Funding rate arbitrage exploits the differences in funding rates between perpetual futures contracts on various cryptocurrency exchanges to generate risk-free profits. Cross-exchange spread trading capitalizes on price discrepancies of the same asset across different markets, enabling traders to buy low on one exchange and sell high on another. Explore these sophisticated trading strategies to understand their mechanisms and potential gains.
Why it is important
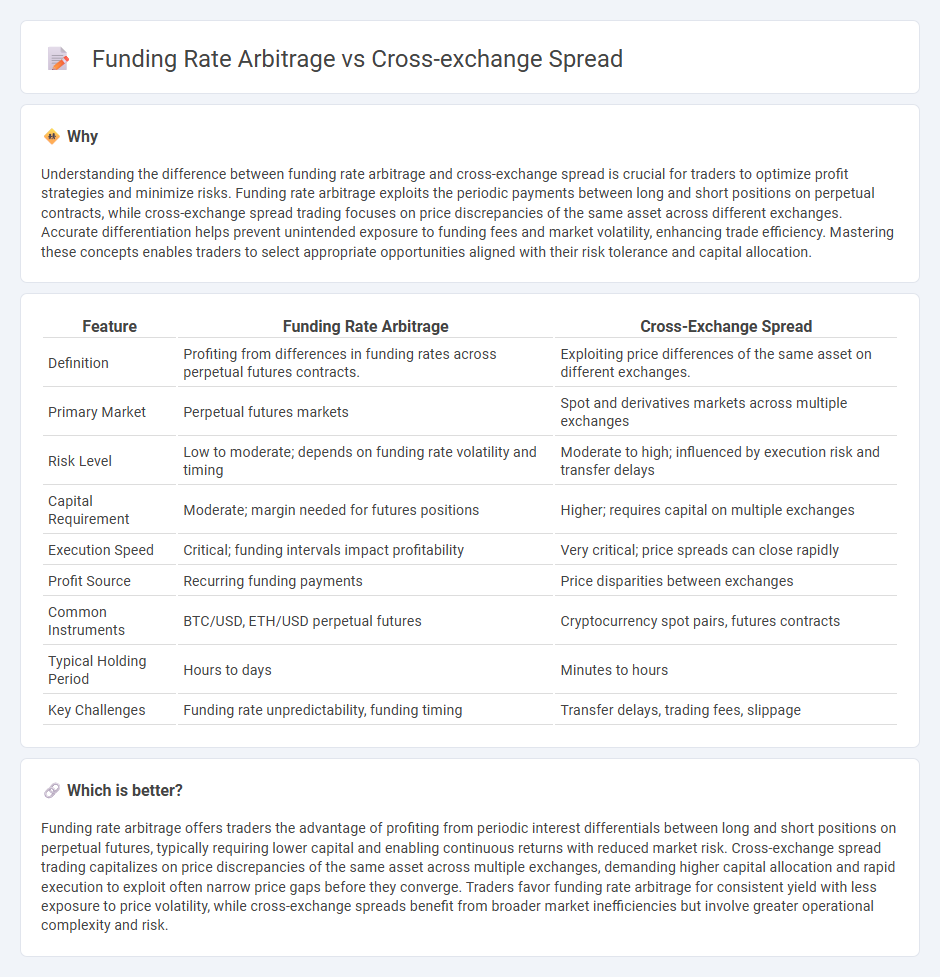
Understanding the difference between funding rate arbitrage and cross-exchange spread is crucial for traders to optimize profit strategies and minimize risks. Funding rate arbitrage exploits the periodic payments between long and short positions on perpetual contracts, while cross-exchange spread trading focuses on price discrepancies of the same asset across different exchanges. Accurate differentiation helps prevent unintended exposure to funding fees and market volatility, enhancing trade efficiency. Mastering these concepts enables traders to select appropriate opportunities aligned with their risk tolerance and capital allocation.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Funding Rate Arbitrage | Cross-Exchange Spread |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from differences in funding rates across perpetual futures contracts. | Exploiting price differences of the same asset on different exchanges. |
| Primary Market | Perpetual futures markets | Spot and derivatives markets across multiple exchanges |
| Risk Level | Low to moderate; depends on funding rate volatility and timing | Moderate to high; influenced by execution risk and transfer delays |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate; margin needed for futures positions | Higher; requires capital on multiple exchanges |
| Execution Speed | Critical; funding intervals impact profitability | Very critical; price spreads can close rapidly |
| Profit Source | Recurring funding payments | Price disparities between exchanges |
| Common Instruments | BTC/USD, ETH/USD perpetual futures | Cryptocurrency spot pairs, futures contracts |
| Typical Holding Period | Hours to days | Minutes to hours |
| Key Challenges | Funding rate unpredictability, funding timing | Transfer delays, trading fees, slippage |
Which is better?
Funding rate arbitrage offers traders the advantage of profiting from periodic interest differentials between long and short positions on perpetual futures, typically requiring lower capital and enabling continuous returns with reduced market risk. Cross-exchange spread trading capitalizes on price discrepancies of the same asset across multiple exchanges, demanding higher capital allocation and rapid execution to exploit often narrow price gaps before they converge. Traders favor funding rate arbitrage for consistent yield with less exposure to price volatility, while cross-exchange spreads benefit from broader market inefficiencies but involve greater operational complexity and risk.
Connection
Funding rate arbitrage exploits differences in perpetual futures funding rates across exchanges to generate riskless profits by taking opposing positions, while cross-exchange spread involves capitalizing on price discrepancies of the same asset between different platforms. Both strategies rely on real-time market inefficiencies and require efficient execution to capitalize on transient opportunities before price or funding rate convergence occurs. Successful implementation demands low-latency infrastructure and precise alignment of position sizes to offset exposure and lock in arbitrage gains.
Key Terms
Price Discrepancy
Cross-exchange spread arbitrage exploits price discrepancies for the same asset across different exchanges, aiming to buy low on one platform and sell high on another. Funding rate arbitrage capitalizes on varying interest rates between perpetual futures contracts to earn risk-free returns by holding opposing positions on different exchanges. Explore how these strategies leverage market inefficiencies by learning more about price discrepancy dynamics in crypto trading.
Funding Rate
Funding rate arbitrage exploits the cost differences in borrowing or lending assets across platforms, enabling traders to profit from discrepancies in perpetual futures contracts. Cross-exchange spread arbitrage involves taking advantage of price differences of the same asset on different exchanges but may not focus directly on funding costs. Explore detailed strategies and risk management techniques behind funding rate arbitrage to enhance your trading insights.
Execution Latency
Cross-exchange spread arbitrage exploits price differences between exchanges while funding rate arbitrage capitalizes on variations in borrowing costs across platforms. Execution latency critically impacts both strategies by affecting the timeliness of order placement and price realization, often determining profitability due to rapid market movements. Explore effective methods to minimize latency and optimize arbitrage execution for enhanced trading outcomes.
Source and External Links
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage - Definition - Cross-exchange spread is the price difference of the same asset between two exchanges, which traders exploit by buying at a lower price on one exchange and selling at a higher price on another to earn a profit.
Cross Exchange Arbitrage: What It Is and How It Works - The cross-exchange spread is the gap in price of the same cryptocurrency across multiple exchanges that traders monitor in real-time to execute buy and sell trades for arbitrage profits.
Cross-Exchange Arbitrage - Definition - The spread in cross-exchange arbitrage specifically refers to the profit margin obtained from the price difference of the same asset traded between two exchanges.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com