Penny jump strategies exploit small price changes caused by minor order imbalances, allowing traders to profit from immediate market movements. Latency arbitrage involves leveraging speed advantages to capitalize on price discrepancies across different exchanges before others can react. Explore how these trading techniques differ in technology requirements and risk profiles.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between penny jump and latency arbitrage is crucial for traders aiming to optimize execution strategies and minimize slippage in fast-moving markets. Penny jump involves exploiting small price increments for profit, while latency arbitrage leverages speed advantages to capitalize on price discrepancies across venues. Correctly identifying these tactics helps prevent losses from adverse selection and improves trade timing. Mastery of these concepts enhances competitive edge in high-frequency and algorithmic trading environments.
Comparison Table
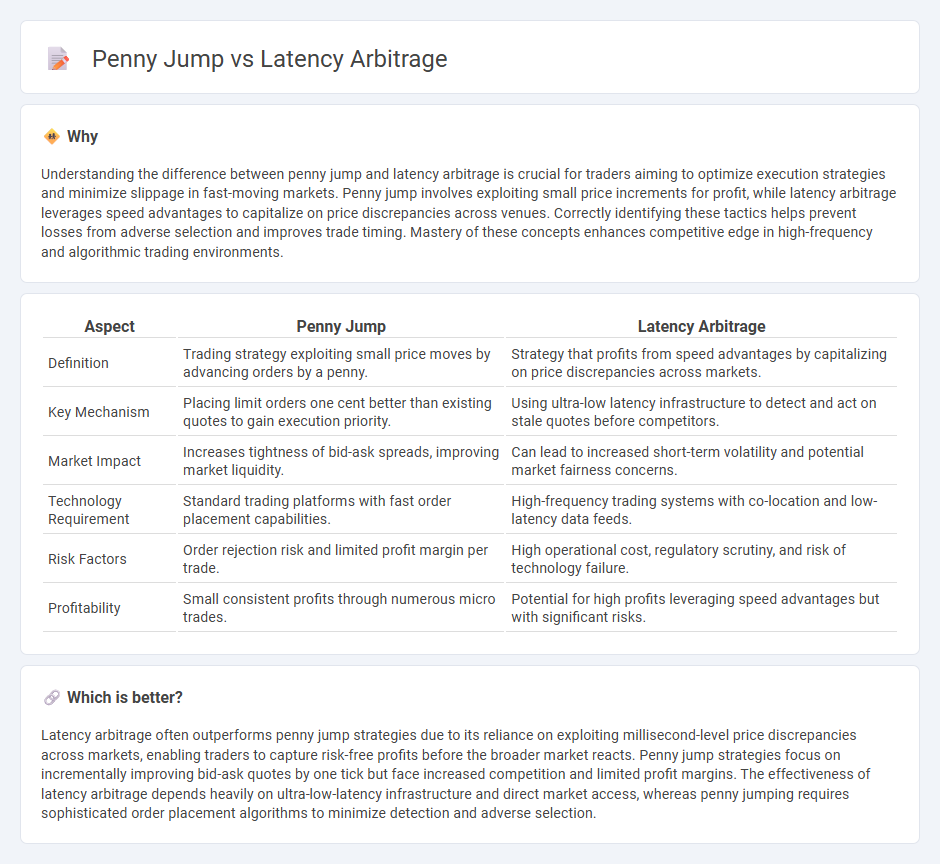
| Aspect | Penny Jump | Latency Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategy exploiting small price moves by advancing orders by a penny. | Strategy that profits from speed advantages by capitalizing on price discrepancies across markets. |
| Key Mechanism | Placing limit orders one cent better than existing quotes to gain execution priority. | Using ultra-low latency infrastructure to detect and act on stale quotes before competitors. |
| Market Impact | Increases tightness of bid-ask spreads, improving market liquidity. | Can lead to increased short-term volatility and potential market fairness concerns. |
| Technology Requirement | Standard trading platforms with fast order placement capabilities. | High-frequency trading systems with co-location and low-latency data feeds. |
| Risk Factors | Order rejection risk and limited profit margin per trade. | High operational cost, regulatory scrutiny, and risk of technology failure. |
| Profitability | Small consistent profits through numerous micro trades. | Potential for high profits leveraging speed advantages but with significant risks. |
Which is better?
Latency arbitrage often outperforms penny jump strategies due to its reliance on exploiting millisecond-level price discrepancies across markets, enabling traders to capture risk-free profits before the broader market reacts. Penny jump strategies focus on incrementally improving bid-ask quotes by one tick but face increased competition and limited profit margins. The effectiveness of latency arbitrage depends heavily on ultra-low-latency infrastructure and direct market access, whereas penny jumping requires sophisticated order placement algorithms to minimize detection and adverse selection.
Connection
Penny jump and latency arbitrage are connected through their reliance on exploiting minute price differences in high-frequency trading. Penny jump involves small price increments that occur when a trader's order slightly outbids others, enabling latency arbitrageurs to capitalize on information delays between markets. By quickly detecting these small price movements caused by penny jumps, latency arbitrage strategies profit from the latency in order execution and market data dissemination.
Key Terms
**Latency Arbitrage:**
Latency arbitrage exploits speed differences in market data transmission to capitalize on price discrepancies between exchanges before others can react, often using co-located servers and advanced algorithms. Penny jump involves placing buy or sell orders marginally ahead of existing bids or asks to secure faster execution at slightly improved prices, but it lacks the cross-market speed advantage inherent in latency arbitrage. Discover deeper insights into how latency arbitrage shapes high-frequency trading strategies and market efficiency.
Market Data Speed
Latency arbitrage exploits minute differences in market data speed to capitalize on price discrepancies across exchanges, leveraging ultra-low-latency connections for faster trade execution. Penny jump strategies involve placing orders slightly ahead of existing bids or offers to gain advantage in order books, relying heavily on real-time market data speed for timing accuracy. Discover more about optimizing trading strategies with advanced market data speed insights.
Execution Delay
Latency arbitrage exploits execution delay differences in trading systems to gain profits by rapidly acting on price updates before others. Penny jump strategies capitalize on minimal price changes but require precise timing to avoid execution slippage caused by delays. Explore detailed analysis and strategies to minimize execution delay effects in high-frequency trading environments.
Source and External Links
Latency Arbitrage, Market Fragmentation, and Efficiency: A Two-Market Model - Latency arbitrage is a high-frequency trading strategy where traders exploit differences in access and response time between fragmented markets to earn profits, but it reduces total market surplus and liquidity efficiency.
Latency Arbitrage in Forex Trading: easy profits? Not really. - Latency arbitrage in forex involves using ultra-fast algorithms and low-latency connections to capitalize on tiny, millisecond price discrepancies caused by delays in data transmission between markets.
What Is Latency Arbitrage in Forex Trading? - B2PRIME - Latency arbitrage exploits time-delay differences between brokers for profit but is often considered unethical or "toxic flow," with many brokers forbidding it and regulators imposing measures to limit its market impact.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com