Gamma scalping involves actively managing options positions to capitalize on changes in an asset's volatility and price movement, optimizing risk and return through dynamic adjustments. Spread trading focuses on entering simultaneous long and short positions in related securities to exploit price differentials while mitigating overall market exposure. Explore the nuances of gamma scalping versus spread trading to enhance your strategic approach in options trading.
Why it is important
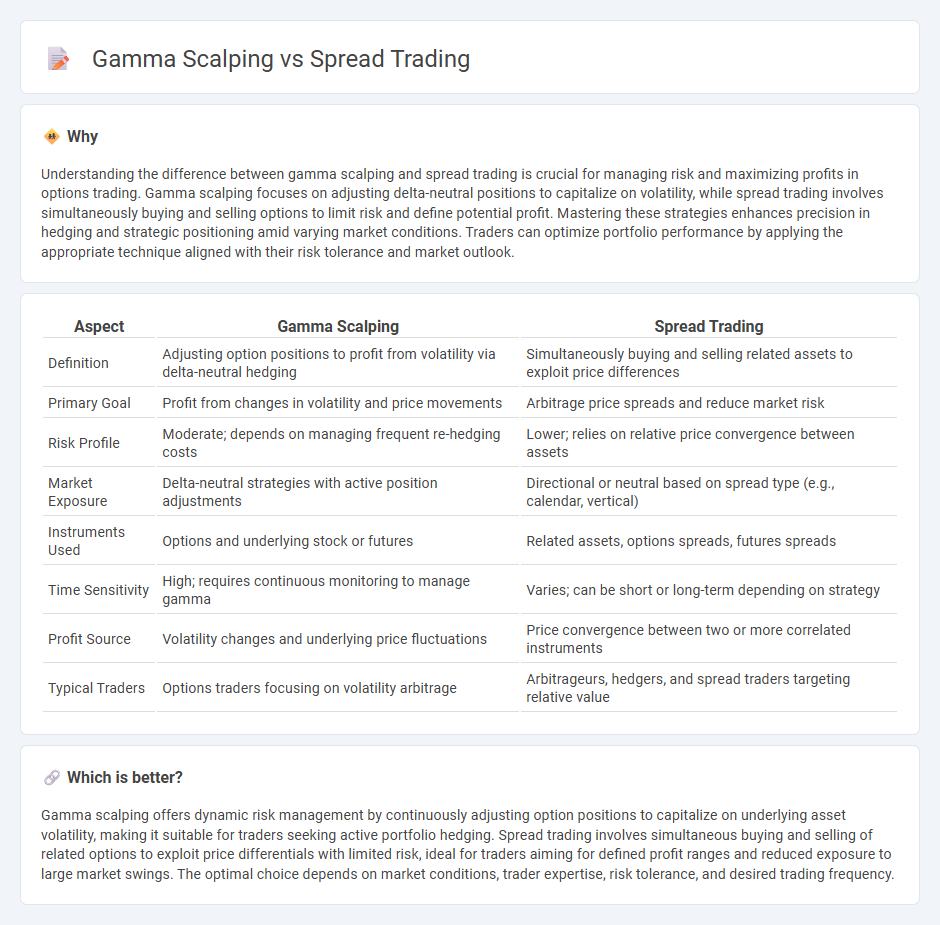
Understanding the difference between gamma scalping and spread trading is crucial for managing risk and maximizing profits in options trading. Gamma scalping focuses on adjusting delta-neutral positions to capitalize on volatility, while spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling options to limit risk and define potential profit. Mastering these strategies enhances precision in hedging and strategic positioning amid varying market conditions. Traders can optimize portfolio performance by applying the appropriate technique aligned with their risk tolerance and market outlook.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Gamma Scalping | Spread Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Adjusting option positions to profit from volatility via delta-neutral hedging | Simultaneously buying and selling related assets to exploit price differences |
| Primary Goal | Profit from changes in volatility and price movements | Arbitrage price spreads and reduce market risk |
| Risk Profile | Moderate; depends on managing frequent re-hedging costs | Lower; relies on relative price convergence between assets |
| Market Exposure | Delta-neutral strategies with active position adjustments | Directional or neutral based on spread type (e.g., calendar, vertical) |
| Instruments Used | Options and underlying stock or futures | Related assets, options spreads, futures spreads |
| Time Sensitivity | High; requires continuous monitoring to manage gamma | Varies; can be short or long-term depending on strategy |
| Profit Source | Volatility changes and underlying price fluctuations | Price convergence between two or more correlated instruments |
| Typical Traders | Options traders focusing on volatility arbitrage | Arbitrageurs, hedgers, and spread traders targeting relative value |
Which is better?
Gamma scalping offers dynamic risk management by continuously adjusting option positions to capitalize on underlying asset volatility, making it suitable for traders seeking active portfolio hedging. Spread trading involves simultaneous buying and selling of related options to exploit price differentials with limited risk, ideal for traders aiming for defined profit ranges and reduced exposure to large market swings. The optimal choice depends on market conditions, trader expertise, risk tolerance, and desired trading frequency.
Connection
Gamma scalping involves dynamically adjusting options positions to maintain a neutral delta, while spread trading uses combinations of options to capitalize on price differentials and volatility changes. Both strategies rely on understanding gamma, the rate of change of delta, to manage risk and optimize returns in volatile markets. Traders use gamma scalping within spread trades to fine-tune exposure and enhance profits by effectively responding to market movements.
Key Terms
Bid-Ask Spread
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related securities to capitalize on price differentials, where the bid-ask spread can significantly impact profitability by influencing entry and exit costs. Gamma scalping, a dynamic options strategy, actively manages delta exposure to benefit from price swings, with the bid-ask spread affecting the frequency and cost-efficiency of adjustments. Explore more insights on how bid-ask spreads shape these trading strategies and optimize execution.
Delta
Spread trading involves simultaneously buying and selling related options to capitalize on price differentials while managing overall Delta exposure, aiming for a neutral or targeted Delta position. Gamma scalping focuses on dynamically adjusting Delta by trading the underlying asset to profit from changes in Gamma, effectively maintaining a Delta-neutral stance as the underlying price fluctuates. Explore detailed strategies and mathematical nuances to master Delta management in these options trading techniques.
Volatility
Spread trading involves simultaneous buying and selling of options to capitalize on volatility differences between strikes or expiration dates, helping traders mitigate directional risk. Gamma scalping exploits gamma exposure by dynamically adjusting positions in response to price movements, aiming to profit from volatility fluctuations while maintaining delta neutrality. Explore detailed strategies on leveraging volatility through spread trading and gamma scalping for enhanced portfolio performance.
Source and External Links
What is Spread Trading: Meaning and Types | Angel One - Spread trading is buying one security and selling another related security simultaneously to profit from price differences, involving strategies like intermarket, intracommodity, and calendar spreads, influenced by factors such as market volatility and liquidity.
What is Spread Trading? Meaning, Strategies and Benefits - Spread trading involves executing two positions (buying and selling) simultaneously on related securities to profit from the price spread, with risk generally lower than outright trades, and profiting when the spread narrows or remains stable.
A Guide to Spread Trading Futures - Spread trading futures involves taking simultaneous long and short positions on related contracts to benefit from price discrepancies, reducing risk compared to directional bets, with profits dependent on the change in the price difference between contracts.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com