Transfer pricing analytics involves examining intercompany transactions to ensure compliance with tax regulations and optimize profit distribution, using data-driven strategies and benchmarking methods. Standard costing focuses on assigning predetermined costs to products or services to measure performance and control expenses through variance analysis. Explore how mastering both methods can enhance financial accuracy and strategic decision-making.
Why it is important
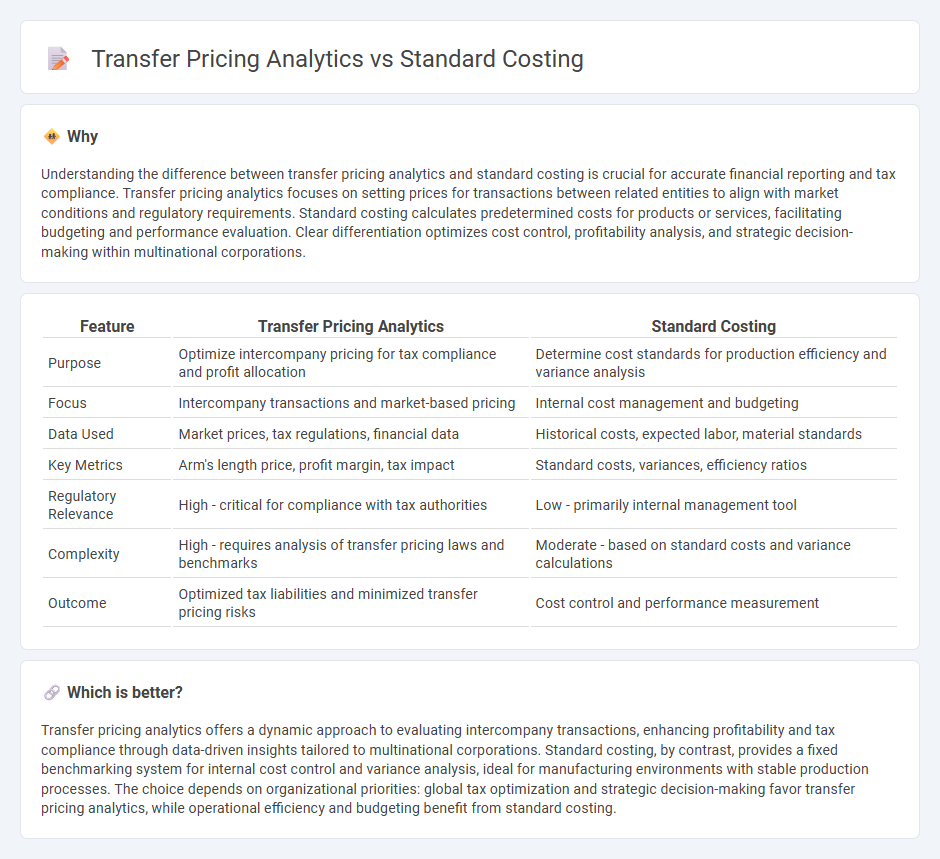
Understanding the difference between transfer pricing analytics and standard costing is crucial for accurate financial reporting and tax compliance. Transfer pricing analytics focuses on setting prices for transactions between related entities to align with market conditions and regulatory requirements. Standard costing calculates predetermined costs for products or services, facilitating budgeting and performance evaluation. Clear differentiation optimizes cost control, profitability analysis, and strategic decision-making within multinational corporations.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Transfer Pricing Analytics | Standard Costing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Optimize intercompany pricing for tax compliance and profit allocation | Determine cost standards for production efficiency and variance analysis |
| Focus | Intercompany transactions and market-based pricing | Internal cost management and budgeting |
| Data Used | Market prices, tax regulations, financial data | Historical costs, expected labor, material standards |
| Key Metrics | Arm's length price, profit margin, tax impact | Standard costs, variances, efficiency ratios |
| Regulatory Relevance | High - critical for compliance with tax authorities | Low - primarily internal management tool |
| Complexity | High - requires analysis of transfer pricing laws and benchmarks | Moderate - based on standard costs and variance calculations |
| Outcome | Optimized tax liabilities and minimized transfer pricing risks | Cost control and performance measurement |
Which is better?
Transfer pricing analytics offers a dynamic approach to evaluating intercompany transactions, enhancing profitability and tax compliance through data-driven insights tailored to multinational corporations. Standard costing, by contrast, provides a fixed benchmarking system for internal cost control and variance analysis, ideal for manufacturing environments with stable production processes. The choice depends on organizational priorities: global tax optimization and strategic decision-making favor transfer pricing analytics, while operational efficiency and budgeting benefit from standard costing.
Connection
Transfer pricing analytics and standard costing are interconnected by their shared focus on cost control and profit optimization within multinational corporations. Transfer pricing analytics evaluates intercompany transaction prices to ensure compliance and profitability, while standard costing establishes benchmark costs against which actual performance is measured. Integrating these methods enhances accuracy in internal cost allocation, regulatory adherence, and strategic financial decision-making.
Key Terms
Variance Analysis
Standard costing involves setting predetermined costs for products or services and analyzing variances between these standards and actual costs to identify performance issues and cost control opportunities. Transfer pricing analytics examines the prices charged for transactions between affiliated entities within a company, focusing on ensuring compliance with tax regulations and optimizing intercompany profit allocation. Explore deeper insights into both methodologies to enhance financial accuracy and strategic decision-making.
Cost Allocation
Standard costing centers on assigning predetermined costs to production activities, streamlining budget control and variance analysis for internal reporting. Transfer pricing analytics evaluates pricing strategies for intercompany transactions, emphasizing fair cost allocation to optimize tax liabilities and profit distribution across multinational entities. Explore in-depth methodologies and best practices to enhance your cost allocation strategies.
Arm's Length Principle
Standard costing provides a benchmark for production costs and efficiency within a company, while transfer pricing analytics determine pricing strategies for transactions between related entities, crucial for tax compliance. The Arm's Length Principle ensures that transfer prices reflect market conditions as if the transactions were between unrelated parties, thus preventing profit shifting and tax evasion. Explore the detailed methodologies and regulatory frameworks guiding both practices to enhance corporate financial strategy.
Source and External Links
Standard costing definition - AccountingTools - Standard costing is the practice of substituting an expected cost for an actual cost in accounting records, with variances recorded to show differences between expected and actual costs, providing accounting efficiencies.
What is standard costing? | Sage Advice US - Standard costing is an accounting method for manufacturers to estimate expected production costs for budgeting, cost control, and variance analysis, helping managers plan and make strategic decisions.
Standard Costing: Meaning, Advantages and Variances - Shiksha - Standard costing assigns predetermined costs to production units based on expected materials, labor, and overhead, serving as benchmarks to measure actual performance and control costs effectively.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com