Market microstructure examines the processes and mechanisms through which securities are traded, focusing on order types, trading platforms, and price formation. Market efficiency evaluates how well asset prices reflect all available information, influencing the predictability of returns and market anomalies. Explore the detailed interplay between market microstructure and market efficiency to understand trading dynamics better.
Why it is important
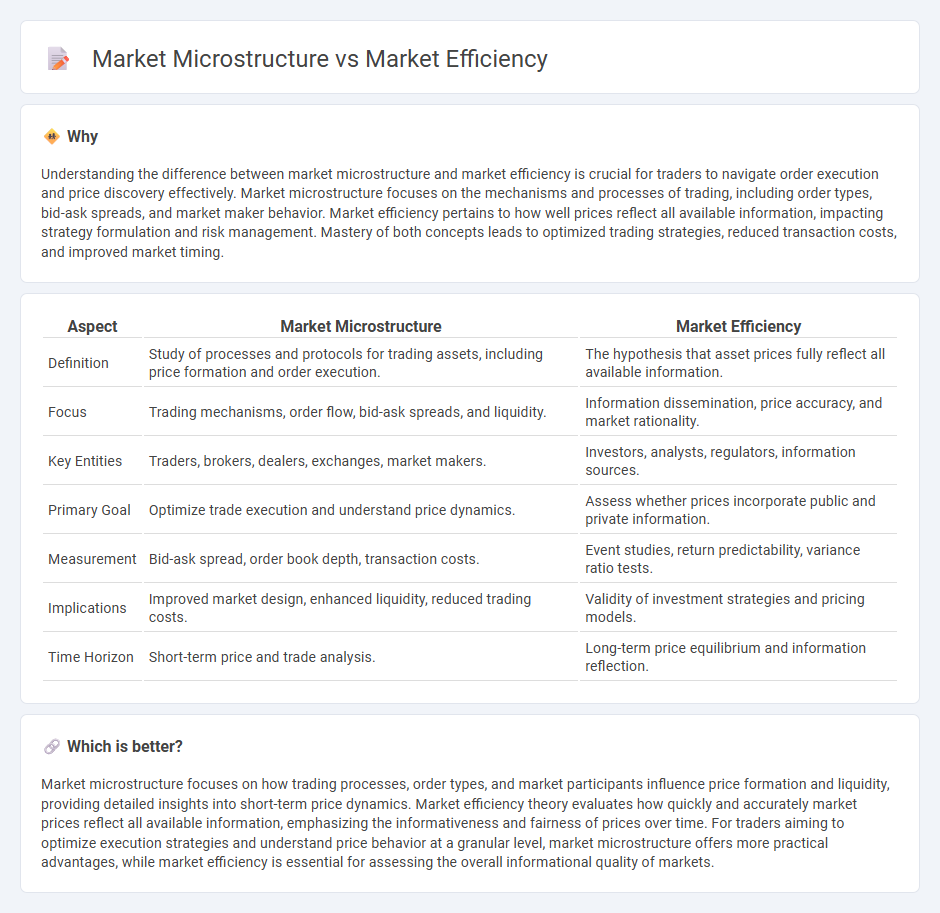
Understanding the difference between market microstructure and market efficiency is crucial for traders to navigate order execution and price discovery effectively. Market microstructure focuses on the mechanisms and processes of trading, including order types, bid-ask spreads, and market maker behavior. Market efficiency pertains to how well prices reflect all available information, impacting strategy formulation and risk management. Mastery of both concepts leads to optimized trading strategies, reduced transaction costs, and improved market timing.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Market Microstructure | Market Efficiency |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Study of processes and protocols for trading assets, including price formation and order execution. | The hypothesis that asset prices fully reflect all available information. |
| Focus | Trading mechanisms, order flow, bid-ask spreads, and liquidity. | Information dissemination, price accuracy, and market rationality. |
| Key Entities | Traders, brokers, dealers, exchanges, market makers. | Investors, analysts, regulators, information sources. |
| Primary Goal | Optimize trade execution and understand price dynamics. | Assess whether prices incorporate public and private information. |
| Measurement | Bid-ask spread, order book depth, transaction costs. | Event studies, return predictability, variance ratio tests. |
| Implications | Improved market design, enhanced liquidity, reduced trading costs. | Validity of investment strategies and pricing models. |
| Time Horizon | Short-term price and trade analysis. | Long-term price equilibrium and information reflection. |
Which is better?
Market microstructure focuses on how trading processes, order types, and market participants influence price formation and liquidity, providing detailed insights into short-term price dynamics. Market efficiency theory evaluates how quickly and accurately market prices reflect all available information, emphasizing the informativeness and fairness of prices over time. For traders aiming to optimize execution strategies and understand price behavior at a granular level, market microstructure offers more practical advantages, while market efficiency is essential for assessing the overall informational quality of markets.
Connection
Market microstructure, which studies the mechanisms and protocols of trading, directly impacts market efficiency by influencing the speed, cost, and transparency of trade executions. Efficient markets rely on well-functioning microstructure elements such as order types, liquidity provision, and price discovery processes to accurately reflect available information in asset prices. Inefficiencies often arise from microstructure frictions like bid-ask spreads, order processing delays, and asymmetric information among market participants.
Key Terms
Informational Efficiency
Market efficiency, particularly informational efficiency, reflects how quickly and accurately asset prices incorporate all available information, minimizing opportunities for abnormal profits. Market microstructure examines the processes and mechanisms, such as order flow, bid-ask spreads, and trading systems, that facilitate price discovery and liquidity, directly impacting informational efficiency. Explore deeper insights into how microstructure elements shape informational efficiency in financial markets.
Bid-Ask Spread
The bid-ask spread serves as a crucial indicator in market microstructure, reflecting liquidity and transaction costs, while market efficiency concerns the extent to which prices fully incorporate available information. Narrow bid-ask spreads typically signal higher liquidity and more efficient price discovery, whereas wider spreads may indicate market frictions or information asymmetry. Explore deeper insights into how bid-ask spreads influence both theoretical market efficiency and practical trading outcomes.
Price Discovery
Price discovery in market efficiency evaluates how quickly and accurately market prices reflect all available information, ensuring fair asset valuation. In contrast, market microstructure studies the mechanisms, such as order types and trading processes, that influence the formation and adjustment of prices at a granular level. Explore more to understand how these concepts interplay to shape trading dynamics and market transparency.
Source and External Links
Definition, Types & Features of Market Efficiency - Groww - Market efficiency is the ability of markets to fully and instantly incorporate all available information into asset prices, making it impossible for traders to consistently outperform the market using public information, as explained by Eugene Fama's Efficient Market Hypothesis (EMH).
Market Efficiency - Corporate Finance Institute - An efficient market perfectly, completely, instantly, and costlessly transmits all information to all participants, so that asset prices fully reflect all available information and no investor can consistently achieve excess returns.
Definition of market efficiency - NYU Stern - Market efficiency means asset prices reflect all relevant information (public and possibly private, depending on the form), implying that strategies like indexing or minimal trading are generally more effective than active research or frequent trading, although prices can still deviate randomly from true value.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com