Quantitative sentiment analysis leverages numerical data, algorithms, and machine learning techniques to measure market emotions through metrics like tweet volumes, sentiment scores, and price movement correlations. Qualitative sentiment analysis focuses on interpreting subjective information from news articles, financial reports, and expert opinions to assess market sentiment nuances. Explore further to understand how each approach can enhance your trading strategies effectively.
Why it is important
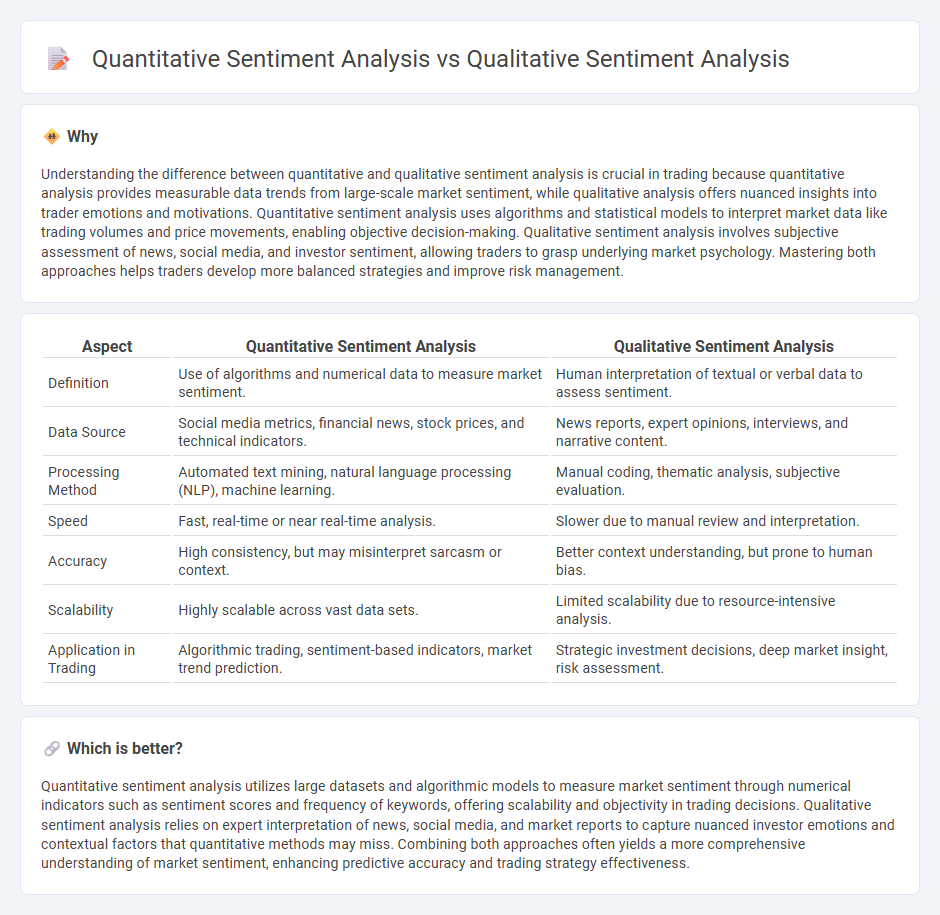
Understanding the difference between quantitative and qualitative sentiment analysis is crucial in trading because quantitative analysis provides measurable data trends from large-scale market sentiment, while qualitative analysis offers nuanced insights into trader emotions and motivations. Quantitative sentiment analysis uses algorithms and statistical models to interpret market data like trading volumes and price movements, enabling objective decision-making. Qualitative sentiment analysis involves subjective assessment of news, social media, and investor sentiment, allowing traders to grasp underlying market psychology. Mastering both approaches helps traders develop more balanced strategies and improve risk management.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Quantitative Sentiment Analysis | Qualitative Sentiment Analysis |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Use of algorithms and numerical data to measure market sentiment. | Human interpretation of textual or verbal data to assess sentiment. |
| Data Source | Social media metrics, financial news, stock prices, and technical indicators. | News reports, expert opinions, interviews, and narrative content. |
| Processing Method | Automated text mining, natural language processing (NLP), machine learning. | Manual coding, thematic analysis, subjective evaluation. |
| Speed | Fast, real-time or near real-time analysis. | Slower due to manual review and interpretation. |
| Accuracy | High consistency, but may misinterpret sarcasm or context. | Better context understanding, but prone to human bias. |
| Scalability | Highly scalable across vast data sets. | Limited scalability due to resource-intensive analysis. |
| Application in Trading | Algorithmic trading, sentiment-based indicators, market trend prediction. | Strategic investment decisions, deep market insight, risk assessment. |
Which is better?
Quantitative sentiment analysis utilizes large datasets and algorithmic models to measure market sentiment through numerical indicators such as sentiment scores and frequency of keywords, offering scalability and objectivity in trading decisions. Qualitative sentiment analysis relies on expert interpretation of news, social media, and market reports to capture nuanced investor emotions and contextual factors that quantitative methods may miss. Combining both approaches often yields a more comprehensive understanding of market sentiment, enhancing predictive accuracy and trading strategy effectiveness.
Connection
Quantitative sentiment analysis uses numerical data and statistical models to measure market sentiment by analyzing metrics such as trading volume, price trends, and social media sentiment scores. Qualitative sentiment analysis interprets the context, tone, and nuances of news articles, earnings reports, and expert opinions to understand trader emotions and market outlooks. Integrating both approaches enables traders to combine objective data with subjective insights, improving prediction accuracy and decision-making in trading strategies.
Key Terms
Subjectivity (Qualitative)
Subjectivity in qualitative sentiment analysis emphasizes understanding emotions, opinions, and intentions expressed in textual data, capturing nuances that quantitative methods might overlook. This approach involves in-depth examination of language context, tone, and subtle cues to interpret sentiment beyond numeric scores. Explore more to uncover how qualitative insights enrich sentiment analysis accuracy.
Statistical Models (Quantitative)
Quantitative sentiment analysis leverages statistical models such as Naive Bayes, Support Vector Machines (SVM), and deep learning algorithms to quantify sentiment by analyzing large datasets and extracting patterns from numerical features like word frequencies or embeddings. These models enable precise sentiment classification (positive, negative, neutral) and can scale efficiently across massive text corpora from social media, reviews, or surveys. Explore advanced statistical techniques to deepen your understanding of quantitative sentiment analysis.
Data Source (e.g., news, social media)
Qualitative sentiment analysis examines textual data from sources like news articles and social media posts to interpret underlying emotions and contextual nuances, providing deep insights into public opinion. Quantitative sentiment analysis uses algorithms to process large volumes of data from these sources, generating measurable sentiment scores to identify trends and patterns over time. Explore our detailed comparison to understand how different data sources impact sentiment analysis outcomes.
Source and External Links
Comprehensive Guide: Sentiment Analysis in Qualitative Research - Qualitative sentiment analysis interprets emotions in text, audio, and visual data using techniques like thematic analysis, coding (open and axial), and sentiment scoring to understand attitudes deeply and aid decision-making.
Sentiment Analysis and How to Leverage It - Sentiment analysis can be rule-based using lexicons or machine learning-based to detect nuances like sarcasm in qualitative data, enabling faster and more accurate understanding of people's feelings.
Thematic Analysis vs. Sentiment Analysis - Unlike simple sentiment analysis, thematic analysis in qualitative research captures nuanced themes and contexts, providing a more accurate and comprehensive interpretation of emotions and underlying patterns in textual data.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com