Front running involves executing trades based on advance knowledge of pending orders to capitalize on price movements before the larger order is filled, often raising regulatory concerns. Momentum ignition aims to initiate a rapid price movement through aggressive trading, triggering others to follow and amplify the trend, often seen in high-frequency trading strategies. Explore these tactics further to understand their impact on market dynamics.
Why it is important
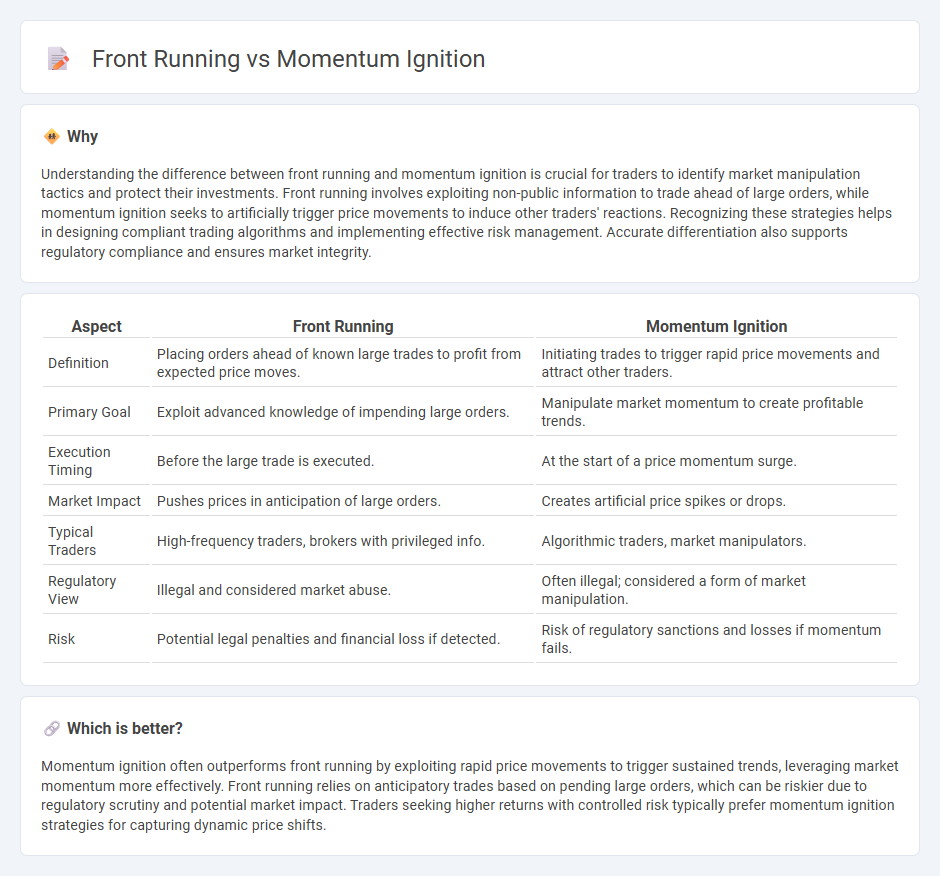
Understanding the difference between front running and momentum ignition is crucial for traders to identify market manipulation tactics and protect their investments. Front running involves exploiting non-public information to trade ahead of large orders, while momentum ignition seeks to artificially trigger price movements to induce other traders' reactions. Recognizing these strategies helps in designing compliant trading algorithms and implementing effective risk management. Accurate differentiation also supports regulatory compliance and ensures market integrity.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Front Running | Momentum Ignition |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Placing orders ahead of known large trades to profit from expected price moves. | Initiating trades to trigger rapid price movements and attract other traders. |
| Primary Goal | Exploit advanced knowledge of impending large orders. | Manipulate market momentum to create profitable trends. |
| Execution Timing | Before the large trade is executed. | At the start of a price momentum surge. |
| Market Impact | Pushes prices in anticipation of large orders. | Creates artificial price spikes or drops. |
| Typical Traders | High-frequency traders, brokers with privileged info. | Algorithmic traders, market manipulators. |
| Regulatory View | Illegal and considered market abuse. | Often illegal; considered a form of market manipulation. |
| Risk | Potential legal penalties and financial loss if detected. | Risk of regulatory sanctions and losses if momentum fails. |
Which is better?
Momentum ignition often outperforms front running by exploiting rapid price movements to trigger sustained trends, leveraging market momentum more effectively. Front running relies on anticipatory trades based on pending large orders, which can be riskier due to regulatory scrutiny and potential market impact. Traders seeking higher returns with controlled risk typically prefer momentum ignition strategies for capturing dynamic price shifts.
Connection
Front running and momentum ignition both manipulate market dynamics by exploiting order flow information to influence asset prices. Front running involves trading ahead of large orders to capitalize on anticipated price movements, while momentum ignition triggers rapid price changes through aggressive order placement, enticing other traders to join the trend. This strategic interplay amplifies price volatility, creating opportunities for profit at the expense of market fairness.
Key Terms
Order Flow
Momentum ignition involves placing a series of aggressive orders to trigger rapid price movements, enticing other traders to follow and amplify the trend. Front running occurs when a trader anticipates large incoming orders and executes trades ahead to capitalize on the expected price change. Explore the nuances of order flow dynamics to better understand these market manipulation strategies.
Price Manipulation
Momentum ignition and front running are two distinct price manipulation strategies in financial markets. Momentum ignition involves placing trades to trigger a rapid price move, encouraging other traders to follow and amplify the effect, while front running occurs when a trader exploits advance knowledge of large pending orders to trade ahead and profit from subsequent price changes. Explore more about how regulatory bodies detect and prevent these manipulative tactics to protect market integrity.
Insider Information
Momentum ignition exploits rapid buying or selling to trigger price surges, often based on public or manipulated data, while front running involves trading ahead of large, non-public orders using insider information. Insider information in front running provides an unfair market advantage by anticipating institutional trades before they are executed. Discover how regulatory frameworks aim to detect and prevent the misuse of inside information in these trading strategies.
Source and External Links
Momentum Ignition - Momentum ignition is a trading strategy where traders trigger a rapid series of buy or sell orders to create a sharp price movement, prompting other market participants and algorithms to join in, allowing the initiator to profit from the resulting price changes.
Market Abuse "Momentum Ignition" - Also known as ramping, momentum ignition is a market manipulation tactic involving unilateral buying or selling to create the illusion of a trend and deceive other investors into following that false direction before the manipulator exits for profit.
What is Momentum Ignition? Insights for Enterprises - Momentum ignition involves deliberately causing rapid price moves to exploit reactions, and modern AI-powered tools help detect such manipulations through pattern recognition and predictive analytics to protect markets.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com