Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly within non-financial platforms, enabling seamless transaction recording and real-time financial data synchronization. Core banking system accounting focuses on centralized management of banking transactions, ensuring standardized compliance, risk management, and detailed ledger maintenance across financial institutions. Explore further to understand how these accounting approaches impact financial accuracy and operational efficiency.
Why it is important
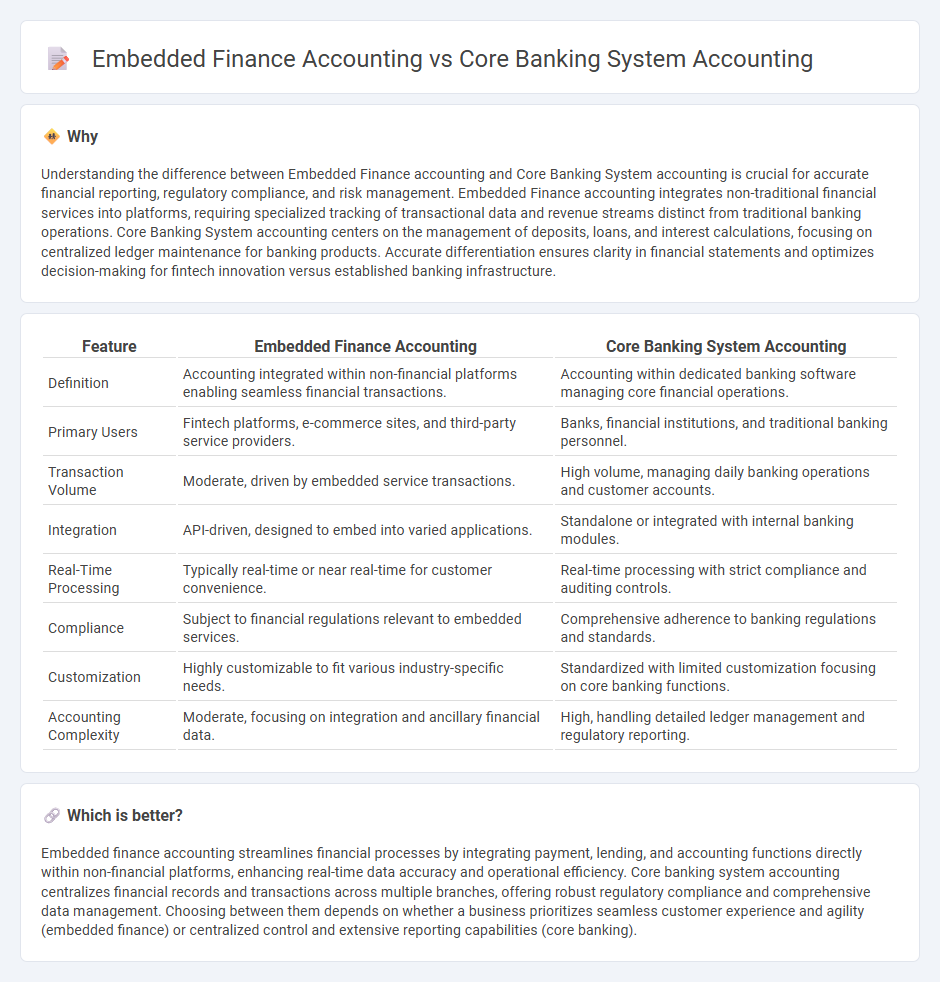
Understanding the difference between Embedded Finance accounting and Core Banking System accounting is crucial for accurate financial reporting, regulatory compliance, and risk management. Embedded Finance accounting integrates non-traditional financial services into platforms, requiring specialized tracking of transactional data and revenue streams distinct from traditional banking operations. Core Banking System accounting centers on the management of deposits, loans, and interest calculations, focusing on centralized ledger maintenance for banking products. Accurate differentiation ensures clarity in financial statements and optimizes decision-making for fintech innovation versus established banking infrastructure.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Embedded Finance Accounting | Core Banking System Accounting |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Accounting integrated within non-financial platforms enabling seamless financial transactions. | Accounting within dedicated banking software managing core financial operations. |
| Primary Users | Fintech platforms, e-commerce sites, and third-party service providers. | Banks, financial institutions, and traditional banking personnel. |
| Transaction Volume | Moderate, driven by embedded service transactions. | High volume, managing daily banking operations and customer accounts. |
| Integration | API-driven, designed to embed into varied applications. | Standalone or integrated with internal banking modules. |
| Real-Time Processing | Typically real-time or near real-time for customer convenience. | Real-time processing with strict compliance and auditing controls. |
| Compliance | Subject to financial regulations relevant to embedded services. | Comprehensive adherence to banking regulations and standards. |
| Customization | Highly customizable to fit various industry-specific needs. | Standardized with limited customization focusing on core banking functions. |
| Accounting Complexity | Moderate, focusing on integration and ancillary financial data. | High, handling detailed ledger management and regulatory reporting. |
Which is better?
Embedded finance accounting streamlines financial processes by integrating payment, lending, and accounting functions directly within non-financial platforms, enhancing real-time data accuracy and operational efficiency. Core banking system accounting centralizes financial records and transactions across multiple branches, offering robust regulatory compliance and comprehensive data management. Choosing between them depends on whether a business prioritizes seamless customer experience and agility (embedded finance) or centralized control and extensive reporting capabilities (core banking).
Connection
Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, allowing real-time transaction processing and data synchronization with core banking system accounting. Core banking systems maintain centralized ledgers and transactional records, enabling seamless reconciliation and compliance when embedded finance solutions generate financial activities. This connection ensures accurate, automated accounting entries, enhances financial reporting, and supports regulatory auditing across both embedded and traditional banking environments.
Key Terms
Core Banking System Accounting:
Core banking system accounting centralizes financial data management, ensuring real-time transaction processing, comprehensive ledger maintenance, and regulatory compliance across multiple branches. It integrates traditional banking activities such as deposits, loans, and payments into a unified platform, enhancing accuracy and operational efficiency. Explore in-depth insights to understand how core banking accounting transforms financial management in modern banking institutions.
General Ledger Integration
Core banking system accounting relies on traditional General Ledger integration, ensuring centralized management of financial transactions across various banking operations with standardized chart of accounts and real-time posting capabilities. Embedded finance accounting, on the other hand, integrates General Ledger dynamically within non-financial platforms, offering seamless transaction recording and reconciliation tailored to diverse ecosystems like e-commerce or fintech apps. Explore how each approach transforms accounting efficiency and compliance in modern financial services.
Transaction Processing
Core banking system accounting centers on traditional financial institutions managing deposits, withdrawals, loans, and interest calculations through secure, real-time transaction processing. Embedded finance accounting integrates financial services directly into non-financial platforms, enabling seamless transactions and data flow within e-commerce, fintech, or service apps. Explore the nuances of transaction processing to understand how these systems shape modern financial ecosystems.
Source and External Links
Core Banking Systems: What They Are & How They're Built - Ramp - A core banking system centralizes account management and records all transactions in real-time, enabling accurate financial reconciliation, compliance tracking, and audit readiness across all banking activities.
Understanding the General Ledger and Accounting Module in Core Banking Software - The General Ledger and Accounting module within core banking software automates transaction recording, reconciliation, and reporting, enhancing financial accuracy, operational efficiency, compliance, and real-time financial insight.
Understanding Core Banking Systems: The Backbone of Financial Institutions - Core banking systems integrate key banking functions like deposit and loan processing, customer account management, and transaction processing into a secure, centralized platform providing real-time updates and strong data protection.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com