Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price patterns and mean-reversion principles to exploit short-term market inefficiencies using quantitative models. Volatility arbitrage focuses on profiting from discrepancies between implied and realized volatility, often through options trading strategies. Discover the distinct mechanics and opportunities behind these advanced trading techniques.
Why it is important
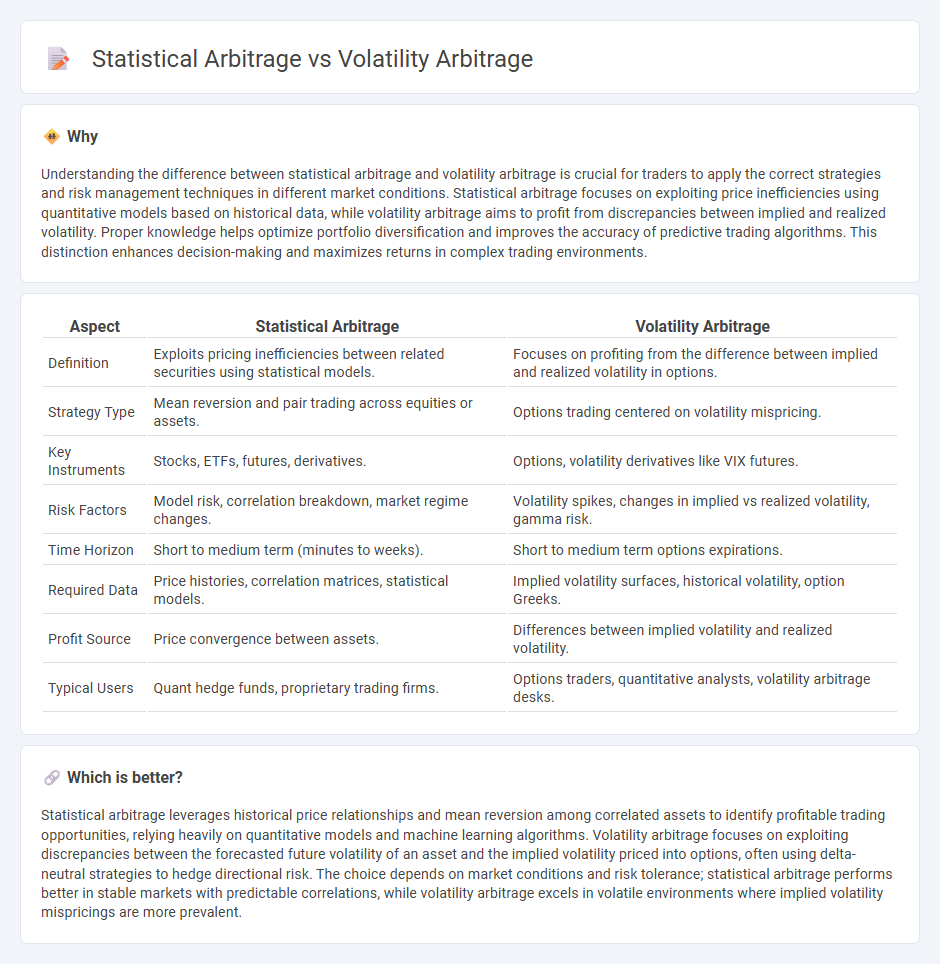
Understanding the difference between statistical arbitrage and volatility arbitrage is crucial for traders to apply the correct strategies and risk management techniques in different market conditions. Statistical arbitrage focuses on exploiting price inefficiencies using quantitative models based on historical data, while volatility arbitrage aims to profit from discrepancies between implied and realized volatility. Proper knowledge helps optimize portfolio diversification and improves the accuracy of predictive trading algorithms. This distinction enhances decision-making and maximizes returns in complex trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Statistical Arbitrage | Volatility Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Exploits pricing inefficiencies between related securities using statistical models. | Focuses on profiting from the difference between implied and realized volatility in options. |
| Strategy Type | Mean reversion and pair trading across equities or assets. | Options trading centered on volatility mispricing. |
| Key Instruments | Stocks, ETFs, futures, derivatives. | Options, volatility derivatives like VIX futures. |
| Risk Factors | Model risk, correlation breakdown, market regime changes. | Volatility spikes, changes in implied vs realized volatility, gamma risk. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term (minutes to weeks). | Short to medium term options expirations. |
| Required Data | Price histories, correlation matrices, statistical models. | Implied volatility surfaces, historical volatility, option Greeks. |
| Profit Source | Price convergence between assets. | Differences between implied volatility and realized volatility. |
| Typical Users | Quant hedge funds, proprietary trading firms. | Options traders, quantitative analysts, volatility arbitrage desks. |
Which is better?
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price relationships and mean reversion among correlated assets to identify profitable trading opportunities, relying heavily on quantitative models and machine learning algorithms. Volatility arbitrage focuses on exploiting discrepancies between the forecasted future volatility of an asset and the implied volatility priced into options, often using delta-neutral strategies to hedge directional risk. The choice depends on market conditions and risk tolerance; statistical arbitrage performs better in stable markets with predictable correlations, while volatility arbitrage excels in volatile environments where implied volatility mispricings are more prevalent.
Connection
Statistical arbitrage and volatility arbitrage both leverage quantitative models to exploit market inefficiencies, focusing on price patterns and volatility discrepancies respectively. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical price relationships and mean-reversion strategies, while volatility arbitrage targets mispricings in implied versus realized volatility in options markets. Both strategies require robust risk management and high-frequency data analysis to capture short-term anomalies and generate consistent returns.
Key Terms
**Volatility Arbitrage:**
Volatility arbitrage exploits differences between implied volatility and realized volatility to generate profits by dynamically hedging options positions, often involving delta-neutral strategies. This approach relies heavily on accurate volatility forecasting and sophisticated models to capture mispricings in derivatives pricing. Explore more about how volatility arbitrage integrates with risk management and market conditions to optimize returns.
Implied Volatility
Volatility arbitrage exploits discrepancies between implied volatility and realized volatility, often trading options to capitalize on mispriced implied volatility levels. Statistical arbitrage relies on quantitative models to identify mean-reverting price patterns and correlations, typically without specific focus on implied volatility. Explore how implied volatility uniquely influences volatility arbitrage strategies in contrast to statistical arbitrage by diving deeper into their mechanisms.
Options Pricing
Volatility arbitrage exploits discrepancies between an option's implied volatility and the expected future volatility of the underlying asset, focusing on pricing inefficiencies derived from volatility forecasts. Statistical arbitrage employs quantitative models analyzing historical price patterns and correlations to identify mispriced options relative to statistical expectations, often involving complex algorithmic trading strategies. Explore the distinct methodologies and risk profiles of volatility and statistical arbitrage in options pricing to optimize your trading approach.
Source and External Links
Volatility arbitrage - Wikipedia - Volatility arbitrage is a financial strategy that exploits differences between the implied volatility of options and the forecasted realized volatility of their underlying assets, typically using delta-neutral portfolios to profit from volatility rather than directional price moves.
Volatility Arbitrage - Overview, How it Works, and Concerns - This strategy involves trading delta-neutral portfolios of options and their underlying assets to capitalize on discrepancies between implied volatility and forecasted volatility, with frequent rebalancing to maintain delta neutrality and generate profits.
Volatility arbitrage indices - S&P Global - Volatility arbitrage strategies focus on the difference between forecasted future volatility and implied volatility of options on the same underlying, often implemented via variance swap strategies and delta-neutral portfolios to profit from volatility movements rather than asset price changes.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com