Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to generate consistent returns by systematically buying low and selling high, capitalizing on price variability regardless of market direction. Statistical arbitrage exploits pricing inefficiencies between correlated assets through quantitative models that identify temporary deviations from their expected relationships. Discover how these advanced trading strategies can enhance portfolio performance and risk management.
Why it is important
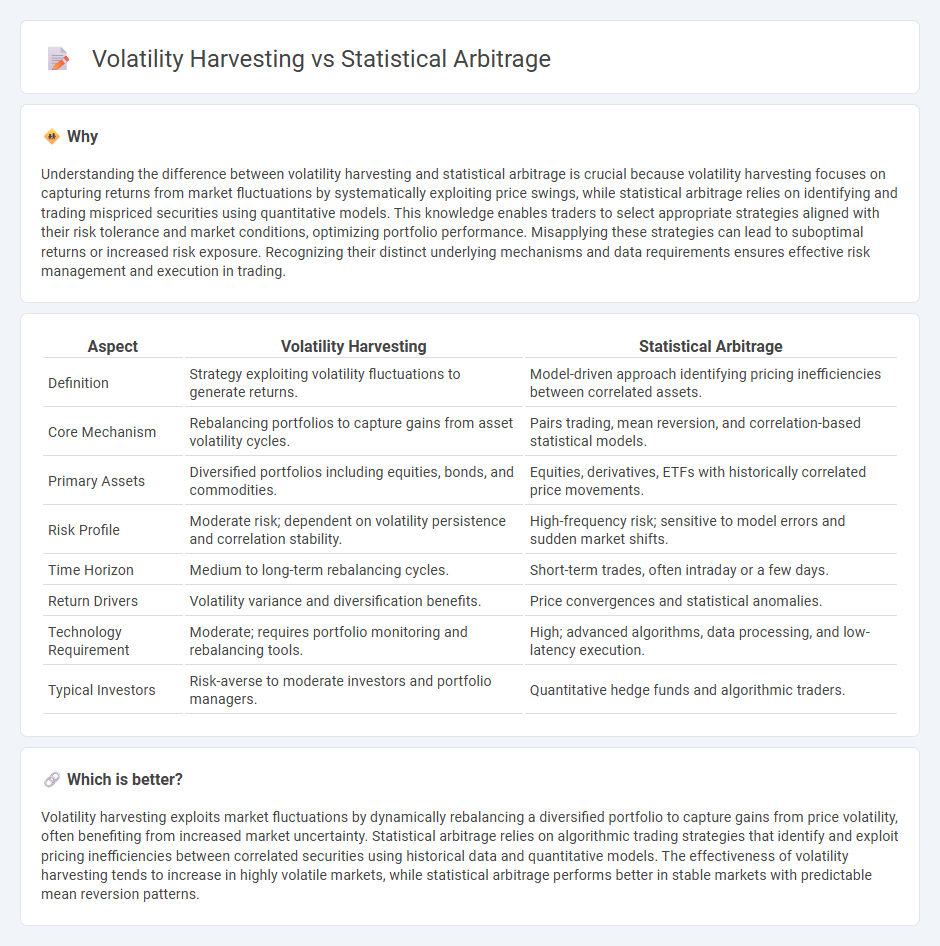
Understanding the difference between volatility harvesting and statistical arbitrage is crucial because volatility harvesting focuses on capturing returns from market fluctuations by systematically exploiting price swings, while statistical arbitrage relies on identifying and trading mispriced securities using quantitative models. This knowledge enables traders to select appropriate strategies aligned with their risk tolerance and market conditions, optimizing portfolio performance. Misapplying these strategies can lead to suboptimal returns or increased risk exposure. Recognizing their distinct underlying mechanisms and data requirements ensures effective risk management and execution in trading.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Volatility Harvesting | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategy exploiting volatility fluctuations to generate returns. | Model-driven approach identifying pricing inefficiencies between correlated assets. |
| Core Mechanism | Rebalancing portfolios to capture gains from asset volatility cycles. | Pairs trading, mean reversion, and correlation-based statistical models. |
| Primary Assets | Diversified portfolios including equities, bonds, and commodities. | Equities, derivatives, ETFs with historically correlated price movements. |
| Risk Profile | Moderate risk; dependent on volatility persistence and correlation stability. | High-frequency risk; sensitive to model errors and sudden market shifts. |
| Time Horizon | Medium to long-term rebalancing cycles. | Short-term trades, often intraday or a few days. |
| Return Drivers | Volatility variance and diversification benefits. | Price convergences and statistical anomalies. |
| Technology Requirement | Moderate; requires portfolio monitoring and rebalancing tools. | High; advanced algorithms, data processing, and low-latency execution. |
| Typical Investors | Risk-averse to moderate investors and portfolio managers. | Quantitative hedge funds and algorithmic traders. |
Which is better?
Volatility harvesting exploits market fluctuations by dynamically rebalancing a diversified portfolio to capture gains from price volatility, often benefiting from increased market uncertainty. Statistical arbitrage relies on algorithmic trading strategies that identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies between correlated securities using historical data and quantitative models. The effectiveness of volatility harvesting tends to increase in highly volatile markets, while statistical arbitrage performs better in stable markets with predictable mean reversion patterns.
Connection
Volatility harvesting leverages market fluctuations to systematically capture gains from price variability, which aligns with statistical arbitrage strategies that exploit pricing inefficiencies using quantitative models. Both approaches rely on advanced statistical analysis and high-frequency data to identify transient market patterns and optimize portfolio returns. Integrating volatility harvesting into statistical arbitrage frameworks enhances risk-adjusted performance by effectively managing the dynamic interplay between asset correlations and volatility.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage involves exploiting temporary mispricings between related financial instruments using quantitative models and historical price data to generate consistent profits. This strategy relies heavily on mean reversion and market inefficiencies within large datasets, often incorporating machine learning algorithms and high-frequency trading techniques. Discover how statistical arbitrage strategies can optimize your trading performance by analyzing complex market patterns.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage capitalizes on mean reversion by exploiting short-term price deviations from historical averages, aiming to profit from asset price corrections. Volatility harvesting leverages fluctuations in asset volatility, repeatedly rebalancing portfolios to benefit from mean-reverting volatility patterns without relying on directional price bets. Explore the nuances of mean reversion in these strategies to optimize risk-adjusted returns and portfolio diversification.
Pair Trading
Statistical arbitrage in pair trading exploits mean reversion by identifying correlated asset pairs to capitalize on price divergences, whereas volatility harvesting seeks to profit from market volatility through systematic rebalancing of the pair. Both strategies rely on rigorous quantitative models and real-time data analysis but differ in their risk exposure and return drivers; statistical arbitrage emphasizes price convergence, while volatility harvesting leverages variance in asset prices. Explore the nuanced mechanics and performance metrics of these approaches to enhance your trading strategy.
Source and External Links
The Power of Statistical Arbitrage in Finance - Statistical arbitrage, or "stat arb," uses quantitative models to identify temporary price discrepancies between related financial instruments, relying on mean reversion and involving data collection, model development, and trade execution steps to exploit short-lived deviations for profit.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage is a short-term trading strategy employing mean reversion models over large, diversified portfolios held for seconds to days, using statistical techniques and automated systems to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies with beta-neutral, multi-factor approaches.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? - CQF - Statistical arbitrage is a popular quant trading strategy in finance that exploits pricing discrepancies or deviations from statistical relationships using quantitative and computational methods.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com