Delta neutral strategy involves balancing options and underlying assets to maintain a portfolio with minimal exposure to price movements, minimizing risk from market fluctuations. Position trading focuses on holding assets for extended periods, capitalizing on long-term trends and fundamental analysis rather than short-term volatility. Explore detailed comparisons and strategic advantages to optimize your trading approach.
Why it is important
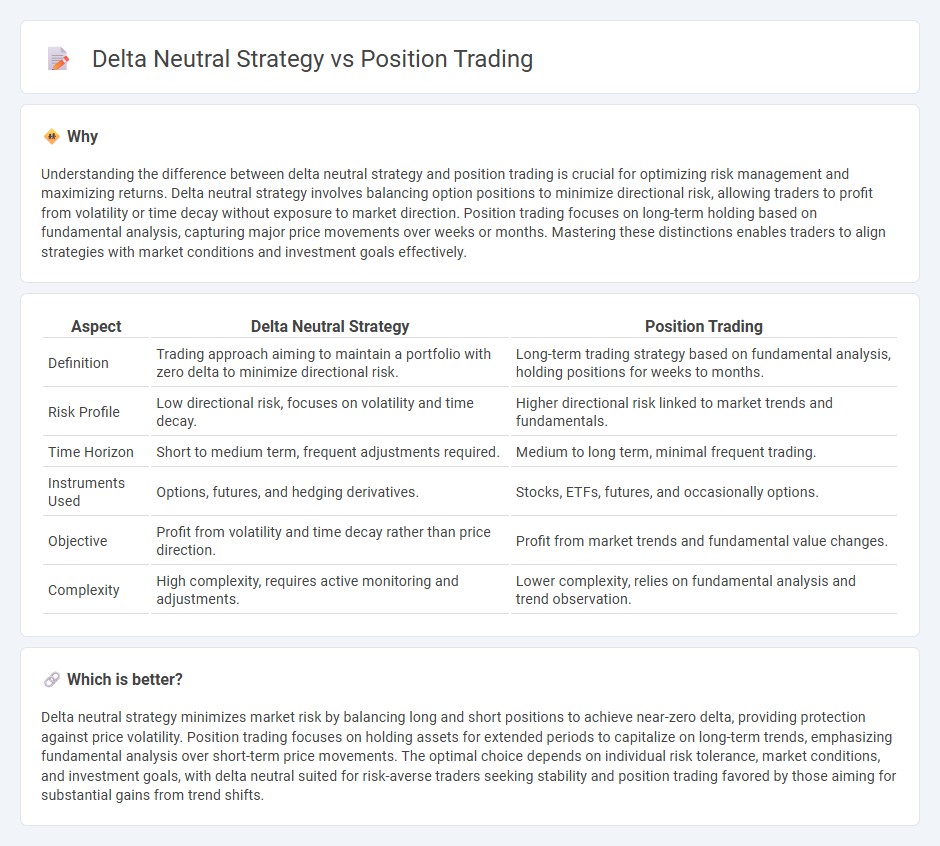
Understanding the difference between delta neutral strategy and position trading is crucial for optimizing risk management and maximizing returns. Delta neutral strategy involves balancing option positions to minimize directional risk, allowing traders to profit from volatility or time decay without exposure to market direction. Position trading focuses on long-term holding based on fundamental analysis, capturing major price movements over weeks or months. Mastering these distinctions enables traders to align strategies with market conditions and investment goals effectively.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta Neutral Strategy | Position Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading approach aiming to maintain a portfolio with zero delta to minimize directional risk. | Long-term trading strategy based on fundamental analysis, holding positions for weeks to months. |
| Risk Profile | Low directional risk, focuses on volatility and time decay. | Higher directional risk linked to market trends and fundamentals. |
| Time Horizon | Short to medium term, frequent adjustments required. | Medium to long term, minimal frequent trading. |
| Instruments Used | Options, futures, and hedging derivatives. | Stocks, ETFs, futures, and occasionally options. |
| Objective | Profit from volatility and time decay rather than price direction. | Profit from market trends and fundamental value changes. |
| Complexity | High complexity, requires active monitoring and adjustments. | Lower complexity, relies on fundamental analysis and trend observation. |
Which is better?
Delta neutral strategy minimizes market risk by balancing long and short positions to achieve near-zero delta, providing protection against price volatility. Position trading focuses on holding assets for extended periods to capitalize on long-term trends, emphasizing fundamental analysis over short-term price movements. The optimal choice depends on individual risk tolerance, market conditions, and investment goals, with delta neutral suited for risk-averse traders seeking stability and position trading favored by those aiming for substantial gains from trend shifts.
Connection
Delta neutral strategy and position trading intersect through their focus on managing risk over extended periods by maintaining balanced portfolios that minimize exposure to directional price movements. Traders employing delta neutral strategies within position trading adjust options and underlying asset positions to neutralize delta, aiming for consistent returns regardless of market direction. This integration helps position traders reduce volatility risk while capitalizing on longer-term market trends.
Key Terms
**Position Trading:**
Position trading involves holding assets for weeks to months to capitalize on long-term market trends, minimizing noise from short-term price fluctuations. This strategy relies heavily on fundamental analysis and trend identification, targeting significant price movements with lower trade frequency and reduced transaction costs. Explore the nuances of position trading to enhance your investment approach and optimize long-term portfolio growth.
Trend
Position trading emphasizes capturing long-term market trends by holding assets over weeks or months to maximize gains from sustained price movements. Delta neutral strategies involve balancing options and underlying assets to minimize directional risk, focusing on short-term price stability rather than trend exploitation. Explore deeper insights into how these approaches align with your trading goals and risk tolerance.
Holding Period
Position trading typically involves holding assets for weeks to months to capitalize on long-term market trends, allowing traders to benefit from significant price movements. Delta neutral strategies focus on minimizing directional risk by balancing options and underlying assets, leading to shorter holding periods that prioritize stability and reduced volatility exposure. Explore detailed comparisons to understand which approach suits your investment goals and risk tolerance better.
Source and External Links
A guide to position trading: definition, examples and strategies - Position trading is a strategy that seeks to identify and benefit from ongoing trends over a longer time frame by holding positions from weeks to months, focusing on major price movements with examples like trading oil futures after supply announcements and employing strategies such as trend trading, breakout trading, and pullback trading.
Position Trading 101: A Beginner's Guide With Examples - Position trading is an active medium- to long-term trading approach lasting weeks to months, designed to ride market trends, often involving both long and short positions, differing from buy-and-hold investing by actively exiting trends and timing the market.
Position Trading Strategy: How To Use It | Capital.com - Position trading involves holding positions for months or years to profit from long-term trends, with benefits like reduced trading frequency, long-term profit potential, and lower transaction costs, and differs from day and swing trading mainly in its time horizon and approach to market movements.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com