Sustainability reporting provides transparent disclosure of a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, enabling stakeholders to assess corporate responsibility and long-term value creation. Assurance reporting independently verifies the accuracy and reliability of sustainability data, enhancing stakeholder confidence and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards like the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) and the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB). Explore more about how sustainability reporting and assurance contribute to trustworthy corporate accountability.
Why it is important
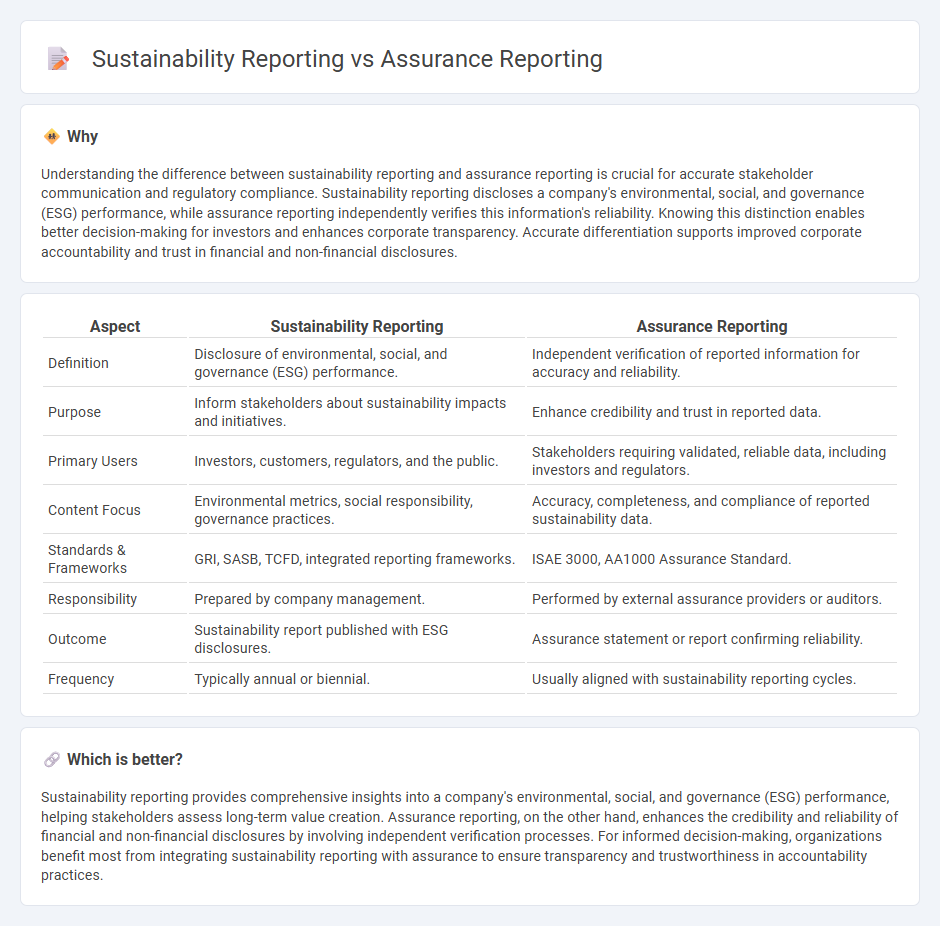
Understanding the difference between sustainability reporting and assurance reporting is crucial for accurate stakeholder communication and regulatory compliance. Sustainability reporting discloses a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, while assurance reporting independently verifies this information's reliability. Knowing this distinction enables better decision-making for investors and enhances corporate transparency. Accurate differentiation supports improved corporate accountability and trust in financial and non-financial disclosures.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Sustainability Reporting | Assurance Reporting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance. | Independent verification of reported information for accuracy and reliability. |
| Purpose | Inform stakeholders about sustainability impacts and initiatives. | Enhance credibility and trust in reported data. |
| Primary Users | Investors, customers, regulators, and the public. | Stakeholders requiring validated, reliable data, including investors and regulators. |
| Content Focus | Environmental metrics, social responsibility, governance practices. | Accuracy, completeness, and compliance of reported sustainability data. |
| Standards & Frameworks | GRI, SASB, TCFD, integrated reporting frameworks. | ISAE 3000, AA1000 Assurance Standard. |
| Responsibility | Prepared by company management. | Performed by external assurance providers or auditors. |
| Outcome | Sustainability report published with ESG disclosures. | Assurance statement or report confirming reliability. |
| Frequency | Typically annual or biennial. | Usually aligned with sustainability reporting cycles. |
Which is better?
Sustainability reporting provides comprehensive insights into a company's environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, helping stakeholders assess long-term value creation. Assurance reporting, on the other hand, enhances the credibility and reliability of financial and non-financial disclosures by involving independent verification processes. For informed decision-making, organizations benefit most from integrating sustainability reporting with assurance to ensure transparency and trustworthiness in accountability practices.
Connection
Sustainability reporting provides transparent data on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) performance, enabling organizations to communicate their impact and progress. Assurance reporting enhances the credibility of sustainability disclosures by independently verifying the accuracy and reliability of reported information. This connection ensures stakeholders receive trustworthy insights for informed decision-making and fosters accountability in corporate sustainability practices.
Key Terms
Assurance Reporting:
Assurance reporting involves the independent verification of financial statements or other data to enhance credibility and accuracy for stakeholders, typically conducted by external auditors following established standards such as ISAE 3000. It ensures transparency and reduces risk by providing reliable information on compliance, controls, and performance metrics. Explore deeper insights into assurance reporting processes, benefits, and frameworks for enhanced corporate governance.
Audit
Assurance reporting focuses on the independent verification of financial statements, ensuring accuracy, compliance, and reliability through systematic audit processes conducted by external auditors. Sustainability reporting, on the other hand, encompasses environmental, social, and governance (ESG) data, with audits verifying the authenticity and completeness of non-financial disclosures to meet stakeholder expectations and regulatory requirements. Explore how audit methodologies differ between assurance and sustainability reporting to enhance transparency and trust in corporate disclosures.
Materiality
Assurance reporting emphasizes verifying the accuracy and reliability of financial and non-financial information, focusing on materiality to ensure that significant misstatements or omissions do not mislead stakeholders. Sustainability reporting highlights the disclosure of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) impacts, prioritizing materiality to address issues most relevant to an organization's long-term value creation and stakeholder interests. Explore further to understand how materiality shapes transparency and accountability in both assurance and sustainability reporting frameworks.
Source and External Links
What is Assurance Reporting and How to Prepare for a Review - Assurance reporting involves summarizing evaluation results to determine if an organization met assurance objectives, often to confirm business processes and governance standards.
Back to Basics - Assurance Reporting - This resource provides an overview of assurance reporting, focusing on elements like executive summaries and risk management for internal audits.
Sustainability Assurance - The proposed ISSA 5000 standard aims to provide a framework for assurance on sustainability reporting, addressing both limited and reasonable assurance across various topics.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com