Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by incorporating a cryptographic receipt issued to a third party, ensuring greater transparency and security in financial records. Blockchain accounting leverages decentralized ledger technology to create immutable and verifiable transaction histories, reducing fraud and increasing trust among stakeholders. Explore the nuances and benefits of these innovative accounting methods to optimize your financial management.
Why it is important
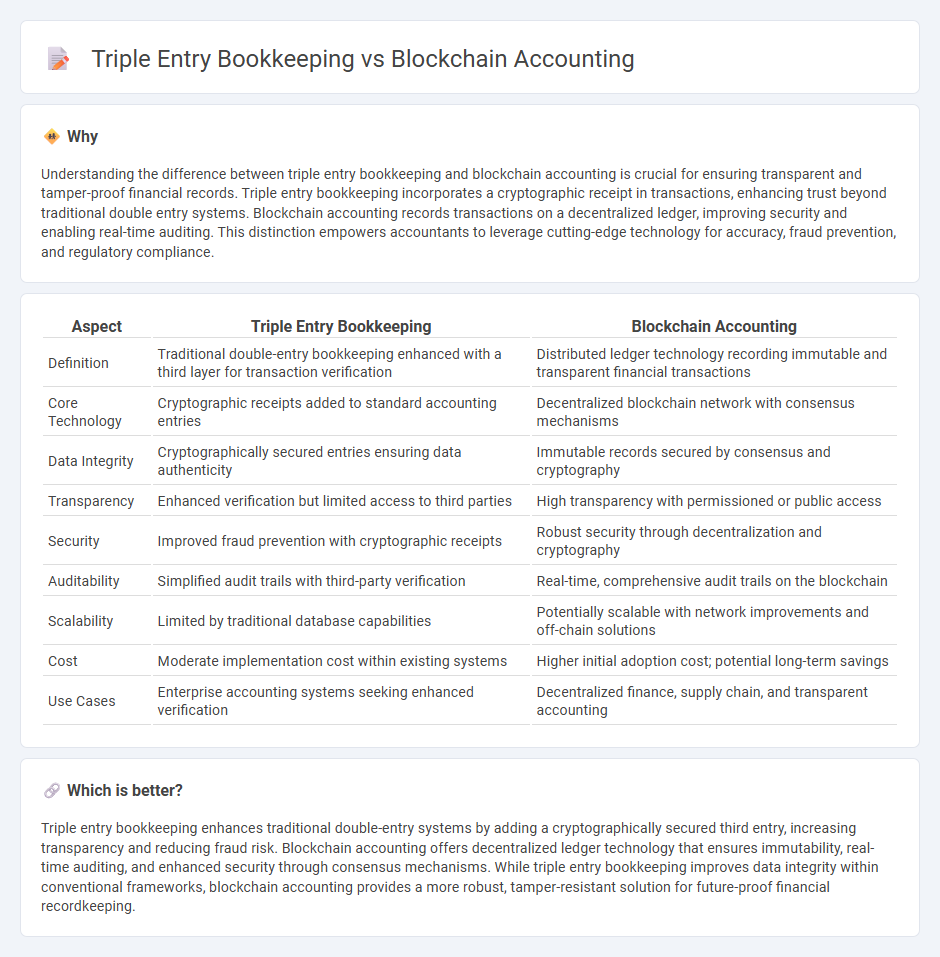
Understanding the difference between triple entry bookkeeping and blockchain accounting is crucial for ensuring transparent and tamper-proof financial records. Triple entry bookkeeping incorporates a cryptographic receipt in transactions, enhancing trust beyond traditional double entry systems. Blockchain accounting records transactions on a decentralized ledger, improving security and enabling real-time auditing. This distinction empowers accountants to leverage cutting-edge technology for accuracy, fraud prevention, and regulatory compliance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Triple Entry Bookkeeping | Blockchain Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Traditional double-entry bookkeeping enhanced with a third layer for transaction verification | Distributed ledger technology recording immutable and transparent financial transactions |
| Core Technology | Cryptographic receipts added to standard accounting entries | Decentralized blockchain network with consensus mechanisms |
| Data Integrity | Cryptographically secured entries ensuring data authenticity | Immutable records secured by consensus and cryptography |
| Transparency | Enhanced verification but limited access to third parties | High transparency with permissioned or public access |
| Security | Improved fraud prevention with cryptographic receipts | Robust security through decentralization and cryptography |
| Auditability | Simplified audit trails with third-party verification | Real-time, comprehensive audit trails on the blockchain |
| Scalability | Limited by traditional database capabilities | Potentially scalable with network improvements and off-chain solutions |
| Cost | Moderate implementation cost within existing systems | Higher initial adoption cost; potential long-term savings |
| Use Cases | Enterprise accounting systems seeking enhanced verification | Decentralized finance, supply chain, and transparent accounting |
Which is better?
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double-entry systems by adding a cryptographically secured third entry, increasing transparency and reducing fraud risk. Blockchain accounting offers decentralized ledger technology that ensures immutability, real-time auditing, and enhanced security through consensus mechanisms. While triple entry bookkeeping improves data integrity within conventional frameworks, blockchain accounting provides a more robust, tamper-resistant solution for future-proof financial recordkeeping.
Connection
Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional accounting by integrating a cryptographic receipt stored on a blockchain, ensuring immutable and transparent transaction records. Blockchain accounting leverages this system to provide real-time verification and reduce fraud through decentralized ledger technology. The synergy between triple entry bookkeeping and blockchain fundamentally transforms financial auditing and trust in accounting data.
Key Terms
Distributed Ledger
Distributed Ledger Technology (DLT) underpins blockchain accounting by enabling decentralized, immutable record-keeping, enhancing transparency and security compared to traditional double-entry systems. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates cryptographic verification within the ledger, creating an automated audit trail that reduces fraud and errors. Explore the transformative impact of Distributed Ledger Technology on financial record accuracy and trust.
Immutable Records
Blockchain accounting utilizes decentralized ledgers to create immutable records, ensuring transparency and preventing data tampering. Triple entry bookkeeping enhances traditional double entry systems by introducing a cryptographic third entry, providing verifiable audit trails and increasing trust between parties. Discover how these technologies revolutionize financial integrity and audit processes by exploring their mechanisms in depth.
Cryptographic Signature
Blockchain accounting leverages cryptographic signatures to ensure data integrity and transaction authenticity in a decentralized ledger, preventing tampering and fraud with immutable records. Triple entry bookkeeping integrates cryptographic signatures into accounting by adding a third ledger, shared among participants, that cryptographically verifies entries, enhancing transparency and trust in financial reporting. Explore how cryptographic signatures revolutionize accounting systems for more secure and reliable financial management.
Source and External Links
Blockchain in Accounting: Transforming Financial Practices - Blockchain introduces a secure, transparent, and immutable ledger that enhances transaction recording, verification, audit trails, fraud detection, and automates reconciliations through smart contracts, transforming accounting processes.
Blockchain Accounting - Guide & Use Cases - Blockchain accounting leverages smart contracts, AI, and immutable triple-entry data to reduce errors, prevent fraud, streamline auditing, and cut costs by automating financial record reconciliation.
What is Blockchain Accounting? - Blockchain supports accountants by providing a transparent, tamper-proof ledger to verify transaction legitimacy in real time, enhancing audit efficiency while still requiring traditional accounting for contextual details.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com