Flash loan arbitrage leverages instantaneous, uncollateralized loans to capitalize on price discrepancies across decentralized exchanges, executing rapid, risk-minimized trades within a single blockchain transaction. Statistical arbitrage employs algorithmic models to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies based on historical and real-time data patterns across multiple markets, relying on quantitative analysis and machine learning techniques. Explore the nuances and strategies behind these advanced trading methods to enhance your market proficiency.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between flash loan arbitrage and statistical arbitrage is crucial for effective risk management and strategy optimization in trading. Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit price disparities across decentralized exchanges within a single transaction. Statistical arbitrage relies on historical data and mathematical models to identify and trade on pricing inefficiencies over time. Traders can maximize profits and minimize losses by selecting the appropriate arbitrage method aligned with market conditions and capital constraints.
Comparison Table
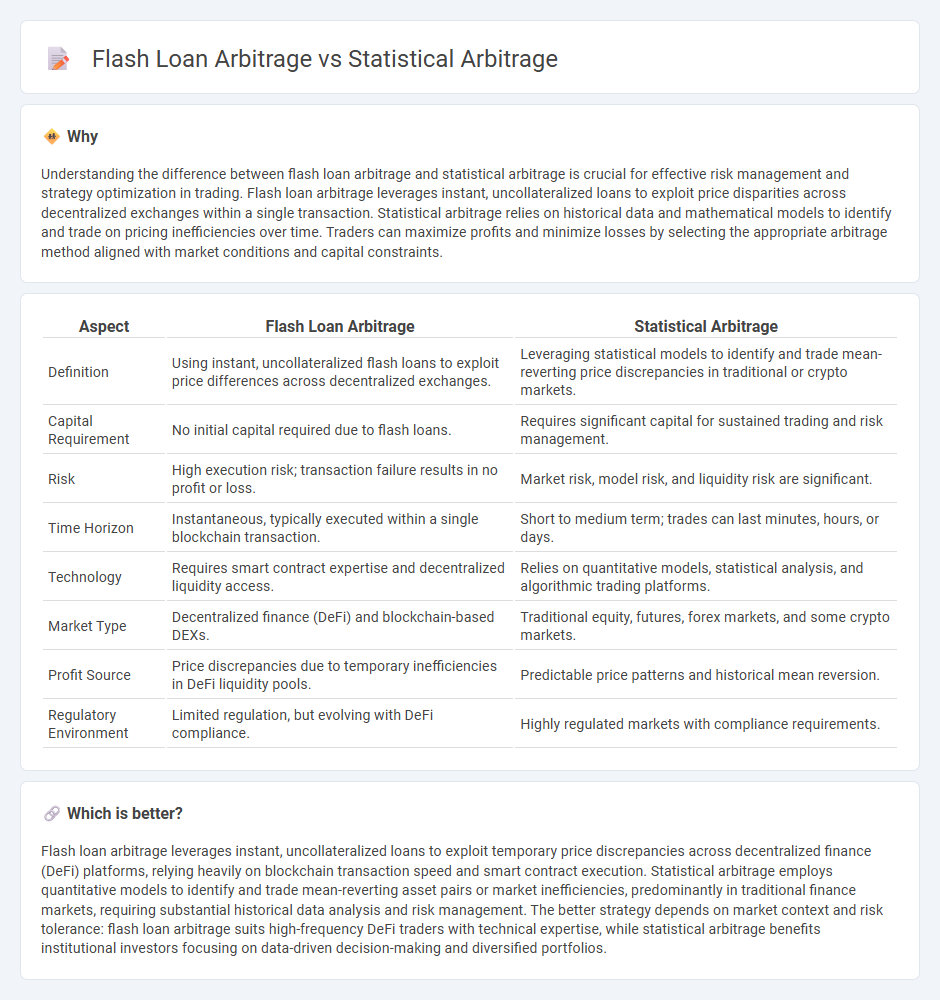
| Aspect | Flash Loan Arbitrage | Statistical Arbitrage |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Using instant, uncollateralized flash loans to exploit price differences across decentralized exchanges. | Leveraging statistical models to identify and trade mean-reverting price discrepancies in traditional or crypto markets. |
| Capital Requirement | No initial capital required due to flash loans. | Requires significant capital for sustained trading and risk management. |
| Risk | High execution risk; transaction failure results in no profit or loss. | Market risk, model risk, and liquidity risk are significant. |
| Time Horizon | Instantaneous, typically executed within a single blockchain transaction. | Short to medium term; trades can last minutes, hours, or days. |
| Technology | Requires smart contract expertise and decentralized liquidity access. | Relies on quantitative models, statistical analysis, and algorithmic trading platforms. |
| Market Type | Decentralized finance (DeFi) and blockchain-based DEXs. | Traditional equity, futures, forex markets, and some crypto markets. |
| Profit Source | Price discrepancies due to temporary inefficiencies in DeFi liquidity pools. | Predictable price patterns and historical mean reversion. |
| Regulatory Environment | Limited regulation, but evolving with DeFi compliance. | Highly regulated markets with compliance requirements. |
Which is better?
Flash loan arbitrage leverages instant, uncollateralized loans to exploit temporary price discrepancies across decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms, relying heavily on blockchain transaction speed and smart contract execution. Statistical arbitrage employs quantitative models to identify and trade mean-reverting asset pairs or market inefficiencies, predominantly in traditional finance markets, requiring substantial historical data analysis and risk management. The better strategy depends on market context and risk tolerance: flash loan arbitrage suits high-frequency DeFi traders with technical expertise, while statistical arbitrage benefits institutional investors focusing on data-driven decision-making and diversified portfolios.
Connection
Flash loan arbitrage exploits instant, uncollateralized loans on decentralized finance (DeFi) platforms to capitalize on temporary price discrepancies across different exchanges. Statistical arbitrage uses quantitative models and historical price data to identify and execute trades based on expected mean reversion or price divergence patterns. Both strategies depend on rapid execution and price inefficiencies, but flash loan arbitrage leverages blockchain technology for immediate capital deployment, while statistical arbitrage relies on algorithmic trading and statistical analysis in traditional markets.
Key Terms
**Statistical Arbitrage:**
Statistical arbitrage leverages historical price data and quantitative models to identify and exploit pricing inefficiencies across correlated financial assets, often using mean reversion and pairs trading strategies. This technique relies heavily on statistical methods, machine learning algorithms, and high-frequency trading infrastructure to achieve consistent returns with controlled risk. Explore the intricacies of statistical arbitrage techniques to enhance your quantitative trading strategies.
Mean Reversion
Statistical arbitrage leverages mean reversion by identifying asset prices that deviate from their historical average, enabling traders to exploit temporary price inefficiencies across correlated securities. Flash loan arbitrage uses instantaneous, uncollateralized loans in decentralized finance (DeFi) to execute rapid trades, capitalizing on price discrepancies before the market adjusts, often involving mean reversion principles in decentralized exchanges. Explore deeper insights into how mean reversion strategies differentiate these arbitrage techniques.
Pair Trading
Statistical arbitrage exploits price inefficiencies in correlated asset pairs through mean-reversion strategies, while flash loan arbitrage leverages uncollateralized loans to capitalize on momentary arbitrage opportunities across decentralized finance platforms. Pair trading in statistical arbitrage involves simultaneous long and short positions in two historically correlated securities to profit from deviations in their price relationship without exposure to market direction. Explore the mechanics and risks of these arbitrage techniques to enhance your trading strategy knowledge.
Source and External Links
Top Statistical Arbitrage Strategies and Their Risks - WunderTrading - Statistical arbitrage is a market-neutral, quantitative trading strategy exploiting pricing discrepancies between related securities using complex algorithms and mean reversion models to achieve consistent returns while managing risk through simultaneous long and short positions.
Statistical arbitrage - Wikipedia - Statistical arbitrage (Stat Arb) is a short-term trading approach involving large diversified portfolios, using beta-neutral and multi-factor mean reversion models, often implemented in automated systems at hedge funds and investment banks to exploit small pricing inefficiencies efficiently.
What is Statistical Arbitrage? | CQF - Statistical arbitrage is a quantitative finance strategy that exploits deviations from expected statistical relationships between related financial instruments, focusing on price discrepancies and using data-driven methods to trade profitably on such inefficiencies.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com