Modular blockchains trading enables enhanced scalability and flexibility by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, optimizing transaction throughput and reducing costs. Atomic swaps facilitate direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, ensuring trustless and instantaneous cross-chain transactions. Explore the differences between these two approaches to discover which method best suits your trading strategy and blockchain ecosystem.
Why it is important
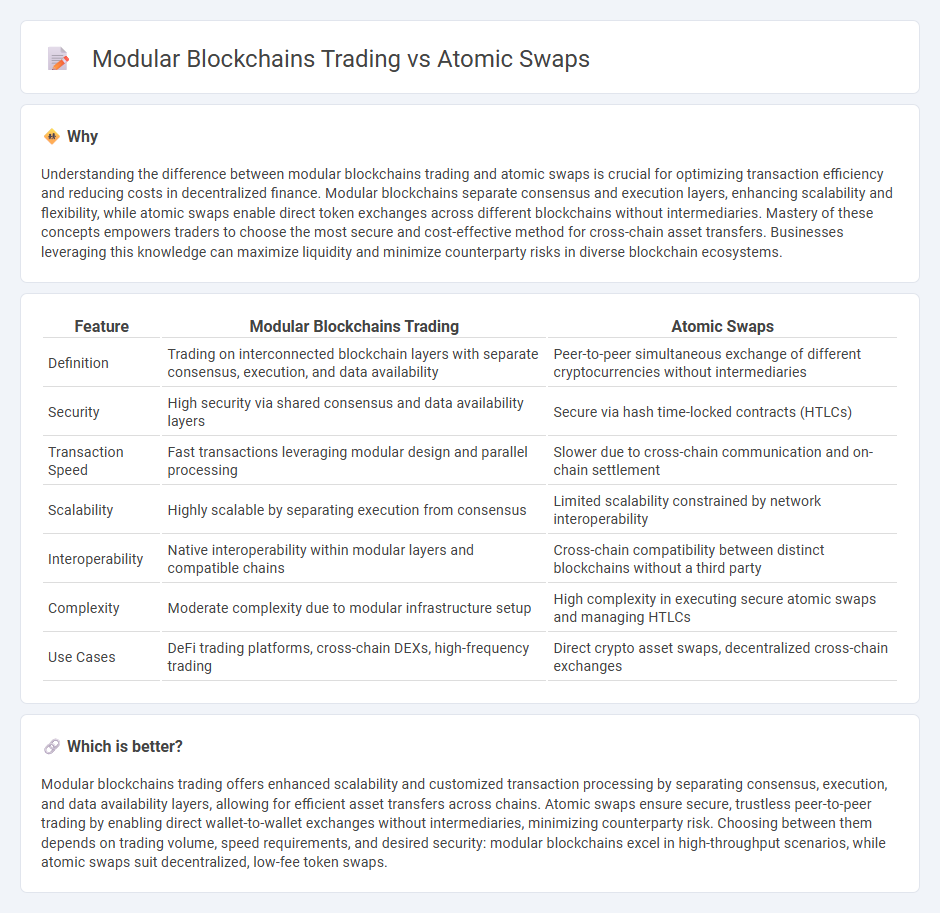
Understanding the difference between modular blockchains trading and atomic swaps is crucial for optimizing transaction efficiency and reducing costs in decentralized finance. Modular blockchains separate consensus and execution layers, enhancing scalability and flexibility, while atomic swaps enable direct token exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries. Mastery of these concepts empowers traders to choose the most secure and cost-effective method for cross-chain asset transfers. Businesses leveraging this knowledge can maximize liquidity and minimize counterparty risks in diverse blockchain ecosystems.
Comparison Table
| Feature | Modular Blockchains Trading | Atomic Swaps |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Trading on interconnected blockchain layers with separate consensus, execution, and data availability | Peer-to-peer simultaneous exchange of different cryptocurrencies without intermediaries |
| Security | High security via shared consensus and data availability layers | Secure via hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) |
| Transaction Speed | Fast transactions leveraging modular design and parallel processing | Slower due to cross-chain communication and on-chain settlement |
| Scalability | Highly scalable by separating execution from consensus | Limited scalability constrained by network interoperability |
| Interoperability | Native interoperability within modular layers and compatible chains | Cross-chain compatibility between distinct blockchains without a third party |
| Complexity | Moderate complexity due to modular infrastructure setup | High complexity in executing secure atomic swaps and managing HTLCs |
| Use Cases | DeFi trading platforms, cross-chain DEXs, high-frequency trading | Direct crypto asset swaps, decentralized cross-chain exchanges |
Which is better?
Modular blockchains trading offers enhanced scalability and customized transaction processing by separating consensus, execution, and data availability layers, allowing for efficient asset transfers across chains. Atomic swaps ensure secure, trustless peer-to-peer trading by enabling direct wallet-to-wallet exchanges without intermediaries, minimizing counterparty risk. Choosing between them depends on trading volume, speed requirements, and desired security: modular blockchains excel in high-throughput scenarios, while atomic swaps suit decentralized, low-fee token swaps.
Connection
Modular blockchains enable efficient trading by separating consensus, execution, and data availability layers, which enhances scalability and reduces transaction costs. Atomic swaps leverage this modular architecture to facilitate trustless, cross-chain token exchanges without intermediaries. This integration promotes seamless interoperability and secure peer-to-peer trading across diverse blockchain networks.
Key Terms
Cross-chain interoperability
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges across different blockchains without intermediaries, leveraging hash time-locked contracts (HTLCs) for secure, trustless transactions. Modular blockchains enhance cross-chain interoperability by separating consensus, execution, and data availability layers, facilitating scalable, efficient asset transfers and smart contract interactions across multiple chains. Explore further to understand how these technologies revolutionize decentralized trading ecosystems.
Trustless exchange
Atomic swaps enable trustless exchanges by allowing users to trade cryptocurrencies directly across different blockchains without intermediaries, using smart contracts to ensure simultaneous transaction execution. Modular blockchains enhance this process by separating consensus, data availability, and execution layers, which improves scalability and security for trustless trading environments. Explore how these technologies revolutionize decentralized trading for deeper insights.
Liquidity fragmentation
Atomic swaps enable direct peer-to-peer cryptocurrency exchanges without intermediaries, reducing liquidity fragmentation by allowing seamless cross-chain asset trades. Modular blockchains enhance liquidity aggregation through specialized layers that optimize transaction processing and interoperability, minimizing liquidity silos. Explore how these innovative methods address liquidity fragmentation in decentralized finance to optimize trading efficiency.
Source and External Links
What Is an Atomic Swap? - An atomic swap is a method that allows the exchange of cryptocurrency across different blockchain networks directly between users without intermediaries, using hashed timelock contracts (HTLC) to ensure both parties fulfill agreed conditions or the funds are returned.
What Is an Atomic Swap? - Atomic swaps enable peer-to-peer decentralized exchanges of crypto assets across separate blockchains via smart contracts that either execute the full swap or refund tokens, maintaining security and trustlessness across networks.
Bitcoin <-> Monero atomic swaps are now live - Atomic swaps, exemplified by Bitcoin and Monero exchanges, allow two parties to safely trade cryptocurrencies directly without trusting each other or third parties, ensuring either the swap completes or no funds move.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com