High frequency trading bots execute thousands of trades per second using complex algorithms to capitalize on minute price movements within milliseconds. Algorithmic arbitrage strategies exploit price discrepancies across different markets or instruments by automatically executing trades to lock in risk-free profits. Explore the differences and advantages of these cutting-edge trading techniques to enhance your market strategy.
Why it is important
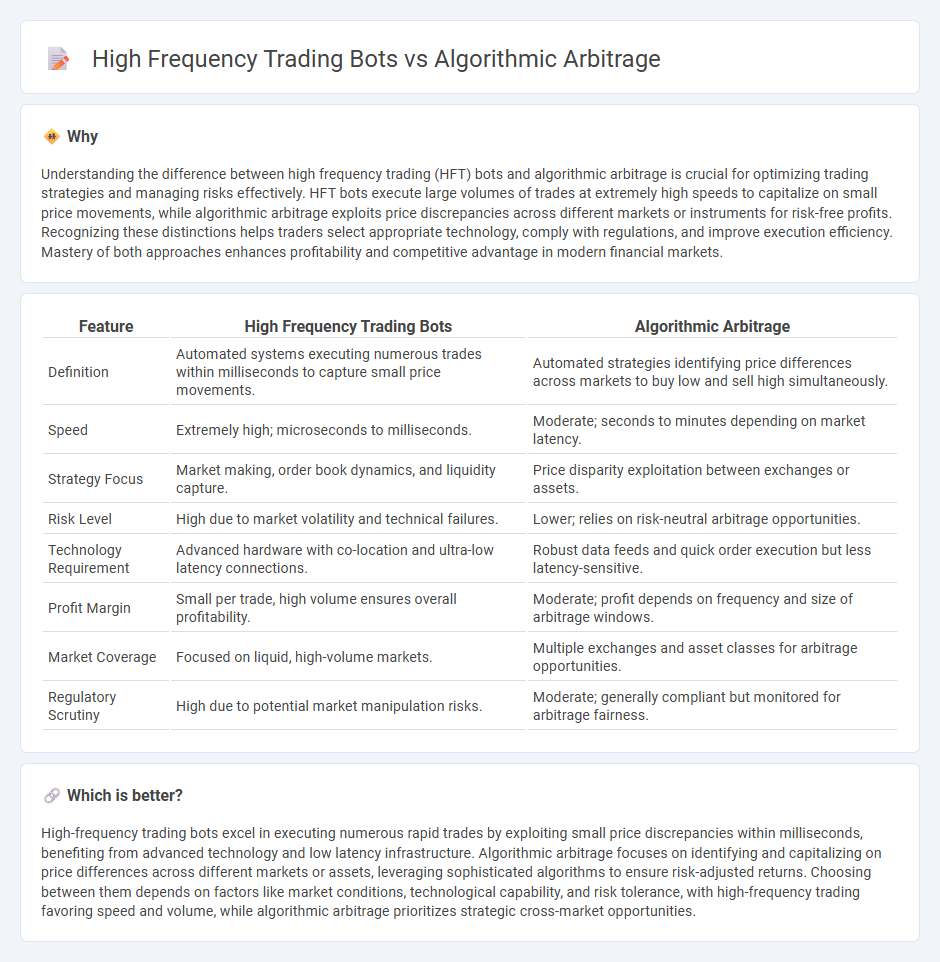
Understanding the difference between high frequency trading (HFT) bots and algorithmic arbitrage is crucial for optimizing trading strategies and managing risks effectively. HFT bots execute large volumes of trades at extremely high speeds to capitalize on small price movements, while algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across different markets or instruments for risk-free profits. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders select appropriate technology, comply with regulations, and improve execution efficiency. Mastery of both approaches enhances profitability and competitive advantage in modern financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | High Frequency Trading Bots | Algorithmic Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Automated systems executing numerous trades within milliseconds to capture small price movements. | Automated strategies identifying price differences across markets to buy low and sell high simultaneously. |
| Speed | Extremely high; microseconds to milliseconds. | Moderate; seconds to minutes depending on market latency. |
| Strategy Focus | Market making, order book dynamics, and liquidity capture. | Price disparity exploitation between exchanges or assets. |
| Risk Level | High due to market volatility and technical failures. | Lower; relies on risk-neutral arbitrage opportunities. |
| Technology Requirement | Advanced hardware with co-location and ultra-low latency connections. | Robust data feeds and quick order execution but less latency-sensitive. |
| Profit Margin | Small per trade, high volume ensures overall profitability. | Moderate; profit depends on frequency and size of arbitrage windows. |
| Market Coverage | Focused on liquid, high-volume markets. | Multiple exchanges and asset classes for arbitrage opportunities. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | High due to potential market manipulation risks. | Moderate; generally compliant but monitored for arbitrage fairness. |
Which is better?
High-frequency trading bots excel in executing numerous rapid trades by exploiting small price discrepancies within milliseconds, benefiting from advanced technology and low latency infrastructure. Algorithmic arbitrage focuses on identifying and capitalizing on price differences across different markets or assets, leveraging sophisticated algorithms to ensure risk-adjusted returns. Choosing between them depends on factors like market conditions, technological capability, and risk tolerance, with high-frequency trading favoring speed and volume, while algorithmic arbitrage prioritizes strategic cross-market opportunities.
Connection
High-frequency trading (HFT) bots utilize algorithmic arbitrage strategies to exploit price discrepancies across multiple markets within milliseconds, enabling rapid execution and profit generation. Both technologies rely on advanced algorithms and real-time data processing to identify and capitalize on minimal price differences before human traders can react. The integration of HFT bots with algorithmic arbitrage enhances market efficiency by tightening bid-ask spreads and increasing liquidity.
Key Terms
Latency
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits price discrepancies across multiple markets by executing trades based on pre-set criteria, requiring rapid data processing but not always ultra-low latency. High frequency trading (HFT) bots prioritize minimizing latency to milliseconds or microseconds to capitalize on fleeting market inefficiencies, often utilizing colocated servers and advanced networking technologies. Explore further to understand how latency optimization differentiates these trading strategies and impacts profitability.
Execution speed
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies across different markets using sophisticated algorithms, while high frequency trading (HFT) bots prioritize ultra-fast execution speed to capitalize on microsecond-level market opportunities. Execution speed in HFT bots is critical, often relying on co-location servers and optimized hardware to gain milliseconds or microseconds advantage over competitors. Discover more about how execution speed shapes competitive strategies in modern trading technologies.
Market inefficiencies
Algorithmic arbitrage exploits market inefficiencies by rapidly identifying and capitalizing on price discrepancies across different exchanges or securities, ensuring risk-averse profits. High-frequency trading bots execute large volumes of trades at millisecond speeds, leveraging minimal latency to gain advantages in order book dynamics and short-term momentum. Explore in-depth how these technologies transform market efficiency and trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Algorithmic arbitrage - FinchTrade - Algorithmic arbitrage is a trading strategy using computer algorithms to identify and quickly exploit price discrepancies across markets for risk-free profit, relying on high-speed execution, liquidity, and effective risk management to correct market inefficiencies and improve liquidity.
ALGO Quantitative Arbitrage Trading - 2025 - Inside Rotman - This case study challenges participants to create adaptable trading algorithms that execute arbitrage strategies automatically in response to rapid market changes, emphasizing programming skills and high-frequency trading execution using APIs.
Arbitrage using Bellman-Ford Algorithm - The Algorists - Arbitrage detection can be formulated algorithmically by converting multiplicative currency exchange rates into an additive logarithmic form to find cycles where the product of rates exceeds one, indicating arbitrage opportunities using graph algorithms like Bellman-Ford.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com