Decentralized ledger accounting utilizes blockchain technology to record transactions across multiple distributed nodes, ensuring transparency, immutability, and security without relying on a central authority. Automated accounting employs software and artificial intelligence to streamline data entry, reconcile accounts, and generate financial reports with increased accuracy and efficiency. Discover how these innovative approaches are transforming traditional accounting practices and improving financial management systems.
Why it is important
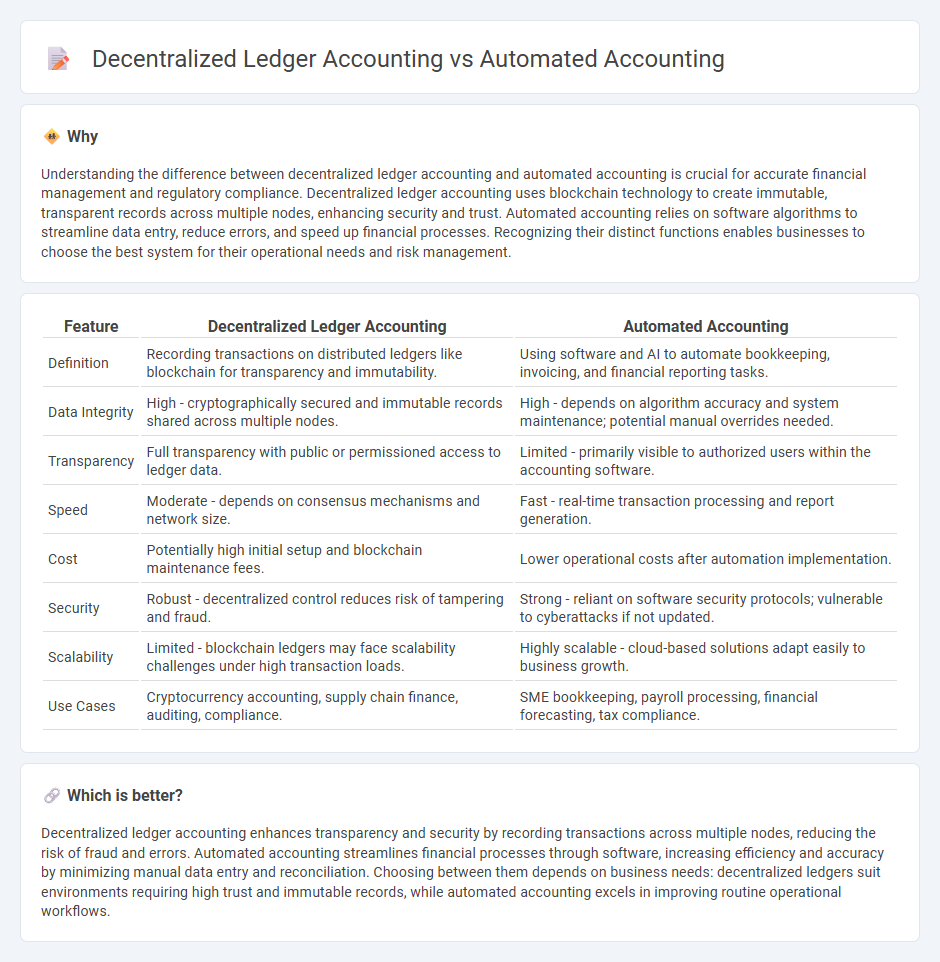
Understanding the difference between decentralized ledger accounting and automated accounting is crucial for accurate financial management and regulatory compliance. Decentralized ledger accounting uses blockchain technology to create immutable, transparent records across multiple nodes, enhancing security and trust. Automated accounting relies on software algorithms to streamline data entry, reduce errors, and speed up financial processes. Recognizing their distinct functions enables businesses to choose the best system for their operational needs and risk management.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Decentralized Ledger Accounting | Automated Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Recording transactions on distributed ledgers like blockchain for transparency and immutability. | Using software and AI to automate bookkeeping, invoicing, and financial reporting tasks. |
| Data Integrity | High - cryptographically secured and immutable records shared across multiple nodes. | High - depends on algorithm accuracy and system maintenance; potential manual overrides needed. |
| Transparency | Full transparency with public or permissioned access to ledger data. | Limited - primarily visible to authorized users within the accounting software. |
| Speed | Moderate - depends on consensus mechanisms and network size. | Fast - real-time transaction processing and report generation. |
| Cost | Potentially high initial setup and blockchain maintenance fees. | Lower operational costs after automation implementation. |
| Security | Robust - decentralized control reduces risk of tampering and fraud. | Strong - reliant on software security protocols; vulnerable to cyberattacks if not updated. |
| Scalability | Limited - blockchain ledgers may face scalability challenges under high transaction loads. | Highly scalable - cloud-based solutions adapt easily to business growth. |
| Use Cases | Cryptocurrency accounting, supply chain finance, auditing, compliance. | SME bookkeeping, payroll processing, financial forecasting, tax compliance. |
Which is better?
Decentralized ledger accounting enhances transparency and security by recording transactions across multiple nodes, reducing the risk of fraud and errors. Automated accounting streamlines financial processes through software, increasing efficiency and accuracy by minimizing manual data entry and reconciliation. Choosing between them depends on business needs: decentralized ledgers suit environments requiring high trust and immutable records, while automated accounting excels in improving routine operational workflows.
Connection
Decentralized ledger accounting leverages blockchain technology to create transparent, tamper-proof records that enable automated accounting processes by ensuring real-time data accuracy and integrity. Automated accounting systems utilize smart contracts within decentralized ledgers to execute financial transactions and record-keeping without manual intervention. This integration enhances auditability and reduces errors, leading to more efficient and secure financial management.
Key Terms
Centralization
Automated accounting relies on centralized systems where a singular authority manages and processes financial data, ensuring quick updates but posing risks of data manipulation or single points of failure. Decentralized ledger accounting, such as blockchain technology, distributes financial records across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and security by eliminating central control. Explore the differences in control, security, and efficiency between these two approaches to modern accounting.
Automation
Automated accounting streamlines financial processes using AI, reducing errors and increasing efficiency, while decentralized ledger accounting, based on blockchain technology, enhances transparency and security by distributing data across multiple nodes. Automation in decentralized ledgers enables real-time transaction verification and immutable record-keeping, transforming traditional accounting workflows. Discover how these technologies redefine financial management and explore their future impact.
Distributed Ledger
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) redefines traditional automated accounting by enabling decentralized, tamper-resistant record-keeping across multiple nodes, enhancing transparency and reducing fraud risks. Unlike centralized automated systems, DLT facilitates real-time transaction verification without intermediaries, improving efficiency and trust in financial processes. Explore the advantages and implementation strategies of distributed ledger accounting to transform your accounting operations.
Source and External Links
Understanding Accounting Automation and its Benefits - Automated accounting uses AI, machine learning, and robotic process automation to make financial processes automatic, improving efficiency, reducing human error, and enabling predictive analytics for better decision-making.
12 Time-Saving Benefits of Automated Accounting - Accounting automation streamlines repetitive tasks like invoice processing and payment authorization, saving time, increasing accuracy, reducing costs, improving compliance, and enabling real-time data analysis through integration with ERP systems.
A Guide to Automated Accounting: Benefits and Tips - Automated accounting software uses AI to handle routine tasks such as data entry and transaction recording, enhancing accounting accuracy and efficiency while freeing CPAs to focus on high-value strategic work.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com