Modular blockchains trading enhances scalability and flexibility by separating execution, consensus, and data availability layers, allowing traders to optimize transaction speed and security. Peer-to-peer trading, on the other hand, enables direct asset exchanges between individuals without intermediaries, increasing privacy and reducing fees. Explore how these innovative trading methods revolutionize market efficiency and user experience.
Why it is important
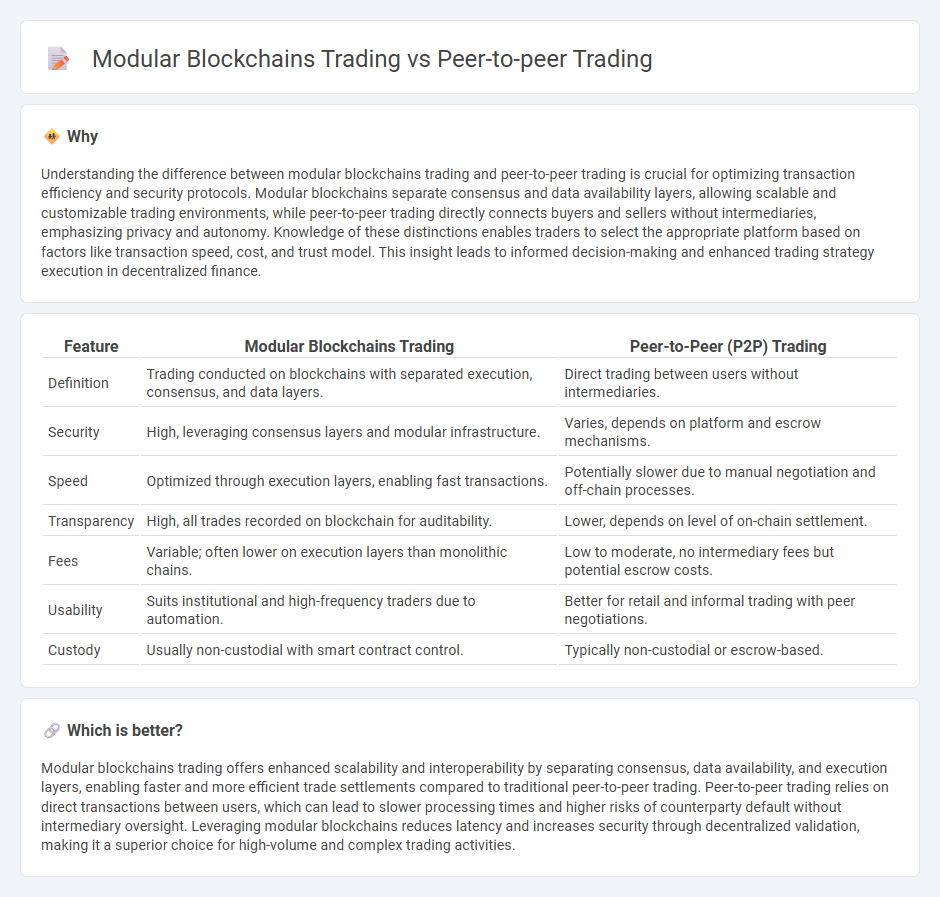
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and peer-to-peer trading is crucial for optimizing transaction efficiency and security protocols. Modular blockchains separate consensus and data availability layers, allowing scalable and customizable trading environments, while peer-to-peer trading directly connects buyers and sellers without intermediaries, emphasizing privacy and autonomy. Knowledge of these distinctions enables traders to select the appropriate platform based on factors like transaction speed, cost, and trust model. This insight leads to informed decision-making and enhanced trading strategy execution in decentralized finance.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Blockchains Trading | Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading conducted on blockchains with separated execution, consensus, and data layers. | Direct trading between users without intermediaries. |
| Security | High, leveraging consensus layers and modular infrastructure. | Varies, depends on platform and escrow mechanisms. |
| Speed | Optimized through execution layers, enabling fast transactions. | Potentially slower due to manual negotiation and off-chain processes. |
| Transparency | High, all trades recorded on blockchain for auditability. | Lower, depends on level of on-chain settlement. |
| Fees | Variable; often lower on execution layers than monolithic chains. | Low to moderate, no intermediary fees but potential escrow costs. |
| Usability | Suits institutional and high-frequency traders due to automation. | Better for retail and informal trading with peer negotiations. |
| Custody | Usually non-custodial with smart contract control. | Typically non-custodial or escrow-based. |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced scalability and interoperability by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, enabling faster and more efficient trade settlements compared to traditional peer-to-peer trading. Peer-to-peer trading relies on direct transactions between users, which can lead to slower processing times and higher risks of counterparty default without intermediary oversight. Leveraging modular blockchains reduces latency and increases security through decentralized validation, making it a superior choice for high-volume and complex trading activities.
Connection
Modular blockchains enhance peer-to-peer trading by enabling specialized layers for transaction settlement, execution, and data availability, which improves efficiency and scalability. Peer-to-peer trading leverages the modular architecture to directly connect buyers and sellers without intermediaries, facilitating faster and more secure asset exchanges. This integration reduces costs and increases transparency, driving broader adoption of decentralized trading platforms.
Key Terms
Decentralization
Peer-to-peer trading enables direct asset exchanges between users without intermediaries, promoting maximum decentralization by leveraging distributed ledger technologies like blockchain. Modular blockchains trading utilizes specialized layers--consensus, execution, and data availability--allowing scalable, secure transactions but introducing specific interoperability and potential centralization trade-offs. Explore detailed comparisons and benefits of each approach to understand their impact on decentralized finance ecosystems.
Counterparty risk
Peer-to-peer trading eliminates intermediaries, reducing counterparty risk by enabling direct asset exchanges between parties on decentralized platforms. Modular blockchains introduce layers that separate execution, settlement, and consensus, which can mitigate counterparty risk through enhanced transparency and built-in smart contract guarantees. Explore how these mechanisms impact security and trust by learning more about their operational differences.
Interoperability
Peer-to-peer trading enables direct transactions between users but often faces limitations in scalability and cross-network compatibility. Modular blockchains enhance interoperability by allowing specialized chains to handle distinct functions while seamlessly communicating through shared consensus layers. Explore how modular blockchain designs are revolutionizing trade efficiency and interoperability.
Source and External Links
What Is Peer-To-Peer Trading and How Do People Use It? - Peer-to-peer (P2P) trading is the direct buying and selling of cryptocurrencies among users without intermediaries, relying on P2P exchanges that provide escrow, ratings, and dispute resolution for secure trades, offering benefits like global access, multiple payment options, and zero fees but facing challenges such as slower speeds and lower liquidity compared to centralized exchanges.
What is P2P Crypto Exchange and How Does Peer-to-Peer Works? - P2P crypto exchanges enable users to trade digital currencies directly with each other without third-party involvement, offering diverse payment options and security measures through ratings and feedback, making it popular in countries with exchange restrictions due to fewer regulations.
Top 10 Peer-to-Peer Exchanges in 2025 for Secure Crypto Trading - P2P exchanges connect buyers and sellers for direct crypto trading by matching orders, securing funds in escrow, and releasing cryptocurrency only after payment confirmation, thereby enhancing trade flexibility, security, and transparency through mechanisms like escrow services, reputation ratings, and dispute resolution.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com