Microstructure modeling focuses on the detailed processes within financial markets, capturing order book dynamics, trade execution, and price formation at the finest granularity. Slippage modeling quantifies the difference between expected transaction prices and actual execution prices, reflecting market impact and liquidity costs. Explore the nuances of these models to enhance trading strategies and execution quality.
Why it is important
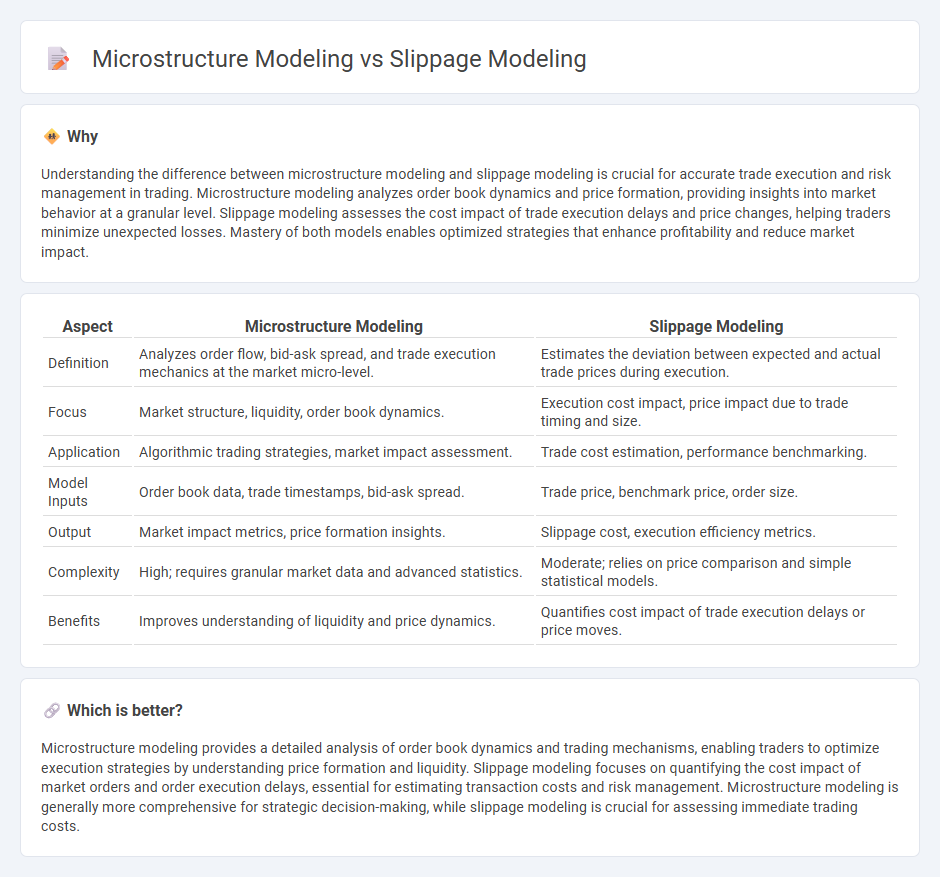
Understanding the difference between microstructure modeling and slippage modeling is crucial for accurate trade execution and risk management in trading. Microstructure modeling analyzes order book dynamics and price formation, providing insights into market behavior at a granular level. Slippage modeling assesses the cost impact of trade execution delays and price changes, helping traders minimize unexpected losses. Mastery of both models enables optimized strategies that enhance profitability and reduce market impact.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Microstructure Modeling | Slippage Modeling |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Analyzes order flow, bid-ask spread, and trade execution mechanics at the market micro-level. | Estimates the deviation between expected and actual trade prices during execution. |
| Focus | Market structure, liquidity, order book dynamics. | Execution cost impact, price impact due to trade timing and size. |
| Application | Algorithmic trading strategies, market impact assessment. | Trade cost estimation, performance benchmarking. |
| Model Inputs | Order book data, trade timestamps, bid-ask spread. | Trade price, benchmark price, order size. |
| Output | Market impact metrics, price formation insights. | Slippage cost, execution efficiency metrics. |
| Complexity | High; requires granular market data and advanced statistics. | Moderate; relies on price comparison and simple statistical models. |
| Benefits | Improves understanding of liquidity and price dynamics. | Quantifies cost impact of trade execution delays or price moves. |
Which is better?
Microstructure modeling provides a detailed analysis of order book dynamics and trading mechanisms, enabling traders to optimize execution strategies by understanding price formation and liquidity. Slippage modeling focuses on quantifying the cost impact of market orders and order execution delays, essential for estimating transaction costs and risk management. Microstructure modeling is generally more comprehensive for strategic decision-making, while slippage modeling is crucial for assessing immediate trading costs.
Connection
Microstructure modeling analyzes the detailed mechanisms of order execution, market liquidity, and price formation, which directly influence slippage experienced during trades. Slippage modeling quantifies the difference between expected and actual trade prices, capturing the impact of microstructural factors like bid-ask spread, order book depth, and market impact. Integrating microstructure and slippage models improves trade execution strategies by accurately predicting cost deviations and optimizing order placement.
Key Terms
Slippage Modeling:
Slippage modeling quantifies the cost incurred from price deviations between order initiation and execution, emphasizing trade impact within volatile or illiquid markets. It incorporates factors like order size, market depth, and execution speed to predict execution risk and optimize trading strategies. Explore detailed methodologies and applications of slippage modeling for enhanced trading performance.
Execution Price Deviation
Slippage modeling quantifies the deviation between the expected execution price and the actual transaction price caused by market impact and liquidity dynamics. Microstructure modeling delves deeper, analyzing order book behavior, bid-ask spreads, and trade timing to understand price formation and temporary price deviations during execution. Explore detailed methodologies to enhance precision in execution price deviation analysis.
Order Size Impact
Slippage modeling quantifies the price impact caused by executing large order sizes, highlighting how market liquidity and order book depth affect trade execution costs. Microstructure modeling examines the detailed mechanisms of order flow and price formation, specifically how varying order sizes influence bid-ask spreads and market resilience. Explore further to understand the interplay between order size and market efficiency in advanced trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Slippage Modelling - Stephen Diehl - Provides an analytical model to estimate expected slippage from recent price history, factoring in order size, average daily volume, volatility, and bid-ask spread to size orders and minimize slippage impact.
Slippage: A Comprehensive Analysis and Non-Linear Modeling with Machine Learning - Discusses advanced slippage modeling using feature engineering and machine learning, highlighting how liquidity and volatility affect slippage and incorporating SHAP for model interpretability and dynamic slippage prediction in backtesting frameworks.
Slippage - Key Concepts - QuantConnect.com - Explains the implementation of slippage models in algorithmic trading backtests via interfaces like ISlippageModel, including examples of custom slippage models to simulate realistic fill price deviations.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com