Liquidity sweep targets large orders by quickly executing trades across multiple venues to capture the best available prices, minimizing market impact. Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) calculates the average price of a security based on volume and price throughout the trading day, guiding traders to execute orders in line with market activity. Explore more on how these strategies optimize trade execution and reduce costs.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweep and Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) is crucial for traders to execute orders optimally and minimize market impact. A liquidity sweep aggressively captures available liquidity across multiple price levels to ensure immediate order fulfillment, whereas VWAP provides an average price benchmark based on traded volume over a specific period, helping traders gauge execution quality relative to market activity. Mastery of these concepts enhances strategic decision-making by balancing trade urgency against price efficiency. This knowledge allows traders to optimize entry and exit points and manage slippage effectively in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
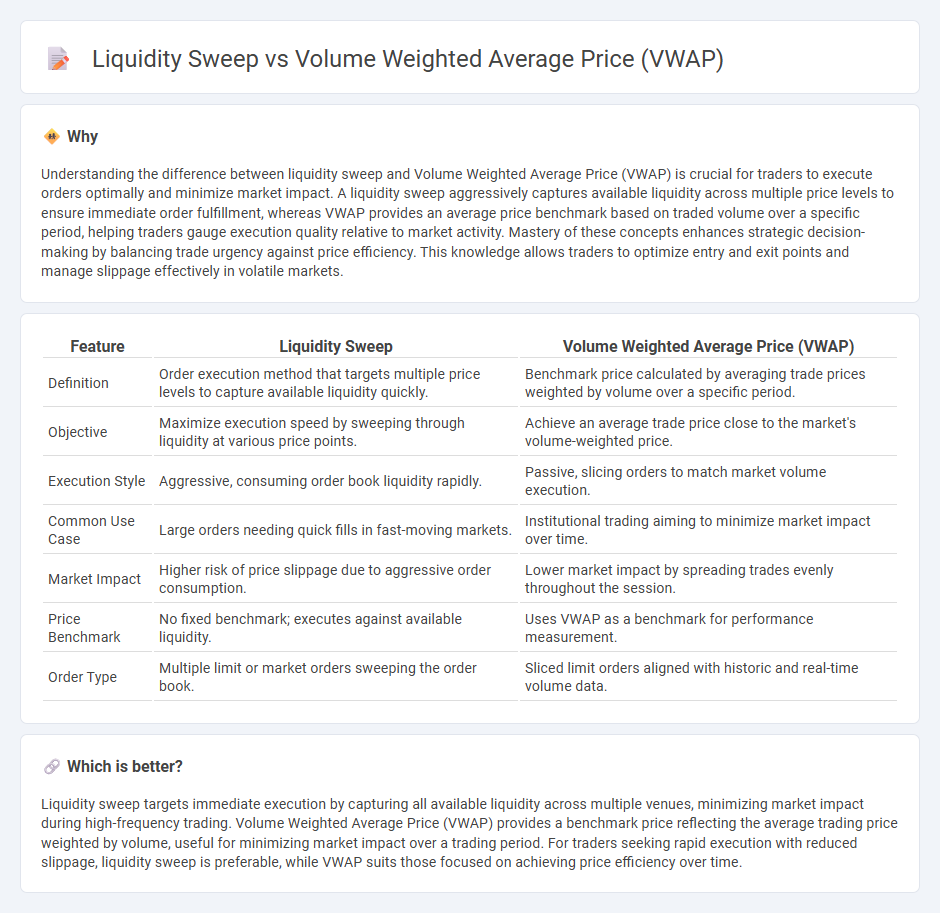
| Feature | Liquidity Sweep | Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Order execution method that targets multiple price levels to capture available liquidity quickly. | Benchmark price calculated by averaging trade prices weighted by volume over a specific period. |
| Objective | Maximize execution speed by sweeping through liquidity at various price points. | Achieve an average trade price close to the market's volume-weighted price. |
| Execution Style | Aggressive, consuming order book liquidity rapidly. | Passive, slicing orders to match market volume execution. |
| Common Use Case | Large orders needing quick fills in fast-moving markets. | Institutional trading aiming to minimize market impact over time. |
| Market Impact | Higher risk of price slippage due to aggressive order consumption. | Lower market impact by spreading trades evenly throughout the session. |
| Price Benchmark | No fixed benchmark; executes against available liquidity. | Uses VWAP as a benchmark for performance measurement. |
| Order Type | Multiple limit or market orders sweeping the order book. | Sliced limit orders aligned with historic and real-time volume data. |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweep targets immediate execution by capturing all available liquidity across multiple venues, minimizing market impact during high-frequency trading. Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) provides a benchmark price reflecting the average trading price weighted by volume, useful for minimizing market impact over a trading period. For traders seeking rapid execution with reduced slippage, liquidity sweep is preferable, while VWAP suits those focused on achieving price efficiency over time.
Connection
Liquidity sweep strategies target large orders executed quickly to capture available market liquidity, often causing significant price movements. Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) serves as a benchmark reflecting the average price weighted by trading volume, helping traders assess execution quality during these liquidity sweeps. By analyzing VWAP relative to order execution, traders optimize timing and minimize market impact when conducting liquidity sweeps.
Key Terms
Order Flow
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) represents the average price of a security weighted by total trading volume, serving as a benchmark for traders to assess trade execution quality. Liquidity sweep involves aggressive order execution to penetrate multiple price levels, capturing hidden liquidity and impacting short-term order flow significantly. Explore deeper insights into how VWAP and liquidity sweeps influence market dynamics and order flow strategies.
Execution Price
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) calculates the average trading price of a security weighted by volume over a specific period, providing a benchmark for trade execution efficiency. Liquidity sweep targets immediate available liquidity across multiple venues to execute large orders quickly, often prioritizing execution speed over price average. Explore deeper insights on optimizing execution price strategies for enhanced trading performance.
Market Impact
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) represents the average price a security has traded at throughout the day, weighted by volume, and is widely used to minimize market impact by executing orders close to the daily average price. In contrast, a liquidity sweep aggressively targets available liquidity across multiple price levels, potentially causing higher market impact due to rapid price movements and immediate consumption of available orders. Explore detailed strategies to balance execution efficiency and market impact in different trading scenarios.
Source and External Links
Volume Weighted Average Price (VWAP) - TradingView - VWAP is a technical analysis tool measuring the average price weighted by volume, commonly used on intraday charts to determine the general price direction, calculated as the cumulative typical price times volume divided by cumulative volume.
Volume Weighted Adjusted Price (VWAP) - Corporate Finance Institute - VWAP is the average price of a stock weighted by total trading volume, calculated daily using intraday data, helping investors compare current prices to a benchmark for better trade timing.
Volume-weighted average price - Wikipedia - VWAP is the ratio of total traded value to total volume over a trading session, used as a trading benchmark to minimize market impact and often employed in algorithmic trading to execute orders aligned with market volume.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com