Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices in trading markets, focusing on quick executions and narrow spreads. Liquidity provision entails supplying buy and sell orders to facilitate market efficiency and stability, often requiring substantial capital and risk management. Explore further to understand how each strategy impacts market dynamics and trader profitability.
Why it is important
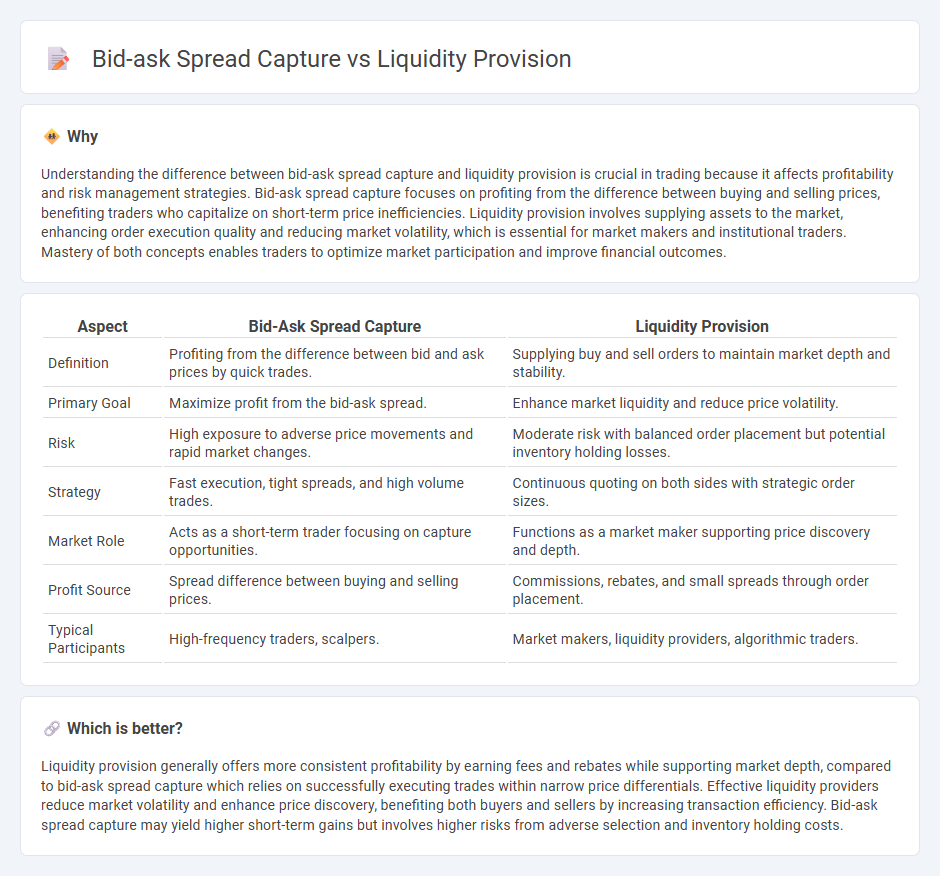
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and liquidity provision is crucial in trading because it affects profitability and risk management strategies. Bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices, benefiting traders who capitalize on short-term price inefficiencies. Liquidity provision involves supplying assets to the market, enhancing order execution quality and reducing market volatility, which is essential for market makers and institutional traders. Mastery of both concepts enables traders to optimize market participation and improve financial outcomes.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Liquidity Provision |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from the difference between bid and ask prices by quick trades. | Supplying buy and sell orders to maintain market depth and stability. |
| Primary Goal | Maximize profit from the bid-ask spread. | Enhance market liquidity and reduce price volatility. |
| Risk | High exposure to adverse price movements and rapid market changes. | Moderate risk with balanced order placement but potential inventory holding losses. |
| Strategy | Fast execution, tight spreads, and high volume trades. | Continuous quoting on both sides with strategic order sizes. |
| Market Role | Acts as a short-term trader focusing on capture opportunities. | Functions as a market maker supporting price discovery and depth. |
| Profit Source | Spread difference between buying and selling prices. | Commissions, rebates, and small spreads through order placement. |
| Typical Participants | High-frequency traders, scalpers. | Market makers, liquidity providers, algorithmic traders. |
Which is better?
Liquidity provision generally offers more consistent profitability by earning fees and rebates while supporting market depth, compared to bid-ask spread capture which relies on successfully executing trades within narrow price differentials. Effective liquidity providers reduce market volatility and enhance price discovery, benefiting both buyers and sellers by increasing transaction efficiency. Bid-ask spread capture may yield higher short-term gains but involves higher risks from adverse selection and inventory holding costs.
Connection
The bid-ask spread captures the cost of liquidity provision, reflecting the difference between the highest price buyers are willing to pay and the lowest price sellers are willing to accept. Market makers and liquidity providers earn profits by buying at bid prices and selling at ask prices while managing inventory risk. Narrower spreads typically indicate higher liquidity, as increased competition among liquidity providers reduces transaction costs for traders.
Key Terms
Order Book Depth
Liquidity provision enhances market stability by supplying substantial order book depth, reducing price volatility and enabling large trades with minimal impact. Bid-ask spread capture targets profits from the price difference but often involves thinner order book depths, increasing risk of slippage during volatile periods. Explore deeper insights on optimizing strategies for order book dynamics and market making.
Market Making
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, reducing bid-ask spreads and enhancing market efficiency. Liquidity provision profits stem from earning the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk, whereas bid-ask spread capture focuses on exploiting short-term price discrepancies without necessarily holding large inventories. Explore how market makers balance these strategies to optimize trading performance and risk management.
Transaction Costs
Liquidity provision reduces transaction costs by narrowing the bid-ask spread, enabling smoother market entries and exits for traders. Bid-ask spread capture exploits price differences within that spread, often incurring higher costs due to adverse selection and market impact. Explore the nuances of these strategies to optimize transaction cost management effectively.
Source and External Links
Remarks on liquidity provision and on the economic outlook and ... - Liquidity provision is a fundamental central bank function, where the Fed lends freely against good collateral to maintain financial stability by reassuring the public and adding liquidity, using tools like the Standing Repo Facility for operational readiness.
DeFi Basics: Liquidity Provision - EMURGO - In decentralized finance (DeFi), liquidity provision involves depositing tokens into liquidity pools on DEXs, enabling token swaps and earning fees, typically requiring a balanced token pair supply like 50/50.
Liquidity Provision by the Federal Reserve - Central banks provide liquidity during crises to meet payment demands and support market functioning, balancing between institutions with liquidity issues and those with solvency problems via various tools including open market operations and lending facilities.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com