Real-time expense recognition captures costs as they occur, enabling immediate reflection of financial obligations, while revenue recognition records income when earned, regardless of cash receipt timing, adhering to accrual accounting principles. Accurate synchronization of these practices ensures financial statements provide a true representation of business performance and economic condition. Explore how mastering these concepts can enhance your accounting accuracy and decision-making.
Why it is important
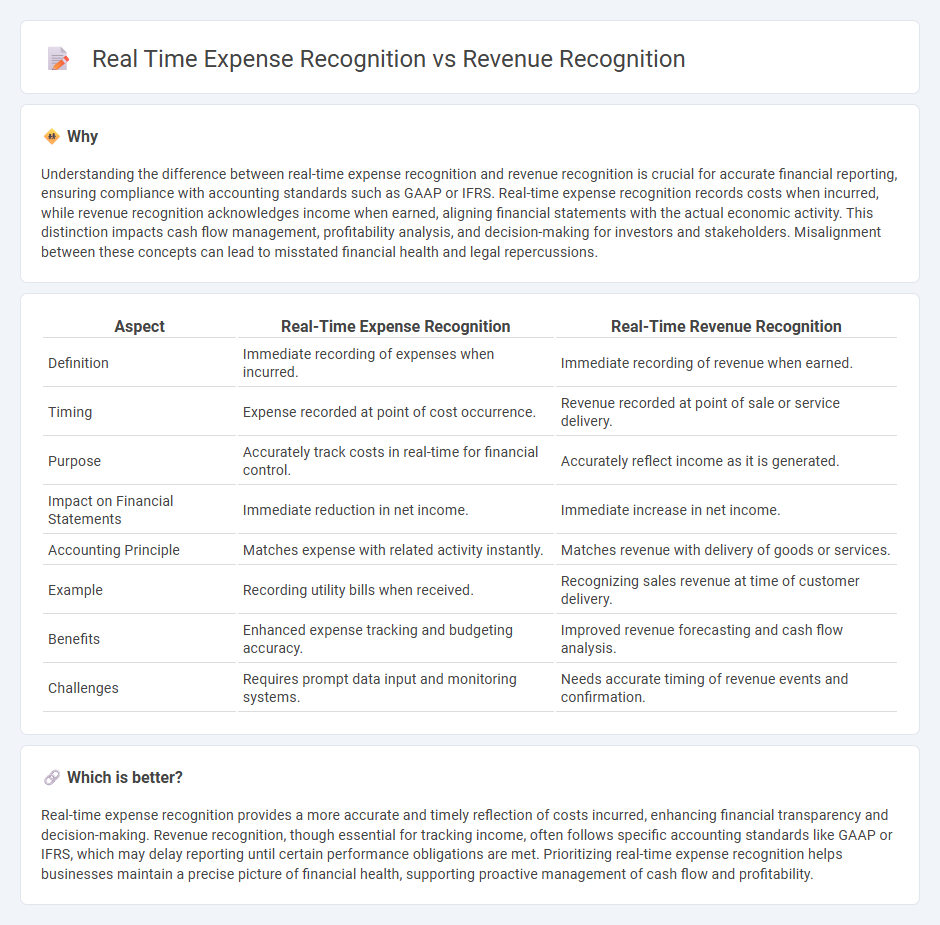
Understanding the difference between real-time expense recognition and revenue recognition is crucial for accurate financial reporting, ensuring compliance with accounting standards such as GAAP or IFRS. Real-time expense recognition records costs when incurred, while revenue recognition acknowledges income when earned, aligning financial statements with the actual economic activity. This distinction impacts cash flow management, profitability analysis, and decision-making for investors and stakeholders. Misalignment between these concepts can lead to misstated financial health and legal repercussions.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Real-Time Expense Recognition | Real-Time Revenue Recognition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Immediate recording of expenses when incurred. | Immediate recording of revenue when earned. |
| Timing | Expense recorded at point of cost occurrence. | Revenue recorded at point of sale or service delivery. |
| Purpose | Accurately track costs in real-time for financial control. | Accurately reflect income as it is generated. |
| Impact on Financial Statements | Immediate reduction in net income. | Immediate increase in net income. |
| Accounting Principle | Matches expense with related activity instantly. | Matches revenue with delivery of goods or services. |
| Example | Recording utility bills when received. | Recognizing sales revenue at time of customer delivery. |
| Benefits | Enhanced expense tracking and budgeting accuracy. | Improved revenue forecasting and cash flow analysis. |
| Challenges | Requires prompt data input and monitoring systems. | Needs accurate timing of revenue events and confirmation. |
Which is better?
Real-time expense recognition provides a more accurate and timely reflection of costs incurred, enhancing financial transparency and decision-making. Revenue recognition, though essential for tracking income, often follows specific accounting standards like GAAP or IFRS, which may delay reporting until certain performance obligations are met. Prioritizing real-time expense recognition helps businesses maintain a precise picture of financial health, supporting proactive management of cash flow and profitability.
Connection
Real-time expense recognition and revenue recognition are interconnected through the principle of matching revenues with the expenses incurred to generate them, ensuring accurate financial reporting. This synchronization enhances the timeliness and reliability of financial statements by reflecting transactions as they occur, aiding in precise profit measurement and cash flow analysis. Businesses leveraging real-time data integration improve decision-making and comply with accounting standards such as GAAP and IFRS.
Key Terms
Accrual Basis
Revenue recognition under the accrual basis records income when earned, regardless of cash receipt, ensuring accurate matching with related expenses. Real-time expense recognition captures costs as they are incurred, aligning with the accrual method to provide a true financial position by matching expenses to the period they benefit. Explore more to understand how these principles impact financial statements and business decision-making.
Matching Principle
Revenue recognition records income when earned, aligning revenues with the period in which they are realized, while real-time expense recognition records expenses as they occur to accurately track costs. The Matching Principle mandates that expenses be matched with the revenues they helped generate within the same accounting period, ensuring financial statements reflect true profitability. Explore how these accounting methods impact financial reporting and compliance in depth.
Timing
Revenue recognition timing determines when income is officially recorded, typically at the point of delivery or completion of a service under GAAP and IFRS standards. Real-time expense recognition records costs immediately as they occur, ensuring up-to-date financial statements and accurate cash flow tracking. Explore the nuances of timing impact on financial reporting and compliance for deeper insights.
Source and External Links
Revenue Recognition: Principles and 5-Step Model - NetSuite - Revenue recognition is an accounting principle that dictates revenue must be recognized as it is earned through a 5-step model including identifying the contract, performance obligations, transaction price, allocation, and recognition of revenue.
Revenue recognition principles & best practices - Stripe - The ASC 606 and IFRS 15 standards require companies to follow a five-step revenue recognition model beginning with identifying customer contracts and specifically defining performance obligations before recognizing revenue.
Revenue recognition examples: 4 different ways to recognize revenue - Revenue recognition is governed by GAAP and requires recording revenue only after delivery of goods or services, differentiating between cash receipt and actual revenue to avoid prematurely counting deferred revenue.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com