Retail flow chasing involves reacting to the buying and selling patterns of individual investors, often leading to increased volatility and momentum-driven price moves. Market making, on the other hand, focuses on providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread while managing inventory risk. Explore the strategies and impacts of both approaches to enhance your trading knowledge.
Why it is important
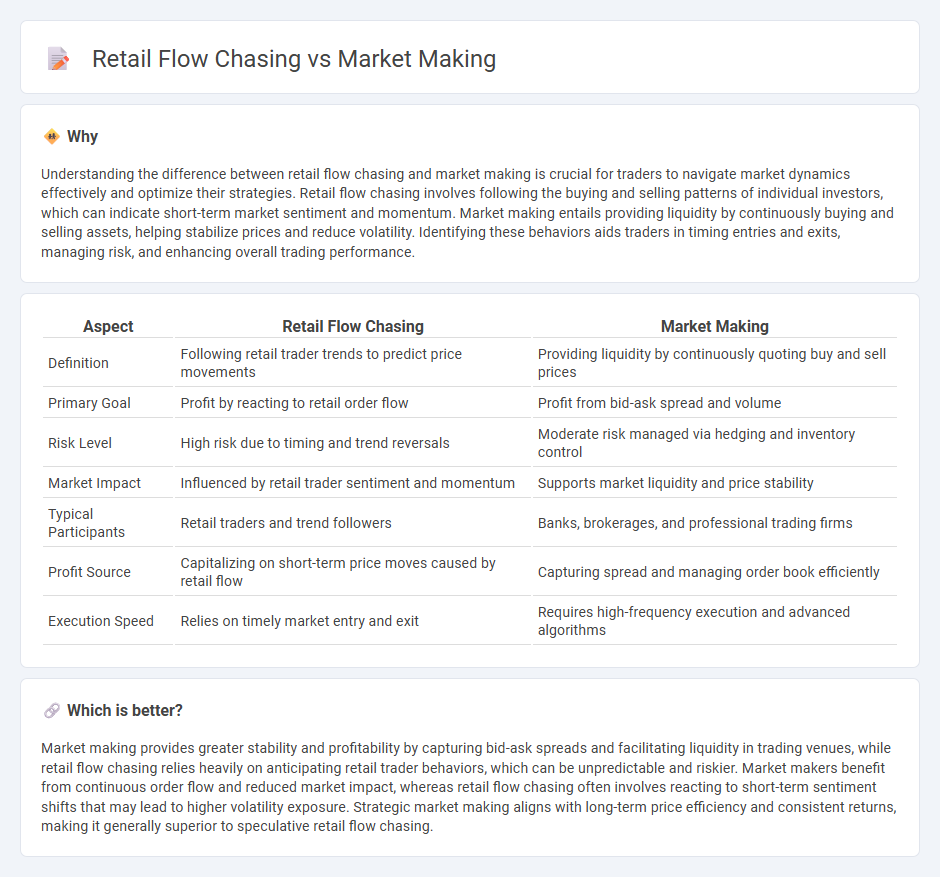
Understanding the difference between retail flow chasing and market making is crucial for traders to navigate market dynamics effectively and optimize their strategies. Retail flow chasing involves following the buying and selling patterns of individual investors, which can indicate short-term market sentiment and momentum. Market making entails providing liquidity by continuously buying and selling assets, helping stabilize prices and reduce volatility. Identifying these behaviors aids traders in timing entries and exits, managing risk, and enhancing overall trading performance.
Comparison Table
| Aspect | Retail Flow Chasing | Market Making |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Following retail trader trends to predict price movements | Providing liquidity by continuously quoting buy and sell prices |
| Primary Goal | Profit by reacting to retail order flow | Profit from bid-ask spread and volume |
| Risk Level | High risk due to timing and trend reversals | Moderate risk managed via hedging and inventory control |
| Market Impact | Influenced by retail trader sentiment and momentum | Supports market liquidity and price stability |
| Typical Participants | Retail traders and trend followers | Banks, brokerages, and professional trading firms |
| Profit Source | Capitalizing on short-term price moves caused by retail flow | Capturing spread and managing order book efficiently |
| Execution Speed | Relies on timely market entry and exit | Requires high-frequency execution and advanced algorithms |
Which is better?
Market making provides greater stability and profitability by capturing bid-ask spreads and facilitating liquidity in trading venues, while retail flow chasing relies heavily on anticipating retail trader behaviors, which can be unpredictable and riskier. Market makers benefit from continuous order flow and reduced market impact, whereas retail flow chasing often involves reacting to short-term sentiment shifts that may lead to higher volatility exposure. Strategic market making aligns with long-term price efficiency and consistent returns, making it generally superior to speculative retail flow chasing.
Connection
Retail flow chasing involves traders reacting to popular retail trading trends, which increases market liquidity and volatility. Market makers capitalize on this by providing continuous bid and ask prices, facilitating smoother trade execution and profiting from the spread. The interaction between retail flow chasing and market making creates a dynamic environment where order flow and price discovery are closely intertwined.
Key Terms
**Liquidity Provision**
Market making involves continuous liquidity provision by placing buy and sell orders to ensure smooth market operations, minimizing bid-ask spreads and price volatility. Retail flow chasing focuses on reacting to retail trader order flow, often adding liquidity temporarily but lacking the consistency of dedicated market makers. Discover how mastering liquidity provision strategies can enhance trading efficiency and market stability.
**Order Flow**
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting both buy and sell orders, capitalizing on bid-ask spreads through precise order flow analysis. Retail flow chasing tracks the aggregated retail trader orders, attempting to predict price movements based on their buying or selling behavior within the order book. Explore detailed strategies to understand how order flow impacts market dynamics and trading profitability.
**Bid-Ask Spread**
Market making involves providing liquidity by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread through rapid transactions and minimizing inventory risk. Retail flow chasing, on the other hand, attempts to predict and capitalize on price movements caused by retail traders, often leading to wider spreads and less efficient execution. Explore the nuances of bid-ask spread dynamics and how these strategies impact market liquidity and trading costs.
Source and External Links
Mastering the Market Maker Trading Strategy | EPAM SolutionsHub - Market makers earn profits primarily by capturing the bid-ask spread, managing inventory to take advantage of price changes, and analyzing order flow to anticipate market movements while providing liquidity and adhering to regulations.
Market Making and Mean Reversion - CIS UPenn - Market making is a trading strategy focused on providing liquidity by quoting buy and sell prices simultaneously, profiting from the spread without accumulating large net positions.
Market Maker - Definition, Role, How They Work - A market maker is a firm or individual who provides two-sided markets by continuously quoting bid and ask prices, profiting from the bid-ask spread and compensated for the risks of holding inventory.
 dowidth.com
dowidth.com