Smart contracts accounting leverages blockchain technology to automate, verify, and record transactions in real-time, ensuring enhanced transparency and reduced errors compared to traditional cash basis accounting, which records transactions only when cash changes hands. This shift enables businesses to improve accuracy in financial reporting and streamline audit processes by embedding contractual terms directly into the ledger. Explore how integrating smart contracts can transform your accounting practices and boost financial efficiency.
Why it is important
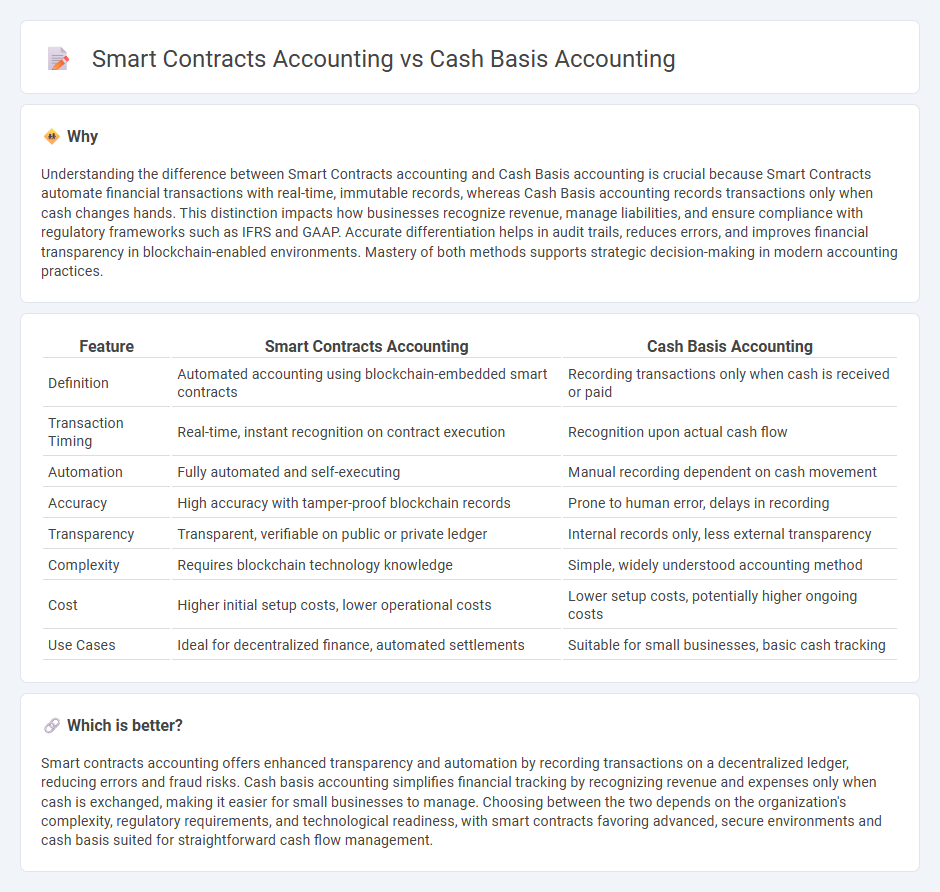
Understanding the difference between Smart Contracts accounting and Cash Basis accounting is crucial because Smart Contracts automate financial transactions with real-time, immutable records, whereas Cash Basis accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands. This distinction impacts how businesses recognize revenue, manage liabilities, and ensure compliance with regulatory frameworks such as IFRS and GAAP. Accurate differentiation helps in audit trails, reduces errors, and improves financial transparency in blockchain-enabled environments. Mastery of both methods supports strategic decision-making in modern accounting practices.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Smart Contracts Accounting | Cash Basis Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated accounting using blockchain-embedded smart contracts | Recording transactions only when cash is received or paid |
| Transaction Timing | Real-time, instant recognition on contract execution | Recognition upon actual cash flow |
| Automation | Fully automated and self-executing | Manual recording dependent on cash movement |
| Accuracy | High accuracy with tamper-proof blockchain records | Prone to human error, delays in recording |
| Transparency | Transparent, verifiable on public or private ledger | Internal records only, less external transparency |
| Complexity | Requires blockchain technology knowledge | Simple, widely understood accounting method |
| Cost | Higher initial setup costs, lower operational costs | Lower setup costs, potentially higher ongoing costs |
| Use Cases | Ideal for decentralized finance, automated settlements | Suitable for small businesses, basic cash tracking |
Which is better?
Smart contracts accounting offers enhanced transparency and automation by recording transactions on a decentralized ledger, reducing errors and fraud risks. Cash basis accounting simplifies financial tracking by recognizing revenue and expenses only when cash is exchanged, making it easier for small businesses to manage. Choosing between the two depends on the organization's complexity, regulatory requirements, and technological readiness, with smart contracts favoring advanced, secure environments and cash basis suited for straightforward cash flow management.
Connection
Smart contracts accounting automates financial transactions by recording entries directly on blockchain ledgers, enhancing transparency and accuracy. Cash basis accounting recognizes revenues and expenses only when cash changes hands, aligning with smart contracts that execute payments in real-time upon contract conditions being met. Integrating smart contracts with cash basis accounting streamlines cash flow management and reduces reconciliation errors in financial reporting.
Key Terms
Revenue Recognition
Cash basis accounting recognizes revenue only when cash is received, providing a straightforward but sometimes delayed reflection of a company's financial performance. Smart contracts accounting utilizes blockchain technology to automate and verify revenue recognition based on predefined criteria, ensuring real-time accuracy and transparency. Explore how smart contracts can revolutionize revenue recognition and enhance financial reporting accuracy.
Immutable Ledger
Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash transactions occur, making it simple but limited in real-time financial accuracy. Smart contracts accounting leverages blockchain technology, providing an immutable ledger that automatically enforces and verifies transactions, enhancing transparency and reducing errors. Explore the transformative impact of immutable ledgers on accounting practices to optimize your financial management.
Real-Time Settlement
Cash basis accounting records transactions only when cash changes hands, causing delays in financial reporting and settlement. Smart contracts accounting leverages blockchain technology to automate and execute financial transactions instantly, ensuring real-time settlement with enhanced transparency and reduced counterparty risk. Explore how integrating smart contracts can revolutionize your financial processes and achieve seamless real-time settlements.
Source and External Links
Cash Basis Accounting: Definition, Example, Pros and Cons - Cash basis accounting is a simple method that records income only when cash is received and expenses when cash is paid, mostly suitable for small cash-based businesses, but it is not accepted under GAAP or IFRS.
Cash-based accounting: A guide to the cash basis - Cash basis accounting records revenues and expenses only when cash is exchanged, focusing on actual cash flow without tracking receivables or payables, making it simpler but less comprehensive than accrual accounting.
What Is Cash Basis Accounting? Definition and Guide - Cash basis accounting recognizes income only upon receipt of cash and expenses when paid, commonly used by small or cash-rich businesses, and excludes credit sales until payment is received.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com