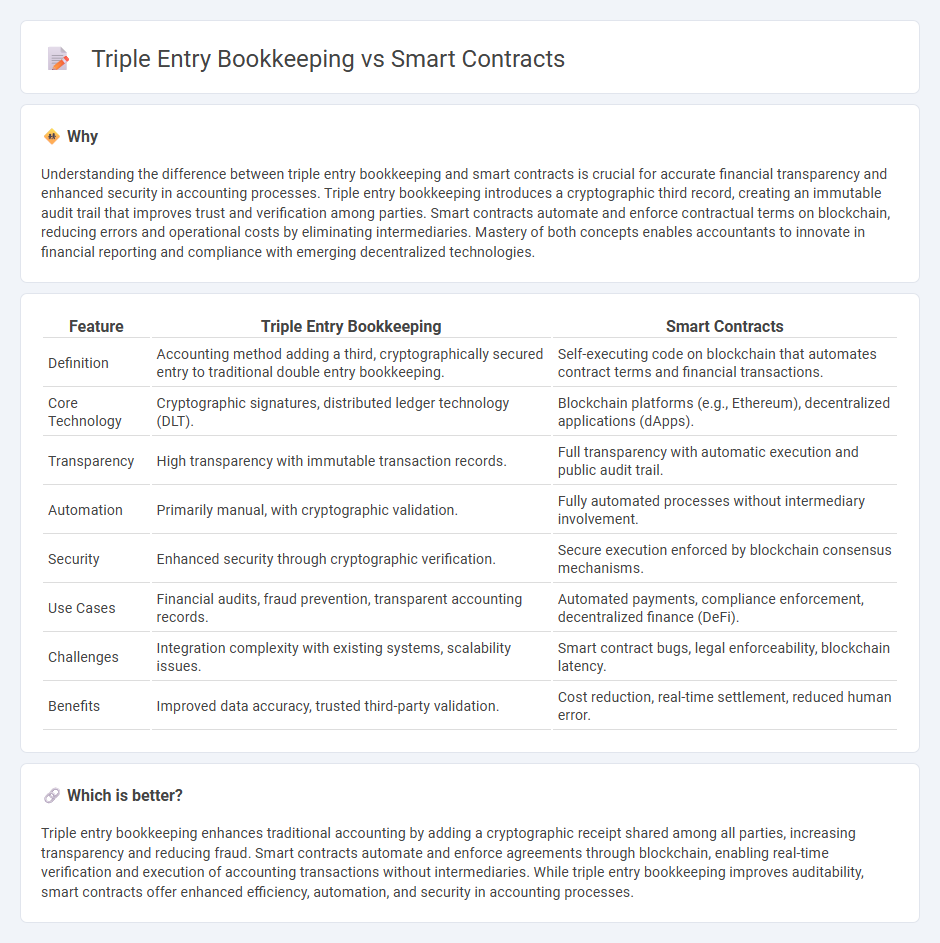
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and smart contracts is crucial for accurate financial transparency and enhanced security in accounting processes. Triple entry bookkeeping introduces a cryptographic third record, creating an immutable audit trail that improves trust and verification among parties. Smart contracts automate and enforce contractual terms on blockchain, reducing errors and operational costs by eliminating intermediaries. Mastery of both concepts enables accountants to innovate in financial reporting and compliance with emerging decentralized technologies.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Smart Contracts |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting method adding a third, cryptographically secured entry to traditional double entry bookkeeping. | Self-executing code on blockchain that automates contract terms and financial transactions. |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic signatures, distributed ledger technology (DLT). | Blockchain platforms (e.g., Ethereum), decentralized applications (dApps). |
| Transparency | High transparency with immutable transaction records. | Full transparency with automatic execution and public audit trail. |
| Automation | Primarily manual, with cryptographic validation. | Fully automated processes without intermediary involvement. |
| Security | Enhanced security through cryptographic verification. | Secure execution enforced by blockchain consensus mechanisms. |
| Use Cases | Financial audits, fraud prevention, transparent accounting records. | Automated payments, compliance enforcement, decentralized finance (DeFi). |
| Challenges | Integration complexity with existing systems, scalability issues. | Smart contract bugs, legal enforceability, blockchain latency. |
| Benefits | Improved data accuracy, trusted third-party validation. | Cost reduction, real-time settlement, reduced human error. |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by adding a cryptographic receipt shared among all parties, increasing transparency and reducing fraud. Smart contracts automate and enforce agreements through blockchain, enabling real-time verification and execution of accounting transactions without intermediaries. While triple entry bookkeeping improves auditability, smart contracts offer enhanced efficiency, automation, and security in accounting processes.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by incorporating cryptographic verification through blockchain technology, ensuring immutable and transparent financial records. Smart contracts automate the execution of accounting entries by triggering transactions based on predefined conditions encoded on the blockchain. This integration reduces fraud risks, increases auditability, and streamlines reconciliation processes in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Immutable Ledger
Smart contracts automate transactions by executing predefined rules on blockchain networks, ensuring transparency and reducing intermediaries. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by recording transactions on an immutable ledger, providing verifiable and tamper-proof financial records. Explore how combining smart contracts with triple entry bookkeeping revolutionizes trust and accountability in digital finance.
Cryptographic Receipt
Smart contracts enable automated, self-executing agreements on blockchain platforms, ensuring transparent and tamper-proof transactions through cryptographic proofs. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates cryptographic receipts into traditional accounting, creating a third ledger that enhances verification, auditability, and fraud resistance beyond double-entry systems. Explore how cryptographic receipts revolutionize financial transparency and trust in decentralized environments.
Automated Reconciliation
Smart contracts enable automated reconciliation by recording transactions in a decentralized ledger, ensuring tamper-proof and real-time updates. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates a cryptographic receipt as a third entry, enhancing transparency and reducing discrepancies between parties. Explore how these innovations transform financial auditing and transaction accuracy by diving deeper into their mechanisms.
Source and External Links
What is a Smart Contract in Blockchain? - Utimaco - Smart contracts are computer programs on blockchain that automatically and immutably execute transfers of digital assets once conditions are met, providing distributed, secure, transparent, and autonomous transactions without intermediaries.
What are smart contracts on the blockchain? 4 real-world use cases - Smart contracts are self-executing blockchain programs using "if-then" logic to perform transactions automatically when predefined conditions are satisfied, enhancing transparency, security, and efficiency across industries like finance and supply chain.
10 Real-World Smart Contract Use Cases - Hedera - Smart contracts eliminate intermediaries by executing agreements automatically on blockchain, making transactions trustless, fast, transparent, and secure, with applications spanning property ownership, financial services, and complex multi-party exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com