Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing decentralization and reducing counterparty risk. Payment channels facilitate off-chain transactions by locking funds in a multi-signature wallet, allowing instant and low-cost transfers before settling on the main blockchain. Explore more to understand how atomic swaps and payment channels revolutionize trading efficiency.
Why it is important
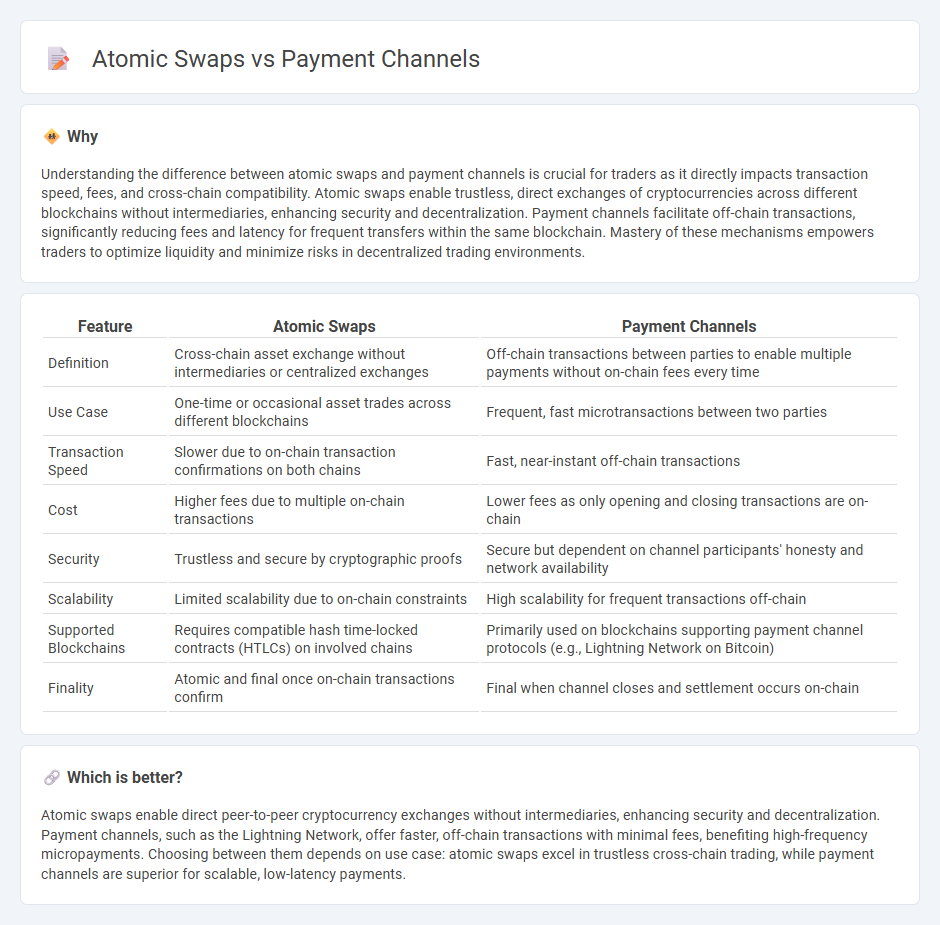
Understanding the difference between atomic swaps and payment channels is crucial for traders as it directly impacts transaction speed, fees, and cross-chain compatibility. Atomic swaps enable trustless, direct exchanges of cryptocurrencies across different blockchains without intermediaries, enhancing security and decentralization. Payment channels facilitate off-chain transactions, significantly reducing fees and latency for frequent transfers within the same blockchain. Mastery of these mechanisms empowers traders to optimize liquidity and minimize risks in decentralized trading environments.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Atomic Swaps | Payment Channels |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cross-chain asset exchange without intermediaries or centralized exchanges | Off-chain transactions between parties to enable multiple payments without on-chain fees every time |
| Use Case | One-time or occasional asset trades across different blockchains | Frequent, fast microtransactions between two parties |
| Transaction Speed | Slower due to on-chain transaction confirmations on both chains | Fast, near-instant off-chain transactions |
| Cost | Higher fees due to multiple on-chain transactions | Lower fees as only opening and closing transactions are on-chain |
| Security | Trustless and secure by cryptographic proofs | Secure but dependent on channel participants' honesty and network availability |
| Scalability | Limited scalability due to on-chain constraints | High scalability for frequent transactions off-chain |
| Supported Blockchains | Requires compatible hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) on involved chains | Primarily used on blockchains supporting payment channel protocols (e.g., Lightning Network on Bitcoin) |
| Finality | Atomic and final once on-chain transactions confirm | Final when channel closes and settlement occurs on-chain |
Which is better?
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing security and decentralization. Payment channels, such as the Lightning Network, offer faster, off-chain transactions with minimal fees, benefiting high-frequency micropayments. Choosing between them depends on use case: atomic swaps excel in trustless cross-chain trading, while payment channels are superior for scalable, low-latency payments.
Connection
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, enhancing decentralized trading efficiency. Payment channels facilitate off-chain transactions that increase scalability and reduce fees by allowing multiple trades to occur without recording each on the blockchain. Together, atomic swaps integrated within payment channels create a seamless and cost-effective method for instant cross-chain asset trading.
Key Terms
Off-chain transactions
Off-chain transactions optimize blockchain scalability by enabling payment channels to conduct secure, instant microtransactions without broadcasting every interaction on-chain, minimizing fees and congestion. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges off-chain, ensuring trustless, cross-chain asset swaps without intermediaries by leveraging smart contract protocols. Explore how these mechanisms revolutionize off-chain transactions and enhance blockchain efficiency.
Cross-chain interoperability
Payment channels enhance cross-chain interoperability by enabling off-chain transactions that reduce fees and settlement times across different blockchain networks. Atomic swaps directly facilitate trustless peer-to-peer asset exchanges between distinct blockchains, ensuring secure and instant cross-chain trades without intermediaries. Explore the nuances and technical implementations of both solutions to deepen your understanding of cross-chain interoperability.
Trustless exchange
Payment channels enable trustless off-chain transactions by locking funds in a multi-signature contract, allowing instant transfers without involving a third party. Atomic swaps facilitate trustless cross-chain exchanges by using cryptographic hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs), ensuring asset swaps occur simultaneously or not at all, eliminating counterparty risk. Explore the mechanics and benefits of trustless exchanges through payment channels and atomic swaps in detail.
Source and External Links
What Are Payment Channels? - A Guide to Payment Methods - A payment channel is a method or system for transferring funds between a customer and a business, including credit cards, ACH transfers, digital wallets, and payment links, which are crucial for improving customer experience and business cash flow by offering diverse and secure payment options.
How To Pick The Best Payment Solutions Channel For Your Business - Payment channels refer to any way customers can pay or merchants can accept payments, such as in-person, eCommerce, or mobile payments, and selecting the right channels depends on business needs and growth stages.
What is a Payment Channel? | Payment Method Examples - CSG Forte - A payment channel includes a payment method and the technical infrastructure that enables secure transaction processing for merchants across various platforms like online, in-person, or phone payments, often managed through unified payment platforms for simplicity.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com