Delta hedging involves adjusting a portfolio to remain neutral against small price changes in the underlying asset, minimizing directional risk. Theta hedging focuses on managing the impact of time decay on options, aiming to preserve option value as expiration approaches. Explore the differences between delta and theta hedging strategies to optimize your trading performance.
Why it is important
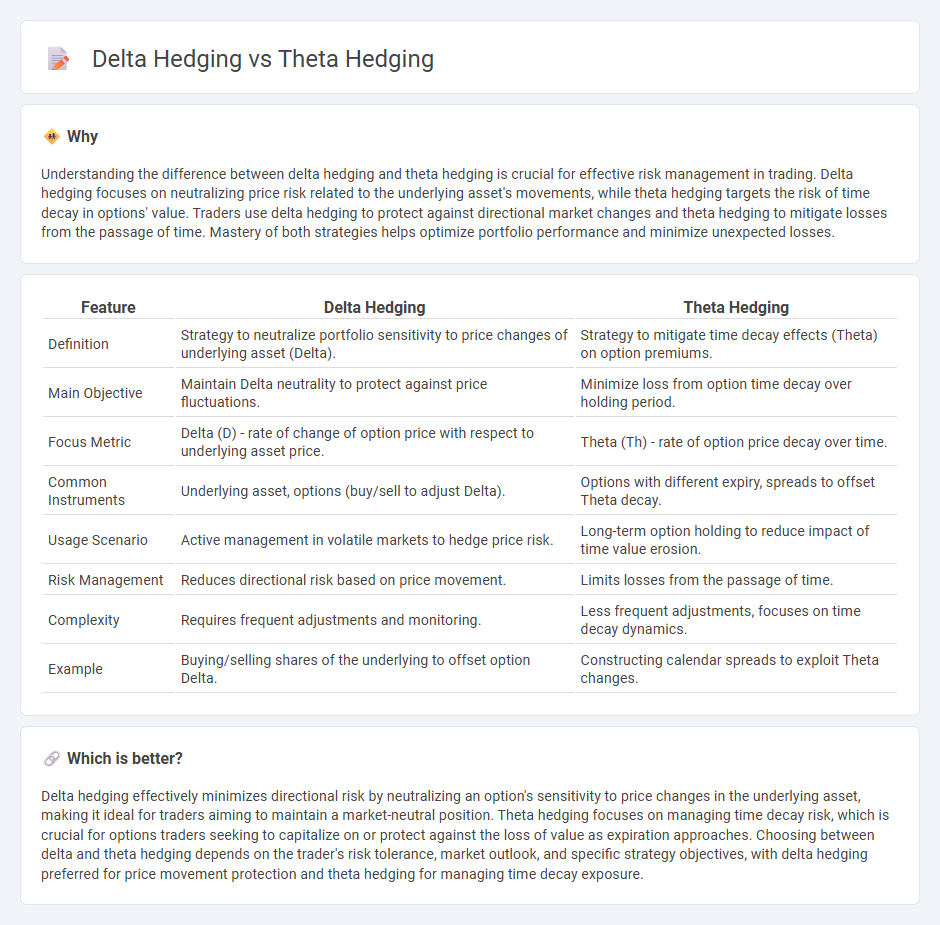
Understanding the difference between delta hedging and theta hedging is crucial for effective risk management in trading. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing price risk related to the underlying asset's movements, while theta hedging targets the risk of time decay in options' value. Traders use delta hedging to protect against directional market changes and theta hedging to mitigate losses from the passage of time. Mastery of both strategies helps optimize portfolio performance and minimize unexpected losses.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Delta Hedging | Theta Hedging |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy to neutralize portfolio sensitivity to price changes of underlying asset (Delta). | Strategy to mitigate time decay effects (Theta) on option premiums. |
| Main Objective | Maintain Delta neutrality to protect against price fluctuations. | Minimize loss from option time decay over holding period. |
| Focus Metric | Delta (D) - rate of change of option price with respect to underlying asset price. | Theta (Th) - rate of option price decay over time. |
| Common Instruments | Underlying asset, options (buy/sell to adjust Delta). | Options with different expiry, spreads to offset Theta decay. |
| Usage Scenario | Active management in volatile markets to hedge price risk. | Long-term option holding to reduce impact of time value erosion. |
| Risk Management | Reduces directional risk based on price movement. | Limits losses from the passage of time. |
| Complexity | Requires frequent adjustments and monitoring. | Less frequent adjustments, focuses on time decay dynamics. |
| Example | Buying/selling shares of the underlying to offset option Delta. | Constructing calendar spreads to exploit Theta changes. |
Which is better?
Delta hedging effectively minimizes directional risk by neutralizing an option's sensitivity to price changes in the underlying asset, making it ideal for traders aiming to maintain a market-neutral position. Theta hedging focuses on managing time decay risk, which is crucial for options traders seeking to capitalize on or protect against the loss of value as expiration approaches. Choosing between delta and theta hedging depends on the trader's risk tolerance, market outlook, and specific strategy objectives, with delta hedging preferred for price movement protection and theta hedging for managing time decay exposure.
Connection
Delta hedging and theta hedging are connected through options trading strategies aimed at managing different types of risk. Delta hedging focuses on neutralizing the sensitivity of an option's price to small changes in the underlying asset's price, while theta hedging addresses the risk associated with time decay in options value. Effective trading strategies often integrate both delta and theta hedging to maintain balanced portfolios that minimize exposure to price fluctuations and time erosion.
Key Terms
Theta
Theta hedging specifically aims to manage the time decay risk in options portfolios by offsetting the negative impact of Theta, which measures the rate at which an option's value erodes as expiration nears. Unlike delta hedging that neutralizes price movement risk through underlying asset adjustments, theta hedging focuses on balancing the portfolio to minimize losses from the passage of time. Explore more about advanced hedging strategies to optimize your options portfolio performance.
Delta
Delta hedging involves managing the sensitivity of an option's price to changes in the underlying asset's price, measured by the delta value, which represents the rate of change of the option's price concerning the underlying. Theta hedging, on the other hand, focuses on managing the time decay of options, which affects their value as expiration approaches, but it is less directly related to delta adjustments. To understand how delta hedging minimizes risk by continuously balancing the option's delta exposure, explore more detailed strategies and examples.
Option Greeks
Theta hedging focuses on managing time decay risk in options, aiming to offset losses as the option's value erodes daily. Delta hedging targets price movement risk by creating a neutral position where the portfolio's sensitivity to underlying asset price changes is minimized. Explore in-depth strategies and practical applications to optimize your options trading portfolio.
Source and External Links
Mastering Theta Hedging Strategies - Number Analytics - Theta hedging is a sophisticated trading strategy used to mitigate risks from time decay, often by implementing delta-neutral positions and adjusting hedge ratios dynamically to maintain hedging effectiveness as market conditions change.
Theta Hedging - FasterCapital - Theta hedging involves offsetting the portfolio's negative theta (time decay) by taking positions in options or derivatives with opposite theta, using techniques such as rolling positions, delta-neutral hedging, and calendar spreads to protect against value erosion.
Trading Theta: A Strategy Exploiting Time Decay by Yunpeng Lu - This paper discusses a trading strategy that profits from shorting theta by maintaining a delta, gamma, and vega neutral position using a combination of SPY, SPX, and E-mini instruments, employing algorithmic methods for hedge calculation and risk management.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com