Liquidity sweeps occur when large orders rapidly consume available liquidity across multiple price levels, causing sharp price movements, while slippage refers to the difference between the expected execution price and the actual price traded due to market volatility or order size. Both concepts are crucial for traders to understand as they impact trade execution quality and cost efficiency. Explore the nuances of liquidity sweeps and slippage to enhance your trading strategies and minimize unexpected losses.
Why it is important
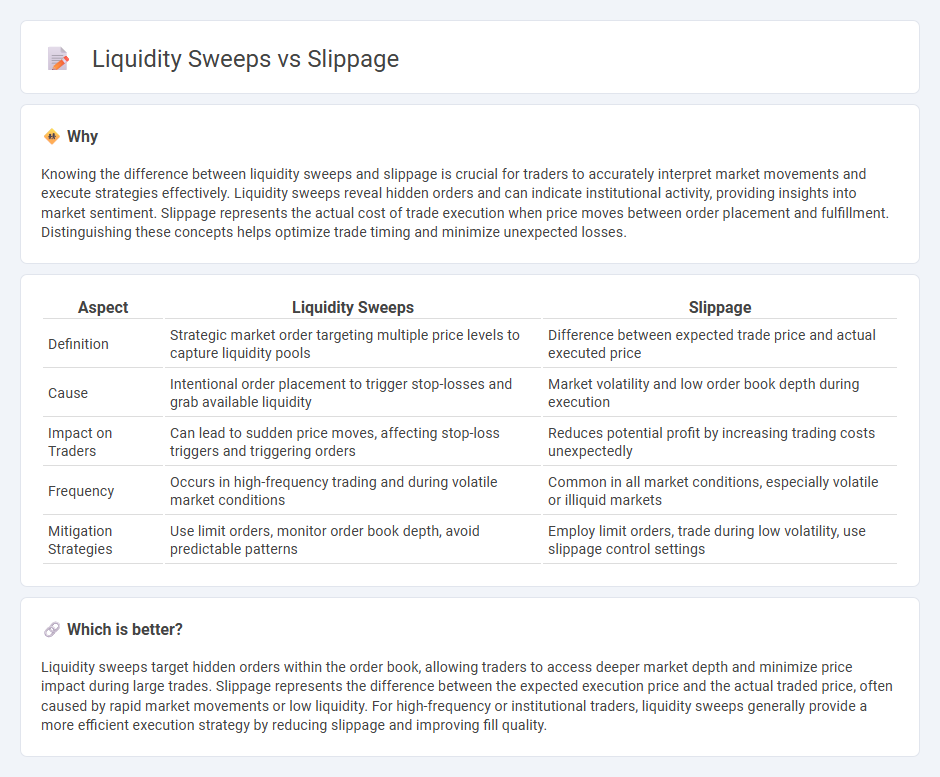
Knowing the difference between liquidity sweeps and slippage is crucial for traders to accurately interpret market movements and execute strategies effectively. Liquidity sweeps reveal hidden orders and can indicate institutional activity, providing insights into market sentiment. Slippage represents the actual cost of trade execution when price moves between order placement and fulfillment. Distinguishing these concepts helps optimize trade timing and minimize unexpected losses.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Liquidity Sweeps | Slippage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Strategic market order targeting multiple price levels to capture liquidity pools | Difference between expected trade price and actual executed price |
| Cause | Intentional order placement to trigger stop-losses and grab available liquidity | Market volatility and low order book depth during execution |
| Impact on Traders | Can lead to sudden price moves, affecting stop-loss triggers and triggering orders | Reduces potential profit by increasing trading costs unexpectedly |
| Frequency | Occurs in high-frequency trading and during volatile market conditions | Common in all market conditions, especially volatile or illiquid markets |
| Mitigation Strategies | Use limit orders, monitor order book depth, avoid predictable patterns | Employ limit orders, trade during low volatility, use slippage control settings |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweeps target hidden orders within the order book, allowing traders to access deeper market depth and minimize price impact during large trades. Slippage represents the difference between the expected execution price and the actual traded price, often caused by rapid market movements or low liquidity. For high-frequency or institutional traders, liquidity sweeps generally provide a more efficient execution strategy by reducing slippage and improving fill quality.
Connection
Liquidity sweeps occur when large market orders consume available liquidity across multiple price levels, directly causing slippage as traders receive less favorable execution prices than expected. Slippage reflects the difference between the anticipated price of a trade and the actual filled price, often exacerbated by liquidity sweeps that deplete order book depth. Understanding the interplay between liquidity sweeps and slippage is crucial for optimizing trade execution strategies and minimizing unexpected transaction costs.
Key Terms
Order Book
Slippage occurs when a trade executes at a worse price than expected due to insufficient order book depth, causing orders to "slip" across multiple price levels. Liquidity sweeps are strategic orders designed to absorb liquidity across the order book rapidly, clearing out available bids or offers and potentially causing significant price impact. Explore how these dynamics affect trading strategies and market efficiency for deeper insights.
Market Impact
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price, often caused by insufficient liquidity or high market volatility. Liquidity sweeps involve aggressively executing large orders to capture available liquidity across multiple price levels, which can significantly impact market prices and increase slippage. Explore further to understand strategies for minimizing market impact during large trades.
Execution Price
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected execution price and the actual price at which a trade is executed, often caused by market volatility and low liquidity. Liquidity sweeps involve quickly consuming available liquidity across multiple price levels to achieve a large order fill, which can impact the execution price by moving the market. Explore how mastering these concepts can optimize your trading strategy and improve execution efficiency.
Source and External Links
Slippage - Definition, Why It Happens, How To Minimize - Slippage occurs when the execution price of a trade differs from the requested price, often due to market volatility or low liquidity causing price changes between order placement and execution.
What is slippage? Understanding Slippage in Trading - Slippage is a natural part of trading in dynamic, fast-moving markets where orders are executed at the next best available price if the requested price cannot be met, commonly occurring during high volatility or low liquidity periods.
What is slippage in crypto and how to minimize its impact? - In crypto trading, slippage describes the difference between expected and actual trade execution prices, caused mainly by market volatility and low liquidity, and can be mitigated using limit orders and setting slippage tolerance.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com