Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues, enhancing order execution by minimizing market impact and safeguarding large trades from public exposure. Algorithmic execution leverages advanced mathematical models and real-time data to optimize trade timing and order slicing, aiming to reduce costs and improve price efficiency. Explore how integrating dark pool aggregation with algorithmic strategies can revolutionize your trading performance.
Why it is important
Understanding the difference between dark pool aggregation and algorithmic execution is crucial for traders to optimize trade execution and minimize market impact. Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from private venues, allowing large orders to be filled discreetly without revealing intentions. Algorithmic execution uses pre-programmed strategies to break orders into smaller pieces, enhancing efficiency and reducing price slippage. Mastery of both methods enables better decision-making in complex trading environments.
Comparison Table
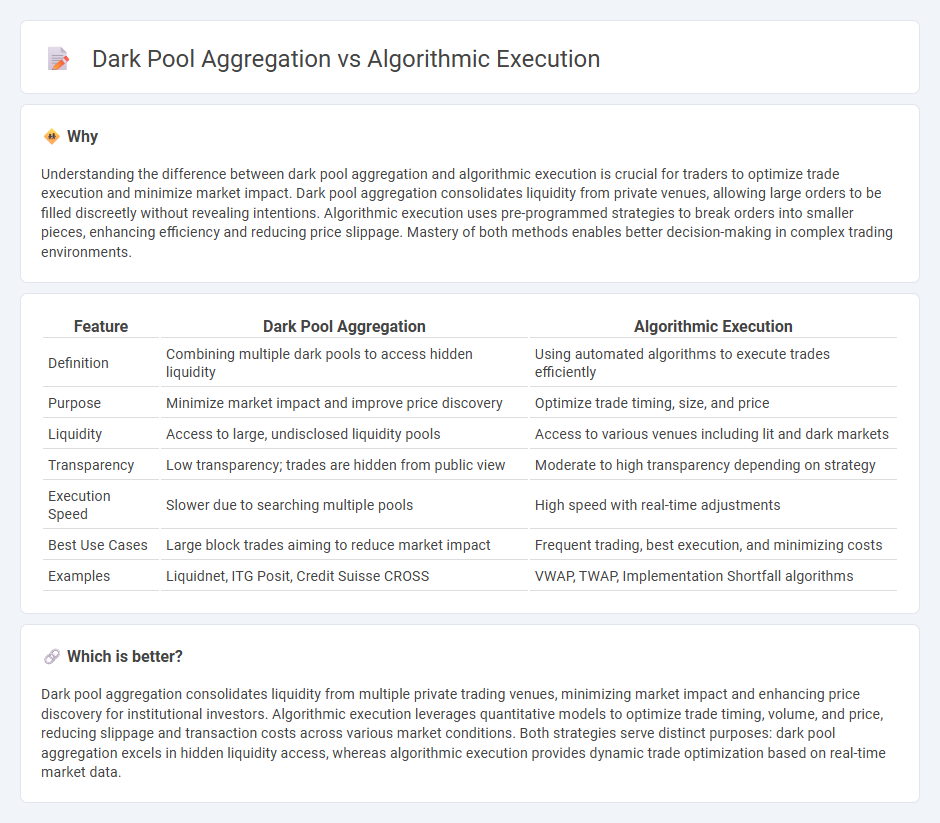
| Feature | Dark Pool Aggregation | Algorithmic Execution |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Combining multiple dark pools to access hidden liquidity | Using automated algorithms to execute trades efficiently |
| Purpose | Minimize market impact and improve price discovery | Optimize trade timing, size, and price |
| Liquidity | Access to large, undisclosed liquidity pools | Access to various venues including lit and dark markets |
| Transparency | Low transparency; trades are hidden from public view | Moderate to high transparency depending on strategy |
| Execution Speed | Slower due to searching multiple pools | High speed with real-time adjustments |
| Best Use Cases | Large block trades aiming to reduce market impact | Frequent trading, best execution, and minimizing costs |
| Examples | Liquidnet, ITG Posit, Credit Suisse CROSS | VWAP, TWAP, Implementation Shortfall algorithms |
Which is better?
Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from multiple private trading venues, minimizing market impact and enhancing price discovery for institutional investors. Algorithmic execution leverages quantitative models to optimize trade timing, volume, and price, reducing slippage and transaction costs across various market conditions. Both strategies serve distinct purposes: dark pool aggregation excels in hidden liquidity access, whereas algorithmic execution provides dynamic trade optimization based on real-time market data.
Connection
Dark pool aggregation enhances algorithmic execution by providing access to multiple non-transparent liquidity sources, enabling algorithms to optimize trade execution with minimal market impact. By integrating dark pool data, algorithmic trading strategies can identify better pricing and improve order routing efficiency. This synergy reduces slippage and enhances overall trade performance in fragmented markets.
Key Terms
**Algorithmic Execution:**
Algorithmic execution leverages advanced quantitative models and real-time market data to automate the trading process, optimizing order placement for minimal market impact and improved execution efficiency. It utilizes pre-defined strategies such as VWAP, TWAP, or percentile slicing to dynamically adapt to changing liquidity and price movements across multiple venues. Explore more to understand how algorithmic execution improves trading outcomes and risk management.
Smart Order Routing
Algorithmic execution leverages complex algorithms to optimize trade execution by dynamically splitting orders across multiple venues based on factors like price, liquidity, and latency. Dark pool aggregation consolidates liquidity from various dark pools to access hidden market depth and minimize market impact. Explore the nuances of Smart Order Routing to understand how it intelligently directs orders between lit markets and dark pools for best execution.
VWAP (Volume Weighted Average Price)
Algorithmic execution leverages VWAP strategies to minimize market impact by slicing large orders into smaller trades executed around the VWAP benchmark, ensuring price efficiency and reduced slippage. Dark pool aggregation also aims to achieve VWAP by pooling liquidity away from public exchanges, enabling large trades to be executed discreetly and often at better prices without revealing intentions to the broader market. Explore deeper insights into how combining algorithmic execution with dark pool liquidity can optimize VWAP trading effectiveness.
Source and External Links
Algorithmic Execution Strategies - QuestDB - Algorithmic execution involves automated trading approaches that break large orders into smaller pieces and execute them over time based on predefined rules to minimize market impact, reduce costs, and optimize prices while managing risks.
Introduction to Execution Algorithms - Algomojo - Execution algorithms are computer programs used by institutional investors to efficiently and cost-effectively buy and sell large securities orders, minimizing market impact and improving trade accuracy by breaking orders into smaller pieces executed over time.
Understanding Algorithmic Trading - ECN EXECUTION - Algorithmic trading uses computer algorithms to execute trades at precise times automatically, enabling high-frequency, emotion-free, efficient transactions based on predefined rules and market conditions.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com