Volatility harvesting leverages fluctuations in asset prices to systematically capture gains from market swings, optimizing returns through dynamic rebalancing strategies. Mean reversion focuses on capitalizing on asset prices returning to their historical average, exploiting deviations to generate profits. Explore the key differences and benefits of these trading approaches to enhance your investment strategy.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and mean reversion is crucial in trading because it guides strategy selection based on market behavior. Volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing assets in volatile markets. Mean reversion assumes that prices will return to their historical average, favoring strategies that capitalize on temporary deviations. Accurate awareness of these concepts optimizes risk management and improves portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
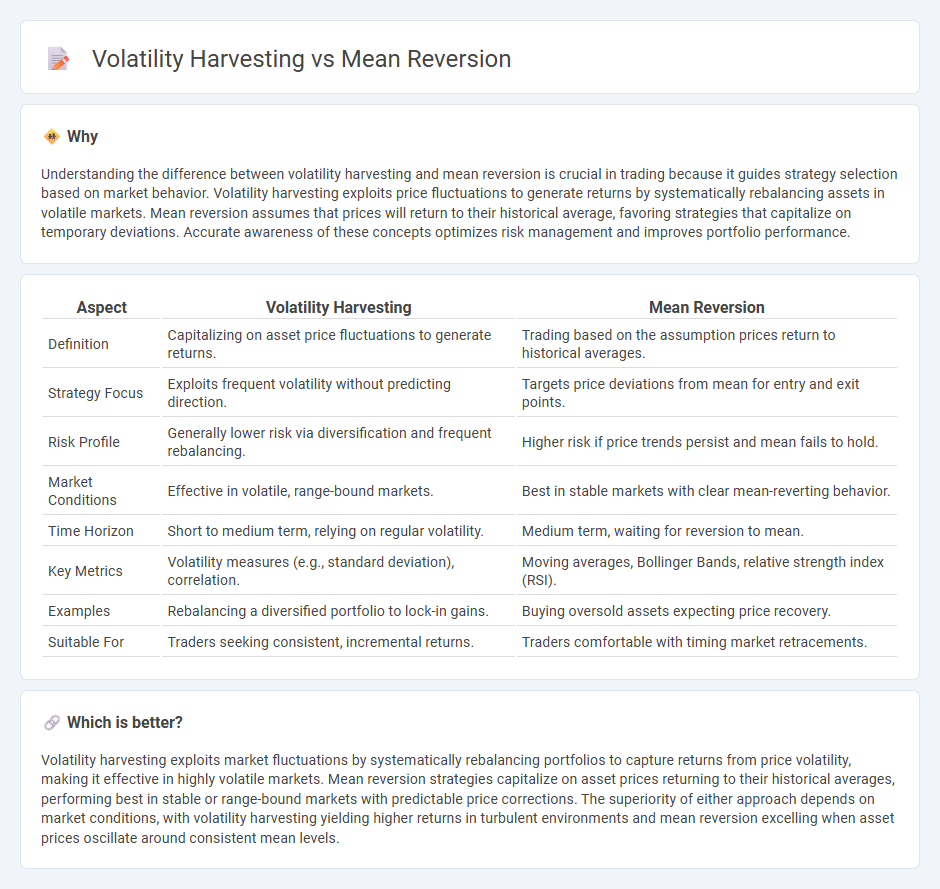
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Mean Reversion |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Capitalizing on asset price fluctuations to generate returns. | Trading based on the assumption prices return to historical averages. |
| Strategy Focus | Exploits frequent volatility without predicting direction. | Targets price deviations from mean for entry and exit points. |
| Risk Profile | Generally lower risk via diversification and frequent rebalancing. | Higher risk if price trends persist and mean fails to hold. |
| Market Conditions | Effective in volatile, range-bound markets. | Best in stable markets with clear mean-reverting behavior. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, relying on regular volatility. | Medium term, waiting for reversion to mean. |
| Key Metrics | Volatility measures (e.g., standard deviation), correlation. | Moving averages, Bollinger Bands, relative strength index (RSI). |
| Examples | Rebalancing a diversified portfolio to lock-in gains. | Buying oversold assets expecting price recovery. |
| Suitable For | Traders seeking consistent, incremental returns. | Traders comfortable with timing market retracements. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting exploits market fluctuations by systematically rebalancing portfolios to capture returns from price volatility, making it effective in highly volatile markets. Mean reversion strategies capitalize on asset prices returning to their historical averages, performing best in stable or range-bound markets with predictable price corrections. The superiority of either approach depends on market conditions, with volatility harvesting yielding higher returns in turbulent environments and mean reversion excelling when asset prices oscillate around consistent mean levels.
Connection
Volatility harvesting leverages price fluctuations to generate returns by systematically rebalancing a portfolio, capitalizing on market variability. Mean reversion underpins this strategy by predicting that prices will revert to their average levels after deviations, enabling consistent profit capture from cyclical asset price movements. Together, these concepts enhance trading strategies that exploit temporal price dynamics for increased risk-adjusted returns.
Key Terms
Price Oscillation
Mean reversion strategies capitalize on price oscillations by identifying asset prices that deviate significantly from their historical average, anticipating a return to the mean. Volatility harvesting exploits fluctuations in price movements, profiting from the natural oscillations in asset prices through systematic rebalancing to capture gains during periods of high volatility. Explore detailed analyses on price oscillation dynamics to enhance your understanding of these advanced trading techniques.
Standard Deviation
Mean reversion strategies exploit the tendency of asset prices to revert to their historical average, often identified using measures like standard deviation to signal overbought or oversold conditions. Volatility harvesting involves capturing gains through rebalancing portfolios by capitalizing on the volatility measured by standard deviation, seeking profits from fluctuating asset prices rather than price direction. Discover how understanding standard deviation enhances these strategies for improved portfolio performance and risk management.
Rebalancing
Mean reversion strategies capitalize on asset prices returning to historical averages, while volatility harvesting exploits price fluctuations to generate incremental returns through systematic rebalancing. Rebalancing involves periodically adjusting portfolio weights to maintain target allocations, enabling investors to sell high and buy low, which amplifies gains in volatile markets. Explore the dynamics of rebalancing further to optimize performance in both mean reversion and volatility harvesting strategies.
Source and External Links
Mean Reversion Strategies: Introduction, Trading ... - Mean reversion is a financial theory that asset prices fluctuate around their historical average and eventually revert to that mean, guiding trading signals such as buying when prices fall below the mean and selling when they rise above it.
Mean reversion (finance) - Mean reversion assumes that asset prices tend to converge to their average price over time, forming the basis of trading strategies that buy assets when prices are below average and sell them when prices are above.
Mean Reversion - Overview, Trading, Impact of Catalysts - This theory implies asset prices gradually move toward a long-term mean and traders use it statistically to decide when to buy below and sell above the mean to capitalize on expected reversions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com