Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) integration in accounting focuses on embedding sustainability factors into financial analysis and decision-making to enhance long-term value. Impact measurement quantifies the specific social and environmental outcomes resulting from investments or business activities, providing data for performance evaluation and reporting. Explore how ESG integration and impact measurement together drive responsible finance and transparent accountability.
Why it is important
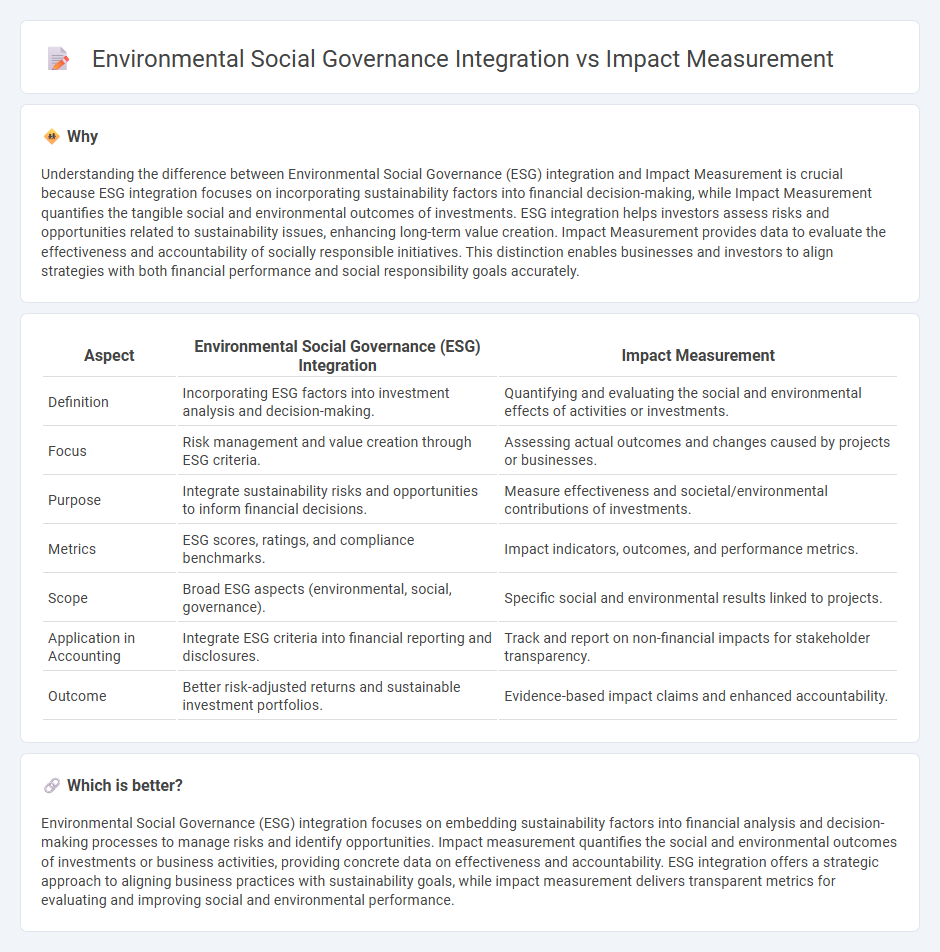
Understanding the difference between Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration and Impact Measurement is crucial because ESG integration focuses on incorporating sustainability factors into financial decision-making, while Impact Measurement quantifies the tangible social and environmental outcomes of investments. ESG integration helps investors assess risks and opportunities related to sustainability issues, enhancing long-term value creation. Impact Measurement provides data to evaluate the effectiveness and accountability of socially responsible initiatives. This distinction enables businesses and investors to align strategies with both financial performance and social responsibility goals accurately.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Environmental Social Governance (ESG) Integration | Impact Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Incorporating ESG factors into investment analysis and decision-making. | Quantifying and evaluating the social and environmental effects of activities or investments. |
| Focus | Risk management and value creation through ESG criteria. | Assessing actual outcomes and changes caused by projects or businesses. |
| Purpose | Integrate sustainability risks and opportunities to inform financial decisions. | Measure effectiveness and societal/environmental contributions of investments. |
| Metrics | ESG scores, ratings, and compliance benchmarks. | Impact indicators, outcomes, and performance metrics. |
| Scope | Broad ESG aspects (environmental, social, governance). | Specific social and environmental results linked to projects. |
| Application in Accounting | Integrate ESG criteria into financial reporting and disclosures. | Track and report on non-financial impacts for stakeholder transparency. |
| Outcome | Better risk-adjusted returns and sustainable investment portfolios. | Evidence-based impact claims and enhanced accountability. |
Which is better?
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration focuses on embedding sustainability factors into financial analysis and decision-making processes to manage risks and identify opportunities. Impact measurement quantifies the social and environmental outcomes of investments or business activities, providing concrete data on effectiveness and accountability. ESG integration offers a strategic approach to aligning business practices with sustainability goals, while impact measurement delivers transparent metrics for evaluating and improving social and environmental performance.
Connection
Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration influences accounting by embedding sustainability metrics into financial reporting frameworks, ensuring transparency and accountability in corporate behavior. Impact measurement provides quantifiable data on a company's environmental and social effects, which are critical for accurate ESG disclosures and risk assessment. Both practices enhance investor confidence and regulatory compliance by aligning financial performance with sustainable development goals.
Key Terms
Double Materiality
Impact measurement assesses the direct effects of business activities on environmental and social outcomes, offering tangible metrics for sustainability performance. Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration embeds these criteria into corporate strategies and decision-making to manage risks and create long-term value, emphasizing financial and non-financial materiality. Explore how Double Materiality connects these frameworks by capturing both the impact on society and the financial implications for enterprises.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Impact measurement centers on evaluating specific outcomes and social or environmental changes using quantitative and qualitative data, while Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration embeds sustainability criteria within core business strategies and decision-making processes. Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) in impact measurement track direct social and environmental results, whereas ESG KPIs assess ongoing compliance and risk management across environmental, social, and governance dimensions. Explore how aligning impact measurement and ESG integration through targeted KPIs enhances comprehensive sustainability reporting and drives responsible business growth.
Non-Financial Reporting
Impact measurement quantifies the specific outcomes and positive changes caused by corporate activities, while Environmental Social Governance (ESG) integration embeds sustainability factors into core business strategies and risk management. In non-financial reporting, impact measurement provides tangible evidence of social and environmental performance, complementing ESG frameworks that guide overall corporate responsibility. Explore detailed methodologies to enhance transparency and stakeholder trust in sustainability disclosures.
Source and External Links
What Is Impact Measurement? - This article discusses how impact measurement helps investors evaluate past investments and informs future strategies using methods like randomized controlled trials and difference-in-differences.
Impact Measurement and Management Actionable Approach - This guide outlines the importance of impact measurement for businesses and investors, emphasizing the use of AI and smart data for evaluating social and environmental outcomes.
Impact Measurement: A Full Introduction & How to Get Started - This introduction explains how impact measurement helps mission-driven organizations evaluate their effectiveness and understand the lasting effects of their initiatives.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com