Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the difference between the buying price (bid) and selling price (ask) of a security without providing continuous liquidity. Market making, on the other hand, requires placing simultaneous buy and sell orders to facilitate trading and maintain market liquidity while earning the spread. Explore the nuances of these strategies to enhance your trading expertise.
Why it is important
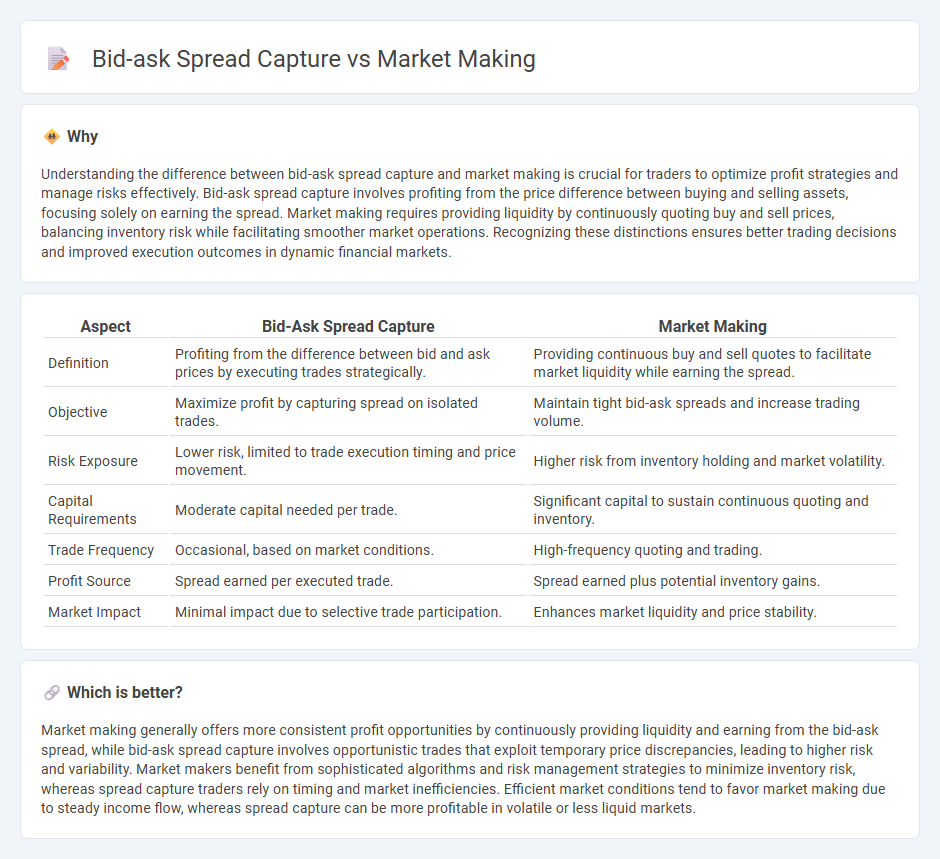
Understanding the difference between bid-ask spread capture and market making is crucial for traders to optimize profit strategies and manage risks effectively. Bid-ask spread capture involves profiting from the price difference between buying and selling assets, focusing solely on earning the spread. Market making requires providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, balancing inventory risk while facilitating smoother market operations. Recognizing these distinctions ensures better trading decisions and improved execution outcomes in dynamic financial markets.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Bid-Ask Spread Capture | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Profiting from the difference between bid and ask prices by executing trades strategically. | Providing continuous buy and sell quotes to facilitate market liquidity while earning the spread. |
| Objective | Maximize profit by capturing spread on isolated trades. | Maintain tight bid-ask spreads and increase trading volume. |
| Risk Exposure | Lower risk, limited to trade execution timing and price movement. | Higher risk from inventory holding and market volatility. |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate capital needed per trade. | Significant capital to sustain continuous quoting and inventory. |
| Trade Frequency | Occasional, based on market conditions. | High-frequency quoting and trading. |
| Profit Source | Spread earned per executed trade. | Spread earned plus potential inventory gains. |
| Market Impact | Minimal impact due to selective trade participation. | Enhances market liquidity and price stability. |
Which is better?
Market making generally offers more consistent profit opportunities by continuously providing liquidity and earning from the bid-ask spread, while bid-ask spread capture involves opportunistic trades that exploit temporary price discrepancies, leading to higher risk and variability. Market makers benefit from sophisticated algorithms and risk management strategies to minimize inventory risk, whereas spread capture traders rely on timing and market inefficiencies. Efficient market conditions tend to favor market making due to steady income flow, whereas spread capture can be more profitable in volatile or less liquid markets.
Connection
The bid-ask spread represents the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept, serving as a key source of profit for market makers. Market makers capture this spread by simultaneously posting buy (bid) and sell (ask) orders, facilitating liquidity and reducing trading friction in financial markets. By managing inventory risk and adjusting spreads based on market volatility, market makers ensure efficient price discovery and continuous trading activity.
Key Terms
Liquidity provision
Market making involves continuously quoting both bid and ask prices to provide liquidity and facilitate smooth trading, whereas bid-ask spread capture focuses on profiting from the difference between buying and selling prices without necessarily committing to constant liquidity provision. Market makers play a crucial role in maintaining market efficiency by ensuring available buy and sell options, while spread capture strategies capitalize on price discrepancies within existing liquidity. Explore the nuances of liquidity provision to understand how these strategies impact market dynamics.
Order book
Market making involves continuously placing buy and sell limit orders in the order book to provide liquidity and profit from the bid-ask spread by capturing the difference between these prices through frequent trades. Bid-ask spread capture strategies focus primarily on exploiting the spread by quickly executing trades on existing order book levels without necessarily maintaining continuous presence, aiming for short-term gains from price discrepancies. Explore deeper insights into how order book dynamics influence these strategies and their risk profiles.
Spread arbitrage
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread by facilitating trades. Bid-ask spread capture, often termed spread arbitrage, exploits price discrepancies in the spread across different markets or instruments to secure riskless profits. Explore deeper insights into spread arbitrage strategies and how they optimize trading efficiency.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy | EPAM SolutionsHub - Market makers profit by providing liquidity through buying at bid prices and selling at higher ask prices, managing inventory risk, analyzing order flow, and adhering to regulations to balance profit and fair market practice.
Market maker: What it is, importance, benefits & examples - StoneX - A market maker actively quotes both buy (bid) and sell (ask) prices, earning profits from the bid-ask spread by continuously buying and selling securities and managing associated inventory risks.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - Market makers maintain liquidity in markets by offering two-sided prices and earning the difference between bid and ask prices, performing trades both for clients and on their own accounts with risk compensation through the spread.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com