Front running involves executing trades based on advance knowledge of pending orders to capitalize on anticipated price movements, often raising regulatory concerns. Shadowing refers to replicating the trades of successful market participants to mimic their strategies without prior insider information. Explore these trading tactics in depth to understand their mechanisms and implications.
Why it is important
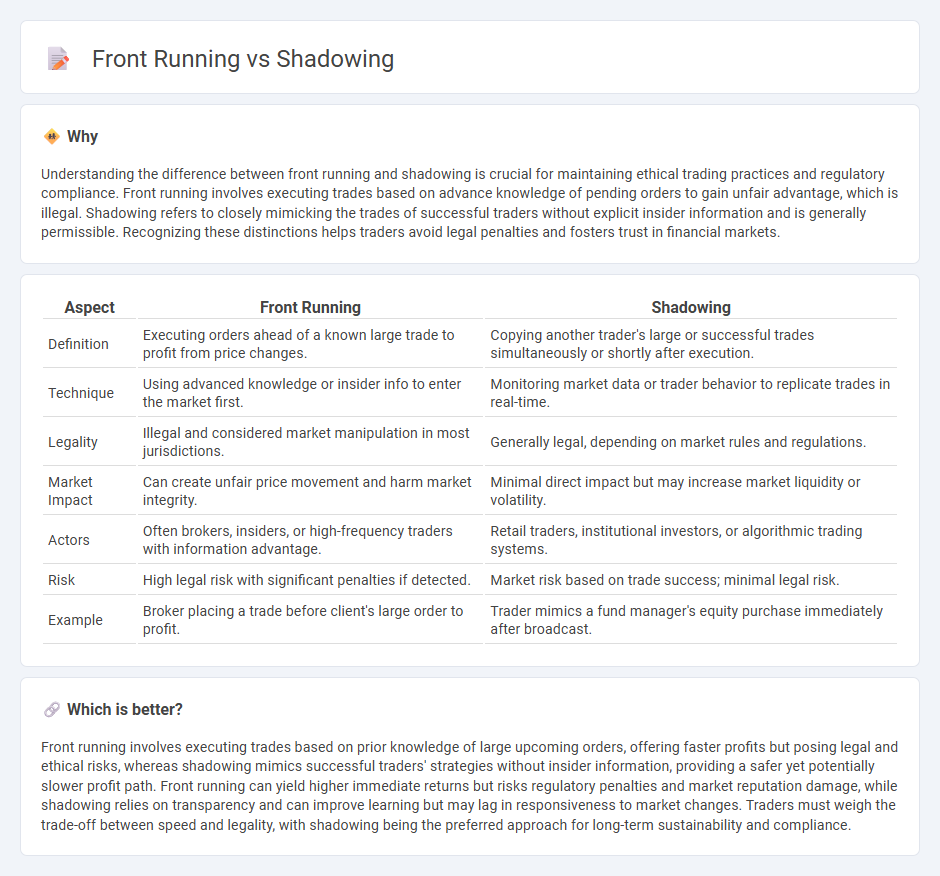
Understanding the difference between front running and shadowing is crucial for maintaining ethical trading practices and regulatory compliance. Front running involves executing trades based on advance knowledge of pending orders to gain unfair advantage, which is illegal. Shadowing refers to closely mimicking the trades of successful traders without explicit insider information and is generally permissible. Recognizing these distinctions helps traders avoid legal penalties and fosters trust in financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Front Running | Shadowing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Executing orders ahead of a known large trade to profit from price changes. | Copying another trader's large or successful trades simultaneously or shortly after execution. |
| Technique | Using advanced knowledge or insider info to enter the market first. | Monitoring market data or trader behavior to replicate trades in real-time. |
| Legality | Illegal and considered market manipulation in most jurisdictions. | Generally legal, depending on market rules and regulations. |
| Market Impact | Can create unfair price movement and harm market integrity. | Minimal direct impact but may increase market liquidity or volatility. |
| Actors | Often brokers, insiders, or high-frequency traders with information advantage. | Retail traders, institutional investors, or algorithmic trading systems. |
| Risk | High legal risk with significant penalties if detected. | Market risk based on trade success; minimal legal risk. |
| Example | Broker placing a trade before client's large order to profit. | Trader mimics a fund manager's equity purchase immediately after broadcast. |
Which is better?
Front running involves executing trades based on prior knowledge of large upcoming orders, offering faster profits but posing legal and ethical risks, whereas shadowing mimics successful traders' strategies without insider information, providing a safer yet potentially slower profit path. Front running can yield higher immediate returns but risks regulatory penalties and market reputation damage, while shadowing relies on transparency and can improve learning but may lag in responsiveness to market changes. Traders must weigh the trade-off between speed and legality, with shadowing being the preferred approach for long-term sustainability and compliance.
Connection
Front running and shadowing are closely connected in trading as both involve exploiting non-public information to gain an unfair advantage. Front running occurs when a trader executes orders based on prior knowledge of upcoming transactions, while shadowing mimics or follows large trader movements to capitalize on their strategies. These practices undermine market integrity by creating asymmetric information and distorting price discovery.
Key Terms
Trade Execution
Shadowing involves replicating the trades of experienced investors to capitalize on their market decisions, whereas front running entails executing orders ahead of large pending trades to gain an unfair advantage. Trade execution in shadowing depends on timely data analysis and mirroring strategies, while front running relies on anticipating order flow for rapid order placements. Explore further to understand how these methods impact market fairness and execution efficiency.
Order Transparency
Order transparency significantly differs between shadowing and front running in trading strategies. Shadowing involves mimicking trades openly, allowing market participants to observe and follow orders transparently, whereas front running exploits prior knowledge of large, pending orders to execute trades ahead, often lacking clear transparency. Explore deeper insights into how order transparency impacts market fairness and trading ethics.
Market Manipulation
Market manipulation techniques such as shadowing involve mimicking large traders' orders to exploit their strategies and profit from subsequent market movements, whereas front running refers to executing trades based on advance knowledge of pending large orders to gain an unfair advantage. Shadowing disrupts market integrity by creating false signals, while front running undermines fairness by leveraging privileged information before others can act. Explore the differences and regulatory implications of shadowing versus front running to safeguard transparent trading environments.
Source and External Links
Job shadow - Wikipedia - Job shadowing is an on-the-job learning method where one follows and observes another employee to learn about their role, skills, and organizational behaviors, often used for training, career development, and leadership growth.
Shadowing Technique: improve your speaking in the most effective ... - Shadowing is a language learning technique involving closely following and imitating a native speaker's speech to improve pronunciation and fluency.
Shadowing a Doctor | Students & Residents - AAMC - Shadowing a doctor means observing a physician during their daily work to gain insight into the medical profession, helping students decide if a career in medicine suits them.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com