Flash loans enable instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single blockchain transaction, optimizing capital efficiency for arbitrage, liquidation, or collateral swapping. Synthetic assets represent derivatives that mirror the value of real-world assets, offering traders exposure without owning the underlying item. Explore the unique advantages and use cases of flash loans versus synthetic assets in decentralized finance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loans and synthetic assets is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and leverage opportunities in decentralized finance (DeFi). Flash loans offer instant, uncollateralized borrowing within a single transaction, enabling arbitrage and quick market moves without upfront capital. Synthetic assets mirror the value of real-world assets, allowing traders to gain exposure to diverse markets without holding the underlying asset. Knowing these distinctions helps traders optimize strategies, avoid liquidations, and exploit DeFi innovations securely.
Comparison Table
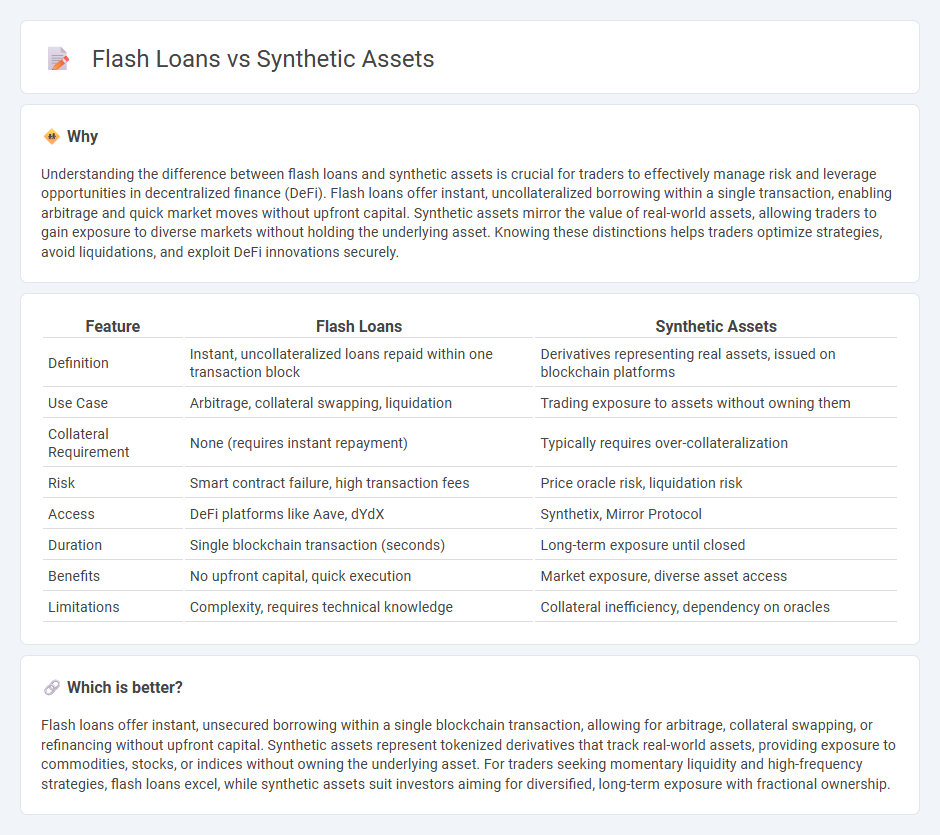
| Feature | Flash Loans | Synthetic Assets |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Instant, uncollateralized loans repaid within one transaction block | Derivatives representing real assets, issued on blockchain platforms |
| Use Case | Arbitrage, collateral swapping, liquidation | Trading exposure to assets without owning them |
| Collateral Requirement | None (requires instant repayment) | Typically requires over-collateralization |
| Risk | Smart contract failure, high transaction fees | Price oracle risk, liquidation risk |
| Access | DeFi platforms like Aave, dYdX | Synthetix, Mirror Protocol |
| Duration | Single blockchain transaction (seconds) | Long-term exposure until closed |
| Benefits | No upfront capital, quick execution | Market exposure, diverse asset access |
| Limitations | Complexity, requires technical knowledge | Collateral inefficiency, dependency on oracles |
Which is better?
Flash loans offer instant, unsecured borrowing within a single blockchain transaction, allowing for arbitrage, collateral swapping, or refinancing without upfront capital. Synthetic assets represent tokenized derivatives that track real-world assets, providing exposure to commodities, stocks, or indices without owning the underlying asset. For traders seeking momentary liquidity and high-frequency strategies, flash loans excel, while synthetic assets suit investors aiming for diversified, long-term exposure with fractional ownership.
Connection
Flash loans enable traders to borrow large sums of capital instantly without collateral, facilitating arbitrage and complex trading strategies within a single transaction. Synthetic assets are blockchain-based derivatives that mimic the value of real-world assets, allowing exposure without ownership. Combining flash loans with synthetic assets enhances liquidity and enables rapid, risk-mitigated trades in decentralized finance (DeFi) ecosystems.
Key Terms
Collateralization
Synthetic assets rely on over-collateralization to maintain stability by locking up digital assets exceeding the synthetic asset's value, ensuring users can redeem their positions without default risk. Flash loans operate without upfront collateral but depend on atomic transactions in smart contracts, requiring full repayment within one blockchain transaction to prevent loan defaults. Explore detailed mechanisms behind collateralization and risk management in decentralized finance to deepen your understanding.
Arbitrage
Synthetic assets replicate the value of real-world assets on blockchain platforms, enabling traders to gain exposure without owning the underlying asset, while flash loans provide instant, uncollateralized borrowing for arbitrage opportunities within a single transaction. Arbitrageurs utilize synthetic assets to exploit price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, whereas flash loans enable executing rapid, capital-efficient arbitrage trades without upfront capital. Explore in-depth strategies and risks behind synthetic assets and flash loan arbitrage to optimize your decentralized finance outcomes.
Smart Contracts
Synthetic assets leverage smart contracts to replicate the value of real-world assets, enabling decentralized trading without actual asset ownership. Flash loans utilize smart contracts for instant, uncollateralized borrowing, requiring repayment within a single transaction block to prevent default risk. Explore the technical details and practical applications of smart contracts in synthetic assets and flash loans to deepen your understanding.
Source and External Links
Crypto synthetic assets, explained - Synthetic assets are blockchain-based digital instruments that mimic the value and performance of real-world assets like stocks, commodities, or currencies, without owning the underlying assets, created using derivatives and smart contracts mainly in DeFi ecosystems.
Synthetic Asset Definition - Synthetic assets, or synths, are tokenized derivatives recorded on blockchains that let investors trade price movements of assets they do not own, bringing added security and traceability by leveraging decentralized ledgers.
What are synthetic crypto assets? - Synthetic crypto assets are blockchain-based derivatives allowing indirect exposure to real-world assets like stocks or commodities via tokens, providing accessibility, transparency, and censorship resistance within the crypto ecosystem.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com