Grid trading exploits predefined price intervals to systematically buy low and sell high, capitalizing on market volatility without relying on predictions. Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models to identify and trade price inefficiencies between related assets, aiming for market-neutral profits. Explore the detailed strategies and risk profiles of grid trading and statistical arbitrage to enhance your trading approach.
Why it is important
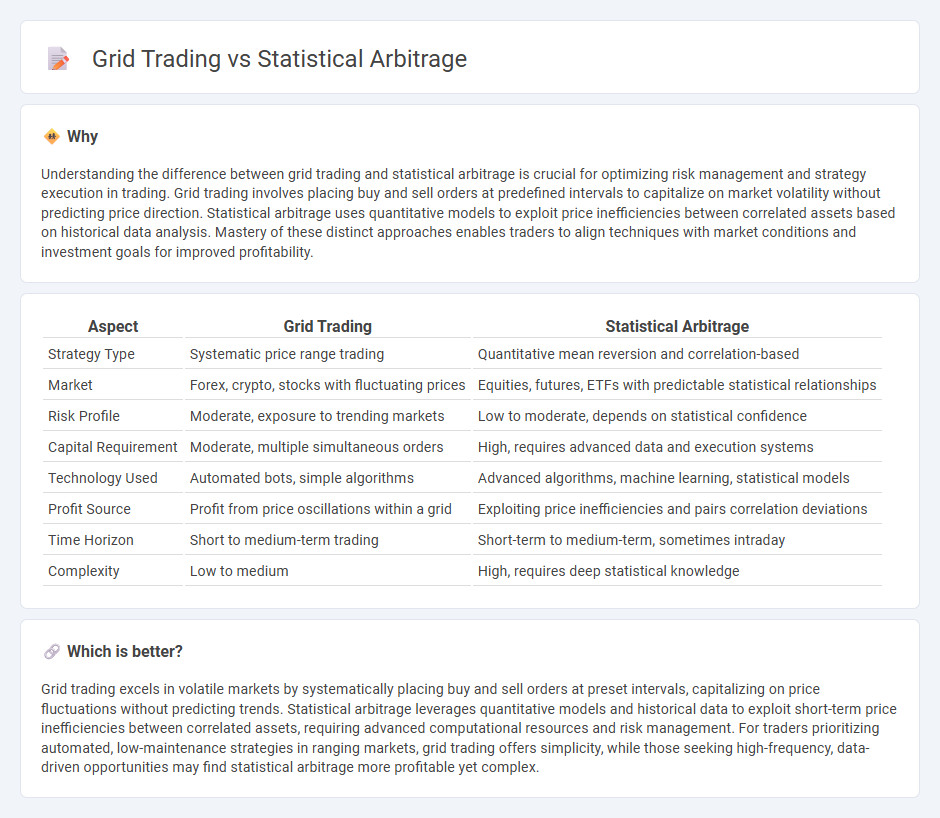
Understanding the difference between grid trading and statistical arbitrage is crucial for optimizing risk management and strategy execution in trading. Grid trading involves placing buy and sell orders at predefined intervals to capitalize on market volatility without predicting price direction. Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models to exploit price inefficiencies between correlated assets based on historical data analysis. Mastery of these distinct approaches enables traders to align techniques with market conditions and investment goals for improved profitability.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Grid Trading | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Strategy Type | Systematic price range trading | Quantitative mean reversion and correlation-based |
| Market | Forex, crypto, stocks with fluctuating prices | Equities, futures, ETFs with predictable statistical relationships |
| Risk Profile | Moderate, exposure to trending markets | Low to moderate, depends on statistical confidence |
| Capital Requirement | Moderate, multiple simultaneous orders | High, requires advanced data and execution systems |
| Technology Used | Automated bots, simple algorithms | Advanced algorithms, machine learning, statistical models |
| Profit Source | Profit from price oscillations within a grid | Exploiting price inefficiencies and pairs correlation deviations |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium-term trading | Short-term to medium-term, sometimes intraday |
| Complexity | Low to medium | High, requires deep statistical knowledge |
Which is better?
Grid trading excels in volatile markets by systematically placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals, capitalizing on price fluctuations without predicting trends. Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models and historical data to exploit short-term price inefficiencies between correlated assets, requiring advanced computational resources and risk management. For traders prioritizing automated, low-maintenance strategies in ranging markets, grid trading offers simplicity, while those seeking high-frequency, data-driven opportunities may find statistical arbitrage more profitable yet complex.
Connection
Grid trading and statistical arbitrage both leverage systematic strategies to exploit market inefficiencies by identifying price discrepancies and executing trades within predefined intervals. Grid trading establishes buy and sell orders at set price levels, creating a "grid" that captures profits from market fluctuations, while statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models and historical data to identify statistically significant price relationships and mean-reverting behaviors. Both methods rely on algorithmic execution, risk management, and market neutrality to generate consistent returns regardless of overall market direction.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage leverages complex quantitative models to exploit short-term price inefficiencies across correlated financial instruments, relying heavily on historical price data and statistical tests such as cointegration and mean reversion. This strategy requires high-frequency data analysis, robust risk management frameworks, and often employs machine learning algorithms to predict asset price movements. Explore more about optimizing statistical arbitrage techniques and algorithmic implementation for enhanced market performance.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage leverages mean reversion by identifying mispriced assets expected to return to their historical average, using complex quantitative models and high-frequency data. Grid trading exploits mean reversion through predefined price intervals, placing buy and sell orders to capture profits as prices oscillate within a set range. Explore deeper insights into the mechanics and risk management of mean reversion strategies.
Cointegration
Statistical arbitrage relies heavily on the concept of cointegration to identify pairs of assets whose price movements show a stable, long-term equilibrium despite short-term divergences, enabling traders to exploit mean reversion for profit. Grid trading, in contrast, does not require cointegration and operates by placing buy and sell orders at preset intervals above and below a set price, profiting from market volatility rather than underlying asset relationships. Explore how cointegration enhances statistical arbitrage strategies and its impact on risk management for a deeper understanding.
Source and External Links
Statistical Arbitrage: Strategies, Examples, and Risks - Statistical arbitrage, or "stat arb," is a quantitative trading strategy that uses statistical and computational methods to identify and exploit price inefficiencies between crypto assets by analyzing historical data and predicting future price movements based on patterns and correlations.
The Power of Statistical Arbitrage in Finance - Statistical arbitrage leverages quantitative models to detect temporary price discrepancies among related financial instruments, typically employing mean reversion, with profits sought from buying undervalued and selling overvalued assets as prices are expected to converge.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage is a class of short-term, automated trading strategies involving large, diversified portfolios of securities, using statistical and econometric models (often mean reversion) to generate trade signals executed rapidly and at low cost.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com