Modular blockchains optimize trading by separating execution, data availability, and consensus layers, enhancing scalability and transaction speed beyond traditional Layer 2 protocols, which rely on mainchain security while processing transactions off-chain. Layer 2 solutions like rollups reduce congestion but face limitations in decentralization and throughput compared to modular blockchain designs. Explore the advantages and trade-offs of each approach to understand the future of decentralized trading infrastructure.
Why it is important
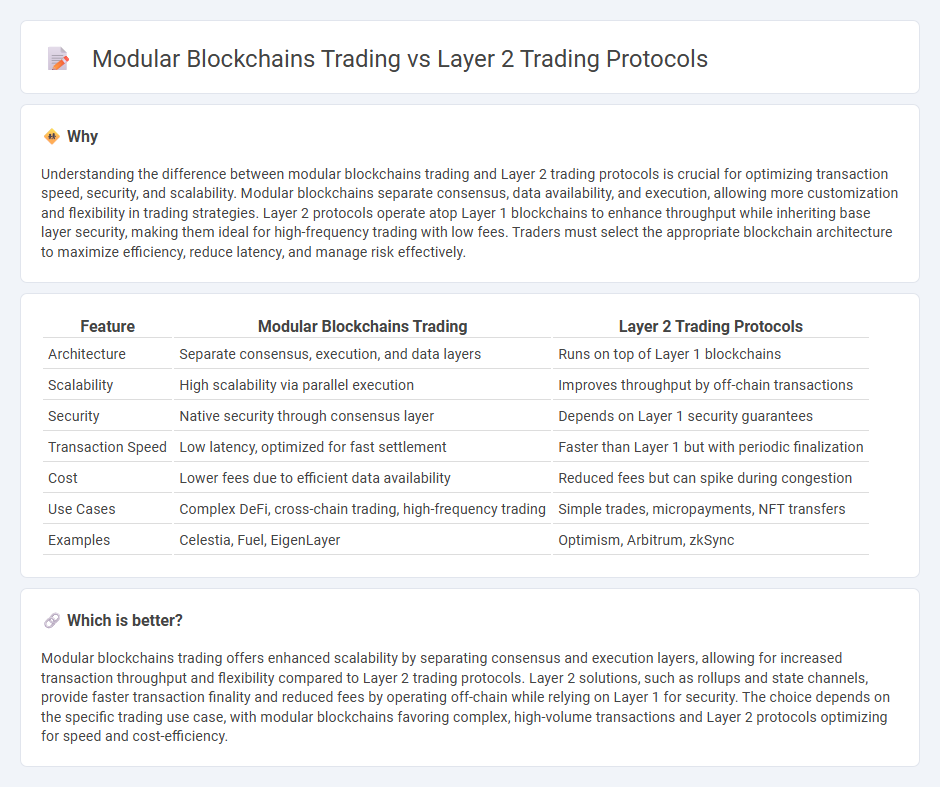
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and Layer 2 trading protocols is crucial for optimizing transaction speed, security, and scalability. Modular blockchains separate consensus, data availability, and execution, allowing more customization and flexibility in trading strategies. Layer 2 protocols operate atop Layer 1 blockchains to enhance throughput while inheriting base layer security, making them ideal for high-frequency trading with low fees. Traders must select the appropriate blockchain architecture to maximize efficiency, reduce latency, and manage risk effectively.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Blockchains Trading | Layer 2 Trading Protocols |
|---|---|---|
| Architecture | Separate consensus, execution, and data layers | Runs on top of Layer 1 blockchains |
| Scalability | High scalability via parallel execution | Improves throughput by off-chain transactions |
| Security | Native security through consensus layer | Depends on Layer 1 security guarantees |
| Transaction Speed | Low latency, optimized for fast settlement | Faster than Layer 1 but with periodic finalization |
| Cost | Lower fees due to efficient data availability | Reduced fees but can spike during congestion |
| Use Cases | Complex DeFi, cross-chain trading, high-frequency trading | Simple trades, micropayments, NFT transfers |
| Examples | Celestia, Fuel, EigenLayer | Optimism, Arbitrum, zkSync |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced scalability by separating consensus and execution layers, allowing for increased transaction throughput and flexibility compared to Layer 2 trading protocols. Layer 2 solutions, such as rollups and state channels, provide faster transaction finality and reduced fees by operating off-chain while relying on Layer 1 for security. The choice depends on the specific trading use case, with modular blockchains favoring complex, high-volume transactions and Layer 2 protocols optimizing for speed and cost-efficiency.
Connection
Modular blockchains trading leverages distinct layers for consensus, data availability, and execution, enhancing scalability and flexibility in transactions. Layer 2 trading protocols operate atop these modular blockchains, enabling faster and cheaper trades by processing transactions off-chain while inheriting security from the base layer. This connection reduces congestion and fees, facilitating high-frequency trading and decentralized exchange activities.
Key Terms
Scalability
Layer 2 trading protocols enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain while leveraging the security of Layer 1 blockchains, enabling faster and cheaper trades. Modular blockchains improve scalability by separating core functions like consensus, data availability, and execution into specialized layers, allowing for parallel processing and optimized performance. Explore how these cutting-edge solutions are reshaping decentralized trading scalability.
Interoperability
Layer 2 trading protocols enhance scalability by processing transactions off-chain while relying on Ethereum's security, enabling faster and cheaper trades but often facing interoperability challenges across different Layer 1 blockchains. Modular blockchains separate consensus, data availability, and execution, creating specialized layers that promote cross-chain compatibility and seamless asset transfers, improving interoperability in decentralized trading ecosystems. Explore the technical nuances and market implications to understand how these approaches shape the future of decentralized finance interoperability.
Settlement layer
Layer 2 trading protocols enhance transaction throughput and reduce fees by conducting trades off-chain while relying on the base layer for settlement security, thereby optimizing decentralized exchange efficiency. Modular blockchains separate execution, settlement, and consensus into specialized layers, enabling more customizable and scalable settlement processes tailored to specific trading needs. Explore deeper insights into how settlement layers impact trading performance and security in emerging blockchain architectures.
Source and External Links
Top 10 Layer-2 Crypto Projects to Watch in 2025 | KuCoin Learn - Layer-2 trading protocols improve transaction speed and efficiency by processing transactions off-chain and then submitting a summarized transaction on the main chain, reducing congestion, lowering costs, and enabling faster trading experiences.
Layer-2 Protocols - Web3 - Meegle - Layer-2 protocols use mechanisms like state channels and rollups (Optimistic and ZK-rollups) to aggregate and verify transactions off-chain, enhancing scalability and maintaining security and decentralization for trading and other blockchain operations.
10 Layer 2 Crypto Projects to Watch in 2024 - Gate.com - Layer-2 trading protocols serve as off-chain transaction networks built on Layer-1 blockchains such as Ethereum, enabling fast transaction throughput and low fees by moving trading activity away from the congested main chain.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com