Delta-neutral strategies focus on maintaining a portfolio with a net zero delta to hedge against price movements in underlying assets, often using options and derivatives to minimize risk. Event-driven strategies capitalize on specific corporate events such as mergers, acquisitions, or earnings announcements by exploiting price inefficiencies before or after the event. Explore how these distinct approaches can be leveraged to optimize trading performance and manage risk effectively.
Why it is important
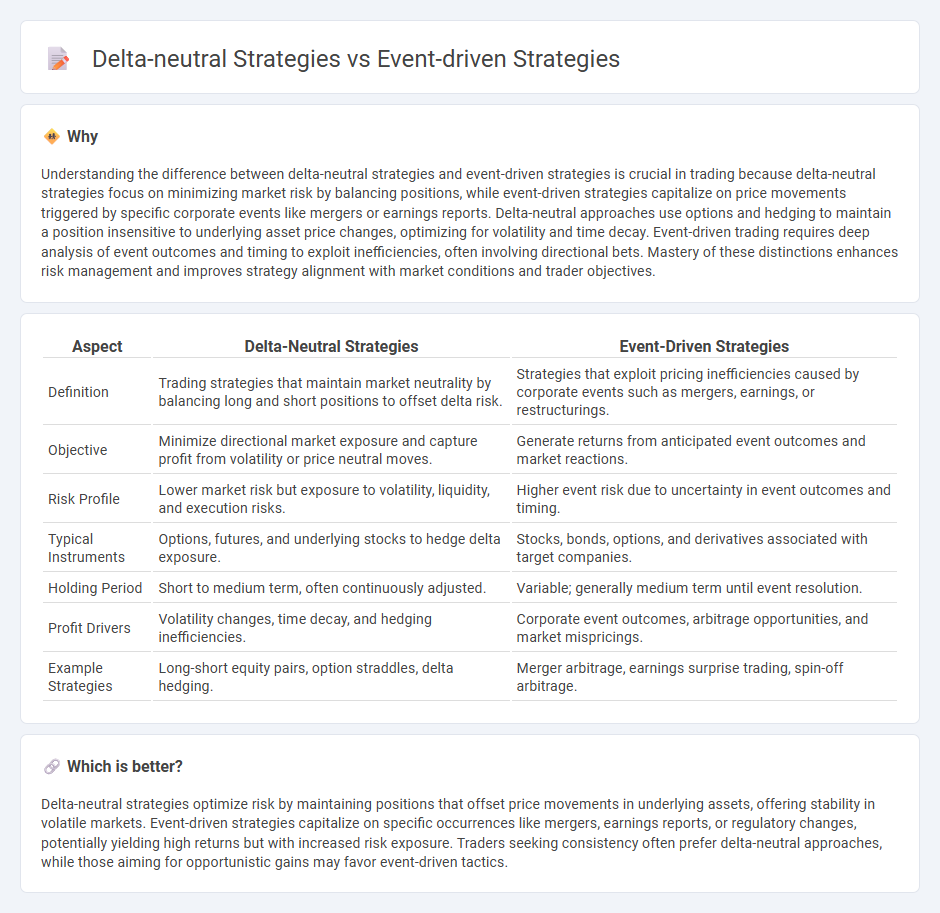
Understanding the difference between delta-neutral strategies and event-driven strategies is crucial in trading because delta-neutral strategies focus on minimizing market risk by balancing positions, while event-driven strategies capitalize on price movements triggered by specific corporate events like mergers or earnings reports. Delta-neutral approaches use options and hedging to maintain a position insensitive to underlying asset price changes, optimizing for volatility and time decay. Event-driven trading requires deep analysis of event outcomes and timing to exploit inefficiencies, often involving directional bets. Mastery of these distinctions enhances risk management and improves strategy alignment with market conditions and trader objectives.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Delta-Neutral Strategies | Event-Driven Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading strategies that maintain market neutrality by balancing long and short positions to offset delta risk. | Strategies that exploit pricing inefficiencies caused by corporate events such as mergers, earnings, or restructurings. |
| Objective | Minimize directional market exposure and capture profit from volatility or price neutral moves. | Generate returns from anticipated event outcomes and market reactions. |
| Risk Profile | Lower market risk but exposure to volatility, liquidity, and execution risks. | Higher event risk due to uncertainty in event outcomes and timing. |
| Typical Instruments | Options, futures, and underlying stocks to hedge delta exposure. | Stocks, bonds, options, and derivatives associated with target companies. |
| Holding Period | Short to medium term, often continuously adjusted. | Variable; generally medium term until event resolution. |
| Profit Drivers | Volatility changes, time decay, and hedging inefficiencies. | Corporate event outcomes, arbitrage opportunities, and market mispricings. |
| Example Strategies | Long-short equity pairs, option straddles, delta hedging. | Merger arbitrage, earnings surprise trading, spin-off arbitrage. |
Which is better?
Delta-neutral strategies optimize risk by maintaining positions that offset price movements in underlying assets, offering stability in volatile markets. Event-driven strategies capitalize on specific occurrences like mergers, earnings reports, or regulatory changes, potentially yielding high returns but with increased risk exposure. Traders seeking consistency often prefer delta-neutral approaches, while those aiming for opportunistic gains may favor event-driven tactics.
Connection
Delta-neutral strategies and event-driven strategies are connected through their shared goal of managing risk while capitalizing on market inefficiencies triggered by specific events such as earnings reports, mergers, or regulatory announcements. Delta-neutral strategies maintain a balanced portfolio to remain insensitive to small price movements in the underlying asset, enabling traders to focus on gains from event-driven price volatility. By combining these approaches, traders can isolate event-specific risks and optimize returns regardless of directional market trends.
Key Terms
Event-Driven Strategies:
Event-driven strategies capitalize on corporate actions such as mergers, acquisitions, restructurings, or bankruptcies to generate alpha by exploiting pricing inefficiencies before market adjustments. These strategies rely heavily on deep fundamental analysis and timely information to identify mispriced securities, aiming to profit from the anticipated event outcomes regardless of broader market trends. Explore detailed insights into event-driven strategies to understand how they manage risk and optimize returns amid corporate action catalysts.
Merger Arbitrage
Event-driven strategies in merger arbitrage capitalize on price discrepancies arising from announced mergers or acquisitions, seeking profits when the deal closes successfully. Delta-neutral strategies aim to hedge against market movements by balancing long and short positions, reducing exposure to directional risks during the merger process. Explore the nuances of these approaches to optimize arbitrage opportunities in merger scenarios.
Catalyst
Event-driven strategies capitalize on specific market catalysts such as mergers, acquisitions, or earnings announcements to generate returns by exploiting anticipated price movements. Delta-neutral strategies maintain a market-neutral position by balancing long and short options or stocks, minimizing directional risk while profiting from volatility or time decay, often adjusted dynamically around catalysts. Explore how integrating catalyst-focused event-driven approaches with delta-neutral hedging can optimize risk-adjusted performance.
Source and External Links
Event Driven Trading Strategies: How They Work and Why They Matter - Event-driven strategies focus on capitalizing on market-moving corporate events, such as earnings announcements or mergers, by analyzing their impact and establishing positions accordingly while managing risks like deal and liquidity risk.
Event-Driven Investing | Fund Strategy + Examples - Wall Street Prep - This strategy seeks to profit from pricing inefficiencies caused by corporate events such as mergers, acquisitions, and spin-offs, with common types including merger arbitrage, distressed investing, and activist investing.
Event-Driven Strategies - The Hedge Fund Journal - Event-driven strategies involve long or short equity investments around significant corporate changes, aiming to exploit special situations like restructurings or management changes, often producing returns with limited correlation to general equity markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com