Liquidity sweep refers to the strategy of quickly fulfilling large orders by tapping into multiple liquidity pools, minimizing market impact and ensuring efficient trade execution. Slippage occurs when the execution price deviates from the expected price due to insufficient liquidity or rapid market movements, resulting in higher trading costs. Explore the differences between liquidity sweep and slippage to optimize trading performance and cost efficiency.
Why it is important
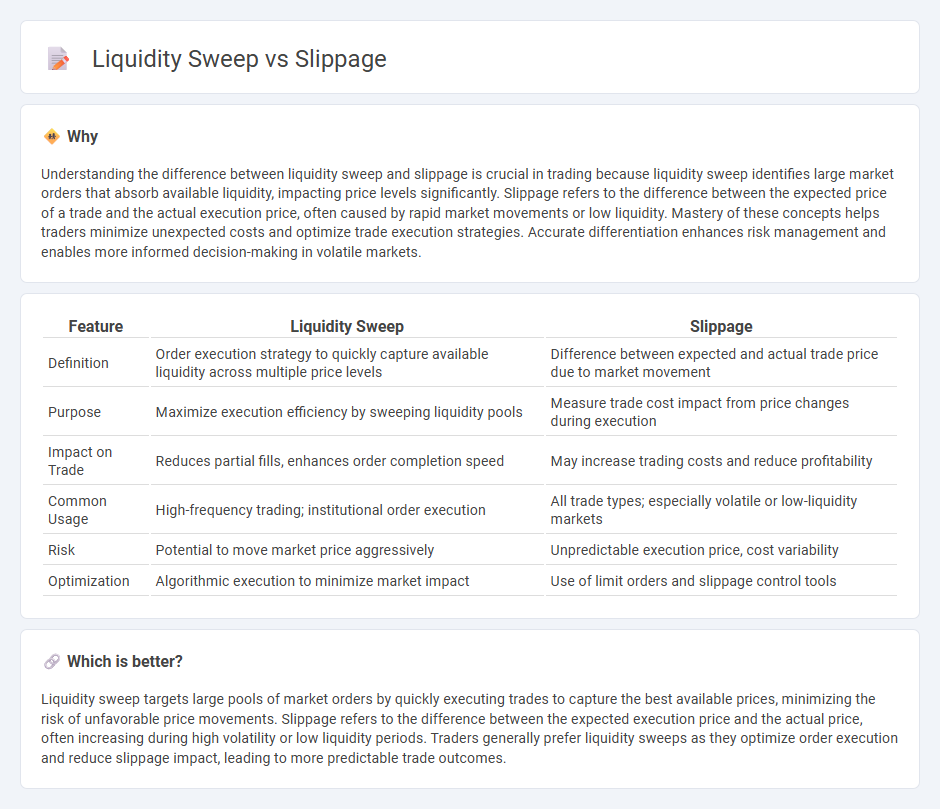
Understanding the difference between liquidity sweep and slippage is crucial in trading because liquidity sweep identifies large market orders that absorb available liquidity, impacting price levels significantly. Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price, often caused by rapid market movements or low liquidity. Mastery of these concepts helps traders minimize unexpected costs and optimize trade execution strategies. Accurate differentiation enhances risk management and enables more informed decision-making in volatile markets.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Liquidity Sweep | Slippage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Order execution strategy to quickly capture available liquidity across multiple price levels | Difference between expected and actual trade price due to market movement |
| Purpose | Maximize execution efficiency by sweeping liquidity pools | Measure trade cost impact from price changes during execution |
| Impact on Trade | Reduces partial fills, enhances order completion speed | May increase trading costs and reduce profitability |
| Common Usage | High-frequency trading; institutional order execution | All trade types; especially volatile or low-liquidity markets |
| Risk | Potential to move market price aggressively | Unpredictable execution price, cost variability |
| Optimization | Algorithmic execution to minimize market impact | Use of limit orders and slippage control tools |
Which is better?
Liquidity sweep targets large pools of market orders by quickly executing trades to capture the best available prices, minimizing the risk of unfavorable price movements. Slippage refers to the difference between the expected execution price and the actual price, often increasing during high volatility or low liquidity periods. Traders generally prefer liquidity sweeps as they optimize order execution and reduce slippage impact, leading to more predictable trade outcomes.
Connection
Liquidity sweep occurs when large market orders consume multiple price levels in the order book, causing a rapid shift in asset prices. Slippage is the price difference experienced between the expected trade execution price and the actual price due to this sudden depletion of liquidity. High liquidity sweeps increase slippage risk, impacting trade execution cost and strategy effectiveness.
Key Terms
Order Book
Slippage occurs when an order executes at a price different from the expected price due to insufficient liquidity in the order book, causing the trade to fill at less favorable prices. Liquidity sweep involves aggressively consuming multiple price levels in the order book to fill a large order quickly, often resulting in higher slippage. Explore the dynamics of order book depth and execution strategies to understand their impact on slippage and liquidity sweep.
Market Impact
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual execution price, often caused by low liquidity or high market volatility, leading to unfavorable market impact. Liquidity sweep involves systematically consuming available liquidity across multiple price levels to fulfill large orders, aiming to minimize market impact by distributing trade execution. Explore further to understand how these strategies affect trading efficiency and market behavior.
Execution Price
Slippage refers to the difference between the expected execution price and the actual transaction price due to market volatility or order size, impacting overall trade cost. Liquidity sweep involves capturing available liquidity across multiple venues or price levels to achieve better execution prices, minimizing slippage risk. Explore detailed comparisons and strategies to optimize execution price in different market conditions.
Source and External Links
Slippage - Definition, Why It Happens, How To Minimize - Slippage occurs when the execution price of a trade differs from the requested price, typically in highly volatile or low liquidity markets, causing the trade to fill at a price different than expected.
What is slippage? Understanding Slippage in Trading - Slippage is a normal part of trading where an order is executed at a different price than requested often due to high volatility or low liquidity, reflecting the dynamic and fast-moving nature of markets.
What is slippage in crypto and how to minimize its impact? - In cryptocurrency trading, slippage refers to the difference between the expected trade price and the actual execution price, caused primarily by market volatility and low liquidity, and can be minimized by using limit orders and setting slippage tolerances.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com