Gamma scalping involves dynamic hedging of options positions to capitalize on price volatility and manage risk exposure, focusing on adjusting delta as the underlying asset moves. Statistical arbitrage employs quantitative models to detect and exploit pricing inefficiencies across correlated assets, leveraging mean reversion and market anomalies for profits. Explore the subtle differences between gamma scalping and statistical arbitrage to enhance your trading strategy.
Why it is important
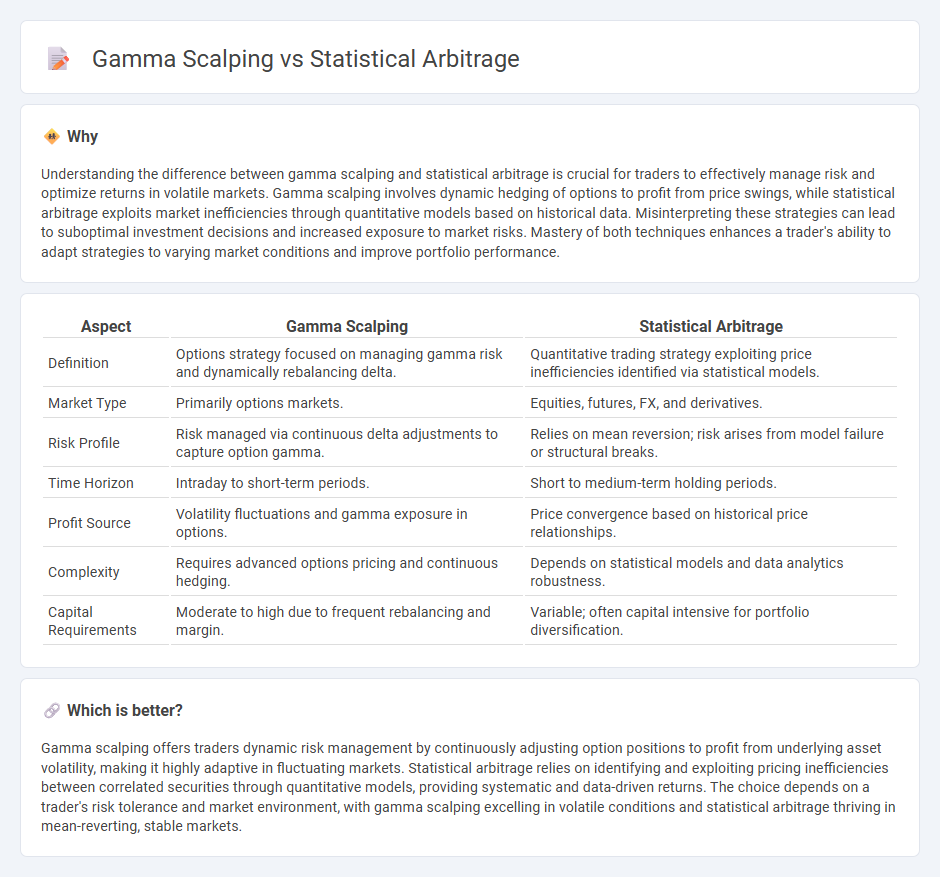
Understanding the difference between gamma scalping and statistical arbitrage is crucial for traders to effectively manage risk and optimize returns in volatile markets. Gamma scalping involves dynamic hedging of options to profit from price swings, while statistical arbitrage exploits market inefficiencies through quantitative models based on historical data. Misinterpreting these strategies can lead to suboptimal investment decisions and increased exposure to market risks. Mastery of both techniques enhances a trader's ability to adapt strategies to varying market conditions and improve portfolio performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Options strategy focused on managing gamma risk and dynamically rebalancing delta. | Quantitative trading strategy exploiting price inefficiencies identified via statistical models. |
| Market Type | Primarily options markets. | Equities, futures, FX, and derivatives. |
| Risk Profile | Risk managed via continuous delta adjustments to capture option gamma. | Relies on mean reversion; risk arises from model failure or structural breaks. |
| Time Horizon | Intraday to short-term periods. | Short to medium-term holding periods. |
| Profit Source | Volatility fluctuations and gamma exposure in options. | Price convergence based on historical price relationships. |
| Complexity | Requires advanced options pricing and continuous hedging. | Depends on statistical models and data analytics robustness. |
| Capital Requirements | Moderate to high due to frequent rebalancing and margin. | Variable; often capital intensive for portfolio diversification. |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers traders dynamic risk management by continuously adjusting option positions to profit from underlying asset volatility, making it highly adaptive in fluctuating markets. Statistical arbitrage relies on identifying and exploiting pricing inefficiencies between correlated securities through quantitative models, providing systematic and data-driven returns. The choice depends on a trader's risk tolerance and market environment, with gamma scalping excelling in volatile conditions and statistical arbitrage thriving in mean-reverting, stable markets.
Connection
Gamma scalping and statistical arbitrage both exploit market inefficiencies using quantitative strategies that incorporate options pricing and price movements. Gamma scalping manages the risk of an options portfolio by dynamically adjusting delta exposure to capture profits from volatility, while statistical arbitrage identifies pricing anomalies across related securities using statistical models. Combining these approaches enhances the ability to hedge options risks while capitalizing on short-term price discrepancies in the market.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and mathematical models to identify and exploit price inefficiencies across correlated assets, aiming for consistent, market-neutral profits. It involves large volumes of trades, quantitative algorithms, and high-frequency execution to capitalize on mean reversion and mispricings in equity pairs or baskets. Explore deeper insights into statistical arbitrage strategies, execution challenges, and risk management techniques.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage leverages mean reversion by identifying price discrepancies between correlated assets and exploiting the expected return to equilibrium. Gamma scalping involves dynamically hedging an options position to benefit from volatility while maintaining exposure to mean-reverting price movements. Explore deeper insights into how these strategies optimize returns through mean reversion mechanisms.
Pairs Trading
Statistical arbitrage in pairs trading exploits mean-reverting price relationships between two correlated assets to generate profits from temporary divergences. Gamma scalping, on the other hand, involves dynamic hedging of options positions to capitalize on volatility and price movements while managing gamma risk. Explore how these strategies differ in risk management and execution to optimize trading performance.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - WunderTrading - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral, quantitative trading strategy that exploits price discrepancies between correlated securities using complex algorithms and statistical models, often through Pair Trading, Basket Trading, and Mean Reversion, with an emphasis on managing risks from historical pattern reliance.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage, or Stat Arb, is a short-term trading strategy that uses mean reversion models across broad portfolios, employing statistical and econometric techniques to generate market-neutral trading signals, often automated to minimize costs and handle large turnover.
Statistical Arbitrage in High Frequency Trading Based on Limit Order ... - Stanford PDF - Statistical arbitrage involves spreading risk over thousands to millions of very short-term trades, aiming to profit from small pricing inefficiencies and quick mean reversion in high-frequency trading contexts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com