Carbon accounting quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to measure an organization's environmental impact, focusing solely on carbon footprints. Triple bottom line accounting expands this scope by evaluating social, environmental, and financial performance, promoting sustainability across multiple dimensions. Explore how integrating these approaches can enhance comprehensive business reporting and decision-making.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between carbon accounting and triple bottom line accounting is crucial for accurately measuring environmental impact versus overall sustainability performance. Carbon accounting focuses specifically on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions to manage carbon footprints. Triple bottom line accounting evaluates social, environmental, and financial performance, providing a comprehensive view of an organization's sustainability. Knowing these distinctions helps businesses implement targeted strategies for climate action and sustainable development goals.
Comparison Table
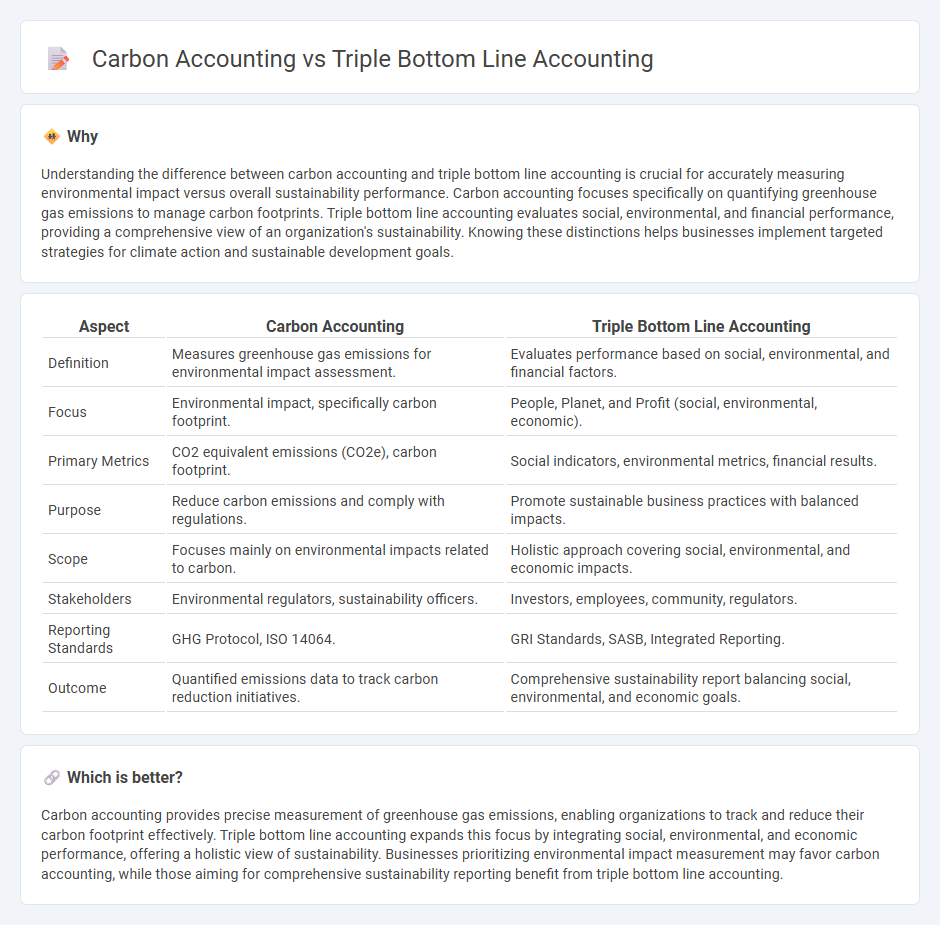
| Aspect | Carbon Accounting | Triple Bottom Line Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Measures greenhouse gas emissions for environmental impact assessment. | Evaluates performance based on social, environmental, and financial factors. |
| Focus | Environmental impact, specifically carbon footprint. | People, Planet, and Profit (social, environmental, economic). |
| Primary Metrics | CO2 equivalent emissions (CO2e), carbon footprint. | Social indicators, environmental metrics, financial results. |
| Purpose | Reduce carbon emissions and comply with regulations. | Promote sustainable business practices with balanced impacts. |
| Scope | Focuses mainly on environmental impacts related to carbon. | Holistic approach covering social, environmental, and economic impacts. |
| Stakeholders | Environmental regulators, sustainability officers. | Investors, employees, community, regulators. |
| Reporting Standards | GHG Protocol, ISO 14064. | GRI Standards, SASB, Integrated Reporting. |
| Outcome | Quantified emissions data to track carbon reduction initiatives. | Comprehensive sustainability report balancing social, environmental, and economic goals. |
Which is better?
Carbon accounting provides precise measurement of greenhouse gas emissions, enabling organizations to track and reduce their carbon footprint effectively. Triple bottom line accounting expands this focus by integrating social, environmental, and economic performance, offering a holistic view of sustainability. Businesses prioritizing environmental impact measurement may favor carbon accounting, while those aiming for comprehensive sustainability reporting benefit from triple bottom line accounting.
Connection
Carbon accounting measures greenhouse gas emissions to quantify environmental impact, forming a critical component of the environmental aspect within triple bottom line accounting. Triple bottom line accounting evaluates financial, social, and environmental performance, integrating carbon accounting data to assess sustainability comprehensively. This interconnected approach enables companies to align carbon reduction strategies with broader economic and social responsibilities, ensuring holistic accountability.
Key Terms
**Triple Bottom Line Accounting:**
Triple Bottom Line (TBL) accounting measures a company's social, environmental, and financial performance, emphasizing sustainable development by balancing people, planet, and profit. It incorporates comprehensive metrics such as community impact, resource usage, and economic value creation to guide ethical business practices. Explore more about how TBL accounting drives long-term corporate responsibility and sustainability initiatives.
People
Triple bottom line accounting evaluates social impact by measuring outcomes related to employee well-being, community engagement, and equitable labor practices, emphasizing the 'People' aspect alongside profit and planet. Carbon accounting primarily focuses on quantifying greenhouse gas emissions without directly assessing social or human factors, making it less comprehensive in addressing social responsibility. Explore more to understand how these accounting methods differ in prioritizing social sustainability.
Planet
Triple bottom line accounting evaluates environmental impact by measuring social, environmental, and economic performance, providing a comprehensive sustainability overview. Carbon accounting specifically quantifies greenhouse gas emissions to track and manage carbon footprints, emphasizing climate-related impacts. Explore further to understand how each approach drives sustainable business strategies focused on planetary health.
Source and External Links
The Triple Bottom Line: What Is It and How Does It Work? - This article discusses the triple bottom line (TBL) accounting framework, which includes social, environmental, and financial dimensions to evaluate organizational performance.
What Is the Triple Bottom Line (TBL)? - The triple bottom line is a sustainability framework focusing on the three P's: people, planet, and profit, to ensure organizations have a positive impact while improving financial performance.
Triple Bottom Line - The triple bottom line is an accounting framework that evaluates an organization's performance across social, environmental, and economic dimensions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com