Embedded finance reporting integrates financial services data within non-financial platforms, streamlining real-time analytics and improving decision-making efficiency. Regulatory reporting focuses on compliance, requiring accurate, standardized, and periodic disclosures to meet legal and financial industry standards. Explore the distinct advantages and challenges of embedded finance reporting compared to regulatory reporting for optimized accounting processes.
Why it is important
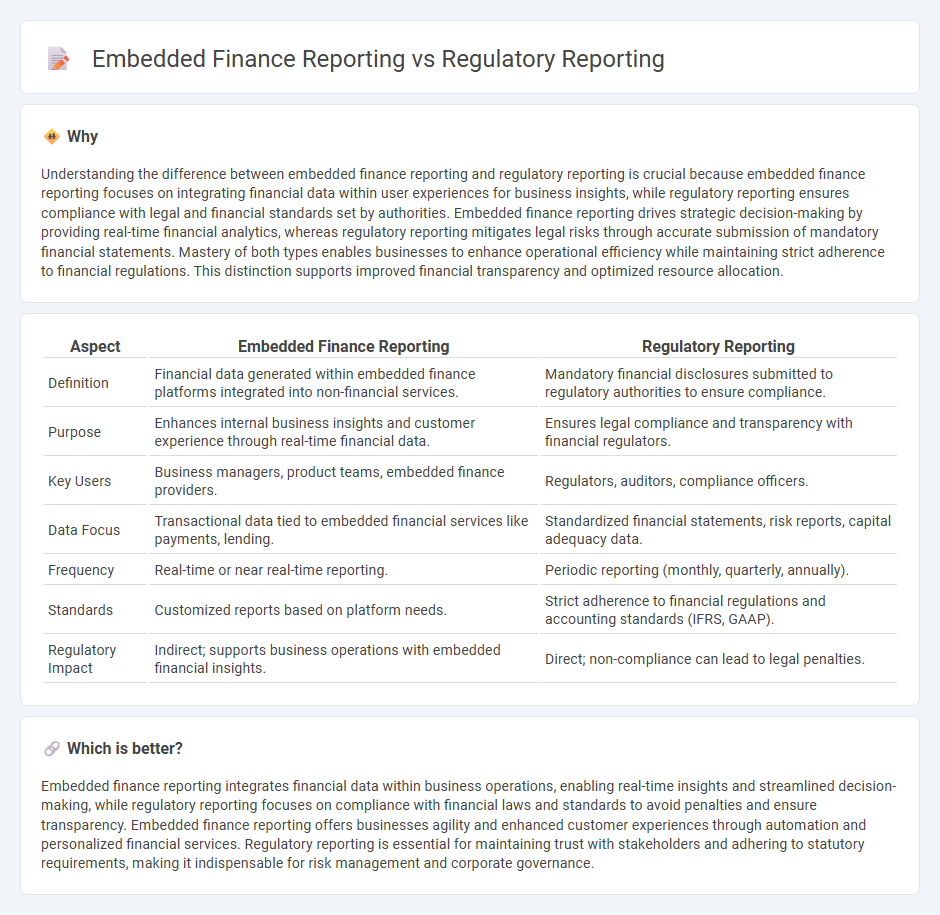
Understanding the difference between embedded finance reporting and regulatory reporting is crucial because embedded finance reporting focuses on integrating financial data within user experiences for business insights, while regulatory reporting ensures compliance with legal and financial standards set by authorities. Embedded finance reporting drives strategic decision-making by providing real-time financial analytics, whereas regulatory reporting mitigates legal risks through accurate submission of mandatory financial statements. Mastery of both types enables businesses to enhance operational efficiency while maintaining strict adherence to financial regulations. This distinction supports improved financial transparency and optimized resource allocation.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Embedded Finance Reporting | Regulatory Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Financial data generated within embedded finance platforms integrated into non-financial services. | Mandatory financial disclosures submitted to regulatory authorities to ensure compliance. |
| Purpose | Enhances internal business insights and customer experience through real-time financial data. | Ensures legal compliance and transparency with financial regulators. |
| Key Users | Business managers, product teams, embedded finance providers. | Regulators, auditors, compliance officers. |
| Data Focus | Transactional data tied to embedded financial services like payments, lending. | Standardized financial statements, risk reports, capital adequacy data. |
| Frequency | Real-time or near real-time reporting. | Periodic reporting (monthly, quarterly, annually). |
| Standards | Customized reports based on platform needs. | Strict adherence to financial regulations and accounting standards (IFRS, GAAP). |
| Regulatory Impact | Indirect; supports business operations with embedded financial insights. | Direct; non-compliance can lead to legal penalties. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance reporting integrates financial data within business operations, enabling real-time insights and streamlined decision-making, while regulatory reporting focuses on compliance with financial laws and standards to avoid penalties and ensure transparency. Embedded finance reporting offers businesses agility and enhanced customer experiences through automation and personalized financial services. Regulatory reporting is essential for maintaining trust with stakeholders and adhering to statutory requirements, making it indispensable for risk management and corporate governance.
Connection
Embedded finance reporting facilitates seamless integration of financial data within business platforms, enhancing the accuracy and timeliness of regulatory reporting. This integration ensures compliance by automating the capture and consolidation of transactional and financial information required by regulatory authorities. Efficient synchronization of embedded finance systems with regulatory frameworks reduces risks of errors and penalties, streamlining audit processes and financial disclosures.
Key Terms
Regulatory reporting:
Regulatory reporting involves the systematic submission of financial, operational, and compliance data to regulatory authorities to ensure transparency, adherence to laws, and risk management in the financial sector. Embedded finance reporting, by contrast, primarily captures transactional data within non-financial platforms integrating financial services, emphasizing user experience and operational metrics. Explore comprehensive insights on regulatory reporting processes and compliance requirements to enhance your financial governance framework.
Compliance
Regulatory reporting mandates financial institutions to submit detailed compliance data to authorities, ensuring adherence to laws and minimizing risks. Embedded finance reporting integrates compliance measures directly within third-party platforms, enabling seamless monitoring and risk management. Explore the distinct compliance strategies and benefits of both reporting methods to optimize your financial operations.
Standardization
Regulatory reporting demands strict adherence to standardized formats such as XBRL and ISO 20022 to ensure compliance with financial authorities globally. Embedded finance reporting integrates seamlessly within non-financial platforms, prioritizing real-time data exchange and standardized APIs to enhance transparency and operational efficiency. Explore the evolving landscape of reporting standards to optimize your financial strategies.
Source and External Links
What is Regulatory Reporting? - SolveXia - Regulatory reporting is a process where financial institutions submit data to regulatory authorities to ensure compliance with statutory and regulatory requirements.
What is Regulatory Reporting: A Beginner's Guide - Finreg-E - This guide explains that regulatory reporting involves collecting and submitting financial and operational information to regulatory bodies to demonstrate compliance with regulations.
What is Regulatory Reporting and Why is it Important? - Prophix - Regulatory reporting is how companies demonstrate compliance with financial and operational regulations, enhancing transparency and trust among stakeholders.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com